Professional Documents
Culture Documents
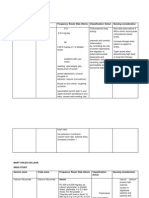
Drug Name Classific-Ation Therapeutic Action Indications Contraindicatio N Adverse Effects Nursing Consider - Ation
Uploaded by
Elyne BicaldoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
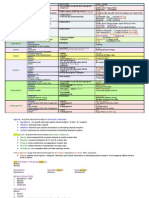
Drug Name Classific-Ation Therapeutic Action Indications Contraindicatio N Adverse Effects Nursing Consider - Ation
Uploaded by
Elyne BicaldoCopyright:
Available Formats
DRUG NAME CLASSIFIC-
ATION
THERAPEUTIC
ACTION
INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIO
N
ADVERSE
EFFECTS
NURSING
CONSIDER-
ATION
Oxytocin
(Pitocin)
Oxytocic;
hormone
Synthetic form of
an endogenous
hormone
produced in the
hypothalamusan
d stored in the
posterior
pituitary;
stimulates the
uterus, especially
the gravid uterus
just before
parturition, and
causes
myoepithelium of
the lacteal
glands to
contract, which
results in milk
ejection in
lactating women.
- Antepartum:
to initiate or
improve
uterine
contractions to
achieve
earlyvaginal
delivery;
stimulation or
reinforcement
of labor in
selected
cases of
uterine inertia;
management
of inevitable or
incomplete
abortion; 2nd
trimester
abortion
- Postpartum:
to produce
uterine
contractions
during the
third stage of
labor tocontrol
postpartum
bleeding or
hemorrhage
Significant
cephalopelvic
disproportion,
unfavorable fetal
positions
orpresentations,
obstetric
emergencies that
favor surgical
intervention,prolonge
d use in severe
toxemia, uterine
inertia, hypertonic
uterine
patterns,induction or
augmentation of
labor when vaginal
delivery is
contraindicated,
previous cesarian
section.
CV: cardiac
arrhythmias,
PVCs,
hypertension
subarachnoid
hemorrhage
Fetal effects:
fetal
bradycardia,
neonatal
jaundice, low
Apgar scores
GI: nauseas,
vomiting
GU:
postpartum
hemorrhage,
uterine
rupture, pelvic
hematoma,
uterinehyperto
nicity, spasm
Ensure fetal
position and
size and
absence of
complication
s that
arecontraindi
cated with
oxytocin
therapy
Ensure
continuous
observation
for induction
of labor; fetal
monitoring
ispreferred.
Regulate
rate of
oxytocin
delivery;
monitor rate
and strength
of
contractions
Monitor BP
during
- Lactation
defieciency
administratio
n
Methylergono
vine maleate
(Methergine)
Oxytocic A partial agonist
or antagonist at
alpha receptors;
as a result, it
increases
thestrength,
duration, and
frequency of
uterine
contractions.
Routine
management
after delivery
of the
placenta.
Treatment of
postpartum
atony and
hemorrhage;
subinvolution
of the uterus.
Uterine
stimulation
during the
second stage
of labor
following the
delivery of the
anterior
shoulder,
under strict
medical
supervision.
Contraindicated with
allergy to
methylergonovine,
hypertension,
toxemia,lactation,
pregnancy.
CNS:
Dizziness,
headache,
tinnitus,
diaphoresis
CV: Transient
hypertensionp
alpitations,
chest pains,
dyspnea
GI: Nausea
and vomiting
Assess
history of
allergy to the
drug.
Administer
by IM
injection or
orally unless
emergency
requires IV
use.Complic
ations are
more
frequent with
IV use.
Monitor
postpartum
women for
BP changes
and amount
and
character of
vaginal
bleeding.
Avoid
prolonged
use of the
drug.
Teach client
to report
difficulty
breathing,
headache,
numb or
coldextremiti
es, severe
abdominal
cramping
Lidocaine
hydrochloride
(Dilocaine)
Local
anesthetic
Blocks the
generation and
conduction of
action potentials
in sensory
nerves by
reducing sodium
permeability,
reducing height
and rate of rise
of the action
potential,
increasing
excitation
threshold, and
slowing
conduction
velocity
Infiltration
anesthesia,
peripheral and
sympathetic
nerve blocks,
central nerve
blocks, spinal
and caudal
anesthesia
Contraindicated with
allergy to lidocaine or
amide-type local
anesthetics, CHF
cardiogenic shock,
2
nd
or 3
rd
degree AV
blocks
CNS:
headache,
backache,
septic
meningitis,
persistent
sensory
CV:
hypotensionD
ermatologic:
urticaria,
pruritus,
erythema,
edema
GU: urinary
retention,
urinary or
fecal
incontinence
Check drug
concentratio
ns carefully
Establish
safety
precautions
if CNS
changes
occur
Teach client
to report
difficulty
speaking,
thick tongue,
numbness,
tingling,diffic
ulty
breathing,
pain or
numbness at
site, swelling
or pain at
site
Terbutaline
Sulfate
(Brethine)
Tocolytic In low doses,
acts relatively
selectively at
beta 2-
adrenergic
receptors to
cause
bronchodilation
and relax the
pregnant uterus;
at higher doses,
beta 1selectivity
is lost and the
drug acts at beta
2 receptors to
cause typical
sympathomimeti
c cardiac effects
Tocolytic to
prevent
preterm labor
Contraindicated with
hypersensitivity to
terbutaline,
tachyarrythmias,
tachycardia,
hypertension,
lactation.
CNS:
restlessness,
apprehension,
anxiety, fear,
CNS
stimulation,
hyperkinesias,
insomnia,
tremors
CV: cardiac
arrhythmias,
palpitations,
angina pain,
changes in BP
and ECG
GI: Nausea,
vomiting,
heartburn,
unusual or
bad taste
Respiratory:
Respiratory
difficulties,
pulmonary
edema,
coughing,
bronchospasm
Use minimal
doses for
minimal
periods of
time; drug
tolerance
can occur
Maintain a
beta-
adrenergic
blocker on
standby in
case cardiac
arrhythmias
occur
Teach client
to report
chest pain,
dizziness,
insomnia,
weakness,
tremor
Nalbuphine
Hydrochloride
(Nubain)
Opioid
agonist-
antagonist
Nalbuphine acts
as antagonist at
specific
relief of
moderate to
severe pain,
Hypersensitivity to
nalbuphine or any
component, including
CNS:
Nervousness,
depression,res
Monitor BP
carefully
during IV
analgesic opioidreceptors
in the CNS
toproduce
analgesia
andsedation but
also acts tocause
hallucinations
andits antagonist
at mureceptors
used as a
supplement to
balanced
anesthesia, for
preoperative
and
postoperative
analgesia, and
for obstetrical
analgesia
during labor
and delivery.
sulfites;
pregnancy(prolonged
use or high dosages
at term)
tlessness,cryin
g,euphoria,flo
ating,hostility,
unusualdream
s,confusion,fai
ntness,halluci
nations
CV:
Hypertension,
hypotension,
bradycardia,
tachycardia
GI: Cramps,
dyspepsia,
bitter taste
administratio
n.
Monitor for
extrapyramid
al reactions,
and consult
physician if
they occur.
Monitor
diabetic
patients,
arrange for
alteration in
insulin dose
or timing if
diabetic
control is
compromise
d by
alterations in
timing of
food
absorption
You might also like
- Delivery Room Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDelivery Room Drug Studymacel sibayan100% (9)
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyVicenia BalloganNo ratings yet
- Drug Study DRDocument6 pagesDrug Study DRBheigh Lomitao AlbueraNo ratings yet
- Oxytocin (Pitocin) : Slide 1Document16 pagesOxytocin (Pitocin) : Slide 1Kalesha JonesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyiszahbelleNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyJoy Jarin100% (1)
- Common Drugs During PregnancyDocument16 pagesCommon Drugs During Pregnancymdsoukar2000No ratings yet
- GI Upset, Anorexia, Nausea, Vomiting, Constipation: and Death With OverdoseDocument4 pagesGI Upset, Anorexia, Nausea, Vomiting, Constipation: and Death With OverdoseNerissa Neri NatataNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug StudyGi Ey ElNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument2 pagesDrugsBhe Bhe RanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Generic Name (Brand Name) Indication Dosage, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Action Adverse Reaction Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilityDocument3 pagesDrug Study Generic Name (Brand Name) Indication Dosage, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Action Adverse Reaction Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilityKimm Charmaine RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study JrodDocument8 pagesDrug Study JrodGaez ﭢ UlpindoNo ratings yet
- Delivery DrugsDocument2 pagesDelivery DrugsBernardNo ratings yet
- Maternity and Newborn MedicationsDocument38 pagesMaternity and Newborn MedicationsJaypee Fabros EdraNo ratings yet
- UNIT XIII Drugs Affecting The Reproductive SystemDocument90 pagesUNIT XIII Drugs Affecting The Reproductive Systemrichardmd2100% (1)
- Methylergonovine maleate postpartum careDocument2 pagesMethylergonovine maleate postpartum careRitamariaNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument6 pagesGeneric NameKimsha ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: ENRIQUEZ, Angelique Jade C. BSN 2 C4Document4 pagesDrug Study: ENRIQUEZ, Angelique Jade C. BSN 2 C4Angelique Jade EnriquezNo ratings yet
- JINGCO - BSN 2-D - Module-6-Drug-StudyDocument16 pagesJINGCO - BSN 2-D - Module-6-Drug-StudyJashtine JingcoNo ratings yet
- Midazolam (Dormicum) GuideDocument8 pagesMidazolam (Dormicum) Guidekarenkaren09No ratings yet
- Drugs StudyDocument6 pagesDrugs StudyMark_Rebibis_8528No ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapeutics in ObstetricsDocument14 pagesPharmacotherapeutics in ObstetricsmercyNo ratings yet
- 15 DrugsDocument10 pages15 Drugscharles babasaNo ratings yet
- Drug Data for Oxytocin, Methergine, Hyoscine, Vitamin K and Eye Care ProphylaxisDocument4 pagesDrug Data for Oxytocin, Methergine, Hyoscine, Vitamin K and Eye Care ProphylaxisJune Dumdumaya67% (3)
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyAthena Irish LastimosaNo ratings yet
- Oxytocin and Methylergonovine Nursing StudyDocument16 pagesOxytocin and Methylergonovine Nursing StudyDinarkram Rabreca EculNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyChristine PunsalanNo ratings yet
- Isoxilan Generic Name: Isoxsuprine: Drug StudyDocument2 pagesIsoxilan Generic Name: Isoxsuprine: Drug StudyJohn Paolo Tamayo OrioNo ratings yet
- Labor and Delivery DrugsDocument8 pagesLabor and Delivery DrugsDing EmilyNo ratings yet
- 5 Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDocument24 pages5 Pregnancy Induced HypertensionHyacinth Mae Virtudazo RaganasNo ratings yet
- DrugDocument11 pagesDrugrihamNo ratings yet
- Mary Chiles College drug study overviewDocument11 pagesMary Chiles College drug study overviewJohn Lucas100% (2)
- Oxytocin Nursing Care Guide: Uses, Side Effects & ResponsibilitiesDocument10 pagesOxytocin Nursing Care Guide: Uses, Side Effects & ResponsibilitiesCieLouie Cauilan-DomingoNo ratings yet
- OB Drug StudyDocument19 pagesOB Drug StudyKismet Summons100% (8)
- Eclampsia Pregnancy CaseDocument13 pagesEclampsia Pregnancy CaseJohn MaglinteNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of Common Prenatal and Post-Partum DrugsDocument4 pagesDrug Study of Common Prenatal and Post-Partum DrugsDonna Mae BoolNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic: Urinary Tract Stimulants Pharmacologic: CholinergicDocument37 pagesTherapeutic: Urinary Tract Stimulants Pharmacologic: CholinergicApple MaeNo ratings yet
- OB Drug ChartsDocument2 pagesOB Drug ChartsNursingSchoolNotesNo ratings yet
- Asssessment Nursing Diagnosis Plan of Care Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesAsssessment Nursing Diagnosis Plan of Care Interventions Rationale EvaluationRoldan VidadNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ShenDocument12 pagesDrug Study ShenLass KazeNo ratings yet
- Pharmacologic Class: Ergot Alkaloid Therapeutic Class: Oxytocic Pregnancy Risk Category CDocument6 pagesPharmacologic Class: Ergot Alkaloid Therapeutic Class: Oxytocic Pregnancy Risk Category CayotanNo ratings yet
- 5 MG Iv BidDocument17 pages5 MG Iv BidhanzreinherNo ratings yet
- Drug Study On Emergency DrugsDocument16 pagesDrug Study On Emergency DrugsJosepNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument15 pagesEmergency Drugsjheverly123100% (1)
- Drug Study On Emergency DrugsDocument15 pagesDrug Study On Emergency DrugsJAy TootNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HydralazineDocument10 pagesDrug Study HydralazineLuige AvilaNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Therapeutic Action Indication & Dosage Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationDocument5 pagesDrug Name Therapeutic Action Indication & Dosage Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationArvan SebastianNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs Crash CartDocument14 pagesEmergency Drugs Crash CartEricson SomeraNo ratings yet
- SyntocinonDocument2 pagesSyntocinonDebarghya MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- NCM 102 Power and PsycheDocument13 pagesNCM 102 Power and Psychelarissedeleon100% (1)
- Gastrointestinal System: Antihistamine Half-Life: Onset: Peaks: DurationDocument3 pagesGastrointestinal System: Antihistamine Half-Life: Onset: Peaks: DurationsyerlyNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument34 pagesDrug StudyMarco MoralesNo ratings yet
- Pre-eclampsia, (Pregnancy with Hypertension And Proteinuria) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandPre-eclampsia, (Pregnancy with Hypertension And Proteinuria) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Hyperthyroidism, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHyperthyroidism, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (2)
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Definition, Causes, SymptomsDocument4 pagesAcute Kidney Injury (AKI) Definition, Causes, SymptomsElyne BicaldoNo ratings yet
- English ExercisesDocument16 pagesEnglish ExercisesElyne BicaldoNo ratings yet
- Main FinalDocument40 pagesMain FinalElyne BicaldoNo ratings yet
- Introduction UgifasfasdDocument2 pagesIntroduction UgifasfasdElyne BicaldoNo ratings yet
- Headnursing (Community)Document5 pagesHeadnursing (Community)Elyne BicaldoNo ratings yet
- A Cyst Is A FluidDocument3 pagesA Cyst Is A FluidElyne BicaldoNo ratings yet
- DOH Program ReactionDocument2 pagesDOH Program ReactionElyne BicaldoNo ratings yet
- Best Chocolate Chip Cookie Recipe Yielding 4 DozensDocument1 pageBest Chocolate Chip Cookie Recipe Yielding 4 DozensElyne BicaldoNo ratings yet
- Almond CupcakesDocument2 pagesAlmond CupcakesElyne BicaldoNo ratings yet
- Palawan NotesDocument2 pagesPalawan NotesElyne BicaldoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CardinalDocument21 pagesDrug Study CardinalDrei LanuzoNo ratings yet
- NomogramaDocument10 pagesNomogramaAndrés Hernández OrtizNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Mechanis M OF ActionDocument9 pagesDrug Study: Mechanis M OF ActionLovely San SebastianNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy MCQSDocument132 pagesPharmacy MCQSomair zafar100% (6)
- Continuous Peripheral Nerve Block For PoDocument5 pagesContinuous Peripheral Nerve Block For PoBinNo ratings yet
- Hemorrhagic Cerebro Vascular DiseaseDocument37 pagesHemorrhagic Cerebro Vascular Diseasejbvaldez100% (1)
- Drugs of MineDocument16 pagesDrugs of MineJoan GungobNo ratings yet
- Drug Used in Orthopedic ConditionsDocument105 pagesDrug Used in Orthopedic ConditionsnavenNo ratings yet
- Nursing Case Analysis of a Displaced Clavicle FractureDocument38 pagesNursing Case Analysis of a Displaced Clavicle FractureCyrill Alexandria TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Asssessment Nursing Diagnosis Plan of Care Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesAsssessment Nursing Diagnosis Plan of Care Interventions Rationale EvaluationRoldan VidadNo ratings yet
- PainDocument90 pagesPainmikErlh100% (4)
- OB1 Lec - AnalgesiaDocument3 pagesOB1 Lec - Analgesiaapi-3700579No ratings yet
- Dr. Aalia Hayat Akhtar QuestionsDocument14 pagesDr. Aalia Hayat Akhtar QuestionsrawalianNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Midterm BlueDocument5 pagesPharmacology Midterm BlueRhealyn LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Type Drug ChartDocument3 pagesType Drug ChartKarina Rodriguez100% (3)
- Myoma Final Power PointDocument45 pagesMyoma Final Power Pointicesexy100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument17 pagesDrug StudyJam CorrosNo ratings yet
- DrugcardsDocument70 pagesDrugcards2liter100% (2)
- NURSING CARE PLAN ANALYSISDocument7 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN ANALYSISCezanne CruzNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - Nalbuphine HydrochlorideDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY - Nalbuphine HydrochlorideCarson BirthNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER SUMMARY-opiod AnalgesicDocument9 pagesCHAPTER SUMMARY-opiod AnalgesicNuttiya WerawattanachaiNo ratings yet
- Compliled DrugstudyDocument15 pagesCompliled DrugstudyApril Jan D. Alagon0% (1)
- TRAMADOL Brands in Pakistan: Ser Brand Name Manufacturer/Mnf. Representative RegionDocument12 pagesTRAMADOL Brands in Pakistan: Ser Brand Name Manufacturer/Mnf. Representative RegionqaisergillNo ratings yet
- Acute Appendicitis in a Patient with Down SyndromeDocument88 pagesAcute Appendicitis in a Patient with Down SyndromeVinzii DrtNo ratings yet
- Treating urinary infection with cefuroximeDocument15 pagesTreating urinary infection with cefuroximeKate Penelope DalidNo ratings yet
- Perminant ExamDocument171 pagesPerminant ExamAsmaa Abdulmajeed ahmed100% (1)
- Practice Bullet In: Obstetric Analgesia and AnesthesiaDocument17 pagesPractice Bullet In: Obstetric Analgesia and AnesthesiaKatherine ReyesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CSDocument7 pagesDrug Study CSFrancis MendozaNo ratings yet
- Ecart DrugsDocument1 pageEcart DrugsKarla JaneNo ratings yet
- Med Org Kodigo CompleteDocument39 pagesMed Org Kodigo CompletePaula PraxedesNo ratings yet