Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Expt 102 Scan
Expt 102 Scan
Uploaded by
Ram RamirezCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Expt 102 Scan
Expt 102 Scan
Uploaded by
Ram RamirezCopyright:
Available Formats
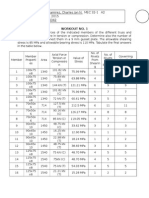
Viloria, Dayron Anthony B.
CE-2
PHY10L/A3
2013151234
4 30
August 30, 2014
August 6, 2014
Prof. Jimenez
65
75
85
95
105
40
50
60
70
80
0.5340
0.6200
0.7394
0.8793
1.0075
74.91
80.65
81.15
79.61
79.40
5
7
9
1
1
13
0
80
80
120
39.1
61.4
72.3
91.0
108.7
938.4
1052.6
964
992.7
1003.4
2.02
1.61
1.49
1.33
1.21
990.2
1.04%
0.04
0.06
0.08
0.09
0.11
1053 987.8 990.7 967.9 944.9 974.4
0.57%
Computations
Part 1.
1
ANALYSIS
1. The ideal graph in the uniform motion experiment is a straight
line with a positive slope. The slope of the graph is constant, and it
is equal to the velocity of the small kart. It indicates that the
velocity of the small kart does not change as it displaces from the
start to the end of travel. The values when plotted may not form a
straight line. The graph deviates from the expected graph, because
the values when interconnected do not form a straight line, but still
a straight line can be made by getting the average value of the
plotted values. The deviation of the graph is caused by an error of
both human and technical error most especially when the smart
timer gives an inaccurate readings.
2. Both methods in finding the angle are accurate. Using H/L in
finding the angle is accurate, because you will just substitute the
values in the given formula. However, using an angle indicator in
finding the angle will also be accurate, because it gives the actual
value of the angle. Despite of the accuracy of both methods, using
the angle indicator would be more accurate for part 2 because it
gives the actual value of the angle and there is lesser source of
errors compared when using the formula H/L.
3. Given that the ideal value of acceleration due to gravity is
9.8m/s or 980cm/s, slight variations in this numerical value to the
second decimal place are dependent primarily upon on altitude,
The acceleration due to gravity increases as it gets closer to the
surface of the earth, and decreases when gets farther, neglecting air
resistance. The smart timer reading must be less than the ideal
value, since the laboratory room is located at 3
rd
floor.
CONCLUSION
1. Describe uniform motion. Give an example of a body moving
with uniform motion.
Uniform motion is the motion of an object at constant speed
on a straight line. It is also the motion without acceleration. A car
going along a straight level road at steady speed is one example of
a uniform motion.
2. How are the acceleration of the cart down the track and the
angle of inclination related? What is the maximum
acceleration that the cart can have and what condition/s will
give this result?
3. How are you going to get the acceleration of the cart down
the track using the setting TIME:TWO GATES? Enumerate
the steps you are going to make and give the equation you are
going to use. (10 points)
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Ce161p A88 q1 MakeupDocument1 pageCe161p A88 q1 MakeupRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Thrust in A Ducted Fan Assembly For HovercarftDocument14 pagesCalculation of Thrust in A Ducted Fan Assembly For HovercarftAndrew Whipple100% (2)
- Sprint Start KinematicsDocument18 pagesSprint Start KinematicsJAson KEan0% (1)
- Authorization Letter SampleDocument1 pageAuthorization Letter SampleRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- Used Sack To Be Used As The Sleeve Material in The Horizontal Bar Lap Splice Instead of Felt PaperDocument8 pagesUsed Sack To Be Used As The Sleeve Material in The Horizontal Bar Lap Splice Instead of Felt PaperRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- Core Requirements For Adult New Applications - Department of Foreign AffairsDocument7 pagesCore Requirements For Adult New Applications - Department of Foreign AffairsRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- Seoul TripDocument2 pagesSeoul TripRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- RMExtractionDocument21 pagesRMExtractionRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- Work Inspection Checklists (11!06!2019)Document53 pagesWork Inspection Checklists (11!06!2019)Ram RamirezNo ratings yet
- Academic Advising FormDocument1 pageAcademic Advising FormRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- Course Expectation AlbaDocument1 pageCourse Expectation AlbaRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- Exp 8 10 ConmatDocument3 pagesExp 8 10 ConmatRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- Name: Ramirez, Charles Jon N. MEC 32-1 A2 July 28, 2015 S#: 2013150342 SNDocument2 pagesName: Ramirez, Charles Jon N. MEC 32-1 A2 July 28, 2015 S#: 2013150342 SNRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- Ramirez, Charles Jon N. Compiled ProbsDocument5 pagesRamirez, Charles Jon N. Compiled ProbsRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- PeerDocument1 pagePeerRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- Final Assesment: Ramirez, Charles Jon N. December 9, 2015 CE121/B2 Engr. BalmorisDocument3 pagesFinal Assesment: Ramirez, Charles Jon N. December 9, 2015 CE121/B2 Engr. BalmorisRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- Course Expectation: Ramirez, Charles Jon N. October 7, 2015 CE-3 / 2013150342 Engr. BalmorisDocument1 pageCourse Expectation: Ramirez, Charles Jon N. October 7, 2015 CE-3 / 2013150342 Engr. BalmorisRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- FW1Document18 pagesFW1Ram RamirezNo ratings yet
- PHY11 Lesson 3jhb Momentum and Collisions 2Q1415Document21 pagesPHY11 Lesson 3jhb Momentum and Collisions 2Q1415Ram RamirezNo ratings yet
- LAB REPORT-Osbourne Reynolds ApparatusDocument20 pagesLAB REPORT-Osbourne Reynolds Apparatusmizizasbonkure9055% (11)
- Microsoft Word MecvinaDocument37 pagesMicrosoft Word MecvinaRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- Application Form For Scholarship: Center For Scholarships and Financial AssistanceDocument3 pagesApplication Form For Scholarship: Center For Scholarships and Financial AssistanceRam RamirezNo ratings yet
- Mathexit 1Q1112Document8 pagesMathexit 1Q1112Ram RamirezNo ratings yet
- Caringal - B25Document1 pageCaringal - B25Ram RamirezNo ratings yet
- FIL11Document8 pagesFIL11Ram Ramirez0% (1)
- Antidifferentiation: MATH22-1 Calculus 2Document11 pagesAntidifferentiation: MATH22-1 Calculus 2Ram RamirezNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Work Energy Power Practice Questions v2 2016 AnswersDocument6 pagesUnit 3 Work Energy Power Practice Questions v2 2016 AnswersJane CongaoNo ratings yet
- Physics: Pearson Edexcel International Advanced LevelDocument28 pagesPhysics: Pearson Edexcel International Advanced LevelD S A DHAKA SPACE AGENCYNo ratings yet
- Kinematics WorksheetDocument44 pagesKinematics Worksheetaliza malikNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Dealing With Numbers: Select One: A. B. C. DDocument8 pages1.3 Dealing With Numbers: Select One: A. B. C. DPaulo BollosaNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument76 pagesEnglishTak ProNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document6 pagesUnit 2humbleavi100% (1)
- Rotation of A Rigid Body About A Fixed AxisDocument14 pagesRotation of A Rigid Body About A Fixed AxisFebrina RahayuNo ratings yet
- Aptitude.... Boats and StreamsDocument8 pagesAptitude.... Boats and StreamsHasrat AfridiNo ratings yet
- Parametric Motion Worksheet #2 (Updated 2021)Document4 pagesParametric Motion Worksheet #2 (Updated 2021)Ian CausseauxNo ratings yet
- CIE - O Level - Physics Syllabus - 2020-2021Document40 pagesCIE - O Level - Physics Syllabus - 2020-2021astargroupNo ratings yet
- IMECE2007-41441: Synthesis and Dynamic Analysis of A Quick-Return Mechanism Using Matlab and SimulinkDocument9 pagesIMECE2007-41441: Synthesis and Dynamic Analysis of A Quick-Return Mechanism Using Matlab and SimulinkPramodVermaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Interactions and Motion: R R R R RDocument13 pagesChapter 1: Interactions and Motion: R R R R RYunsung Francisco JoNo ratings yet
- Definitions To Learn For O Level PhysicsDocument3 pagesDefinitions To Learn For O Level PhysicsWilliam SkyNo ratings yet
- Ch05 Rectilinear Motion PDFDocument24 pagesCh05 Rectilinear Motion PDFMuhammadKhalidRehanChNo ratings yet
- Physics-2.1 Linear Motion 1Document13 pagesPhysics-2.1 Linear Motion 1Rais RahimiNo ratings yet
- Case Study Class 9Document4 pagesCase Study Class 9JAYA BALDEV DasNo ratings yet
- Topic Test QP (Work, Energy & Power) 2023 (F)Document9 pagesTopic Test QP (Work, Energy & Power) 2023 (F)gladnesstshepiso061No ratings yet
- 2.2 Analysing Motion GraphDocument46 pages2.2 Analysing Motion GraphreanizaNo ratings yet
- CH - 3 Physics Motion in A Straight LineDocument12 pagesCH - 3 Physics Motion in A Straight LineVENKATESH CHAKRABORTYNo ratings yet
- Force and Motion - Session 01 - Newton's First LawDocument29 pagesForce and Motion - Session 01 - Newton's First LawJoyae ChavezNo ratings yet
- Due Date: March 1 2018: Christ Church Foundation School 3 Form Physics AssignmentDocument8 pagesDue Date: March 1 2018: Christ Church Foundation School 3 Form Physics AssignmentuweeNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics - Ce198-1/A06: QuestionsDocument37 pagesEngineering Mechanics - Ce198-1/A06: QuestionsLisa Valois PedrigalNo ratings yet
- Additional Applications of Newton's Laws: Conceptual ProblemsDocument152 pagesAdditional Applications of Newton's Laws: Conceptual Problemsgueropapas713No ratings yet
- Speed, Distance and Time: 1. (3 MarksDocument14 pagesSpeed, Distance and Time: 1. (3 MarksAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Angular ImpulseDocument15 pagesChapter 13 Angular ImpulseRoger MelkoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Rotation of Rigid BodiesDocument18 pagesChapter 5 - Rotation of Rigid BodiesJackhyBSyNo ratings yet
- Analytical Synthesis and Analysis of Mechanisms Using Matlab and SimulinkDocument15 pagesAnalytical Synthesis and Analysis of Mechanisms Using Matlab and SimulinkFrancisco Jaime SilvaNo ratings yet
- Tutorials 3 - Motion in One Dimension and Two DimensionsDocument6 pagesTutorials 3 - Motion in One Dimension and Two DimensionsSamson ManyanyeNo ratings yet