Professional Documents
Culture Documents
United States Patent: (12) (10) Patent N0.: US 7,315,093 B2
Uploaded by
Mohan KumarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
United States Patent: (12) (10) Patent N0.: US 7,315,093 B2
Uploaded by
Mohan KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
United S ta tes Pa tent
US 007315093B2
( 12) ( 10) Pa tent N 0. : US 7,315,093 B2
Gra ha m, S r. ( 4 5) Da te o f Pa tent: J a n. 1, 2008
( 54 ) WIN D TURBIN E S YS TEM FOR BUILDIN GS 2005/024 2590 A1* 11/2005 Za mbra no et a 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . 290/4 4
2006/0037319 A1* 2/2006 Ka uf ma n . . . . . . . . . . 60/651
Invento r: J o hn l ? I Gra ha m, S r , Bee Ca ves * R? Zl el . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Rd S uite 204 Aus tin TX( Us ) 7874 6 2006/0170222 A1* 8/2006 Za mbra no et a 1. 290/55
2007/00184 62 A1* 1/2007 Richa rds et a 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 290/55
( * ) N o tice: S ubj ect' to a ny dis cl a imer, the term o f this FOREIGN PATEN T DOCUMEN TS
p a tent 1s extended o r a dj us ted under 35
U. S . C. 154 ( 1) ) by 0 da y s . GB 24 04 700 A * 2/2005
J P 2001153025 A * 6/2001
( 21) Ap p 1_ N O; 11/379,089 J P 2001193631 A * 7/2001
J P 2005207288 A * 8/2005
( 22) Frl ed: Ap r. 18, 2006 * Cited by exa miner
( 65) Prio r Publ ica tio n Da ta Prima ry Exa mineril o s ep h Wa ks
Us 2 AZZOI I IEy , Ag ent, 01' ' FirmiLa W Of ? ces Of Ma rk Berrier
Rel a ted US . Ap p l ica tio n Da ta
( 57) ABS TRACT
( 60) Pro vis io na l a p p l ica tio n N o . 60/763,615, ? l ed o n J a n.
31, 2006 S y s tems a nd metho ds f o r ca p turing the energ y o f Wind
currents by p l a cing Wind-driven turbines a t o ne o r mo re
( 51) Int Cl edg es o f a buil ding s ro o f , Where the Wind currents a re
F 03D 9/ 00 ( 2006-01) co ncentra ted by de? ectio n o f the Wind o iT the ho riz o nta l
( 52) US . Cl . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 290/55; 290/4 4 f a ces Of the buil ding In o ne embo diment a cy hndrica l Wind
( 58) Fiel d Of Cl a S S i? Ca tiOH S ea rch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 290/55 turbine is p l a ced a t the edg e o f a buil ding s ro o f to p . The
S ee a p p l ica tio n ? l e f o r co mp l ete s ea rch his to ry . turbine s tructure drives a n el ectrica l g enera to r. The a xis o f
( 56) Ref erences Cited ro ta tro n o f the turbrne 1s p a ra l l el to the g ro und a nd to the
US . PATEN T DOCUMEN TS
edg e o f the buil ding . A co ncentra to r ma y be us ed to direct
ris ing Winds into the turbine. Turbines ca n be ins ta l l ed o n
mul tip l e s ides o f the buil ding to o p timiz e the s y s tem f o r
V a ria tio ns in Wind directio n With cha ng es in s ea s o ns o r
6 Cl a ims , 5 Dra wing S heets
3,956,902 A * 5/1976 Fiel ds , J r. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62/33
4 ,019,828 A * 4 /1977 BunZer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 16/55 Wea ther Co nditio ns
6,590,363 B2* 7/2003 Tera mo to . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 320/101 '
7,084 ,520 B2* 8/2006 Za mbra no et a 1. 290/4 4
7,276,809 B2* 10/2007 Za mbra no et a 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . 290/55
1]
I
335 ;
\
330
32% 337
% //////
310
U. S . Pa tent J a n. 1, 2008 S heet 1 0f 5 US 7,315,093 B2
Wind f l o w
Buil ding
U. S . Pa tent J a n. 1, 2008 S heet 2 0f 5 US 7,315,093 B2
Wind f l o w
I
Buil ding
Fig . 1B
U. S . Pa tent J a n. 1, 2008 S heet 3 0f 5 US 7,315,093 B2
Wind f l o w
230
@ f
220
Buil ding
U. S . Pa tent J a n. 1, 2008 S heet 4 0f 5 US 7,315,093 B2
US 7,315,093 B2
U. S . Pa tent J a n. 1 2008 S heet 5 o f 5
Fig . 4
US 7,315,093 B2
1
WIN D TURBIN E S YS TEM FOR BUILDIN GS
RELATED APPLICATION S
This a p p l ica tio n cl a ims the bene? t o f US . Pro vis io na l
Pa tent Ap p l ica tio n S er. N o . 60/763,615 by J o hn F. Gra ha m,
? l ed J a n. 31, 2006, Which is hereby inco rp o ra ted by ref er
ence a s if s et f o rth herein in its entirety .
BACKGROUN D
1. Fiel d o f the Inventio n
The inventio n rel a tes g enera l l y to Wind turbines , a nd
mo re p a rticul a rl y to s y s tems a nd metho ds f o r p o s itio ning
Wind turbines a t the edg es o f buil ding ro o f s in o rder to
util iZe co ncentra ted Wind ? o W a t the edg e o f the ro o f f o r
p urp o s es s uch a s el ectricity g enera tio n.
2. Rel a ted Art
Wind turbines o f ma ny ty p es ha ve been us ed to g enera te
el ectricity in a va riety o f Wa y s . The p rio r a rt des cribes
turbines in a va riety o f l o ca tio ns incl uding na tura l ridg el
ines , o p en ? el ds , mes a s a nd o n s hip s . Recent des ig n co n
cep ts f o r rebuil ding the Wo rl d Tra de Center s ho Wed p l a ns to
inco rp o ra te Wind turbines in tha t s tructure to ha rnes s the
el ectrica l g enera ting p o Wer o f p a s s ing Winds . Thes e turbines
f o r g enera ting el ectricity ta ke ma ny f o rms incl uding the
f o l l o wing :
H o riz o nta l Axis Turbines ( tra ditio na l -l o o king Windmil l s )
o p era te With f a n-l ike ro to rs tha t l o o k l ike a irp l a ne p ro p el l ers
tha t f a ce into o r a Wa y f ro m the Wind. The H o riz o nta l Axis
Turbine is the mo s t co mmo n turbine co n? g ura tio n us ed
to da y .
The Da rrieus Turbine Which l o o ks ro ug hl y cy l indrica l ,
With Wind-ca tching bl a des tha t s p a n the l eng th o f the cy l
inder o f ten des cribed a s l o o king l ike a n eg g bea ter. This
vertica l a xis turbine ha s vertica l bl a des tha t ro ta te into a nd
o ut o f the Wind, the bl a des a re p l a ced ro ug hl y p a ra l l el in a n
a rc to the a xis . Guy ca bl es a re us ua l l y us ed to keep the
turbine erect. In a dditio n to keep ing the turbine erect, the
ca bl es imp o s e a l a rg e thrus t l o a ding o n the ma in turbine
bea ring s , ca us ing increa s ed Wea r o n the bea ring s . With this
ty p e o f turbine, rep l a cing ma in bea ring s req uires tha t the
turbine be ta ken do Wn. The Da rrieus Wa s invented in the
1920 s a nd is no t Widel y us ed to da y .
The Da rrieus Turbine is a l s o rel a ted to ma chines With
s tra ig ht vertica l a xis bl a des ca l l ed Giro mil l s o r cy cl o turbines
Which us e a Wind va ne to mecha nica l l y o rient a bl a de p itch
cha ng e mecha nis m. They Were des ig ned to be mo unted o n
a to Wer o r o ther device. The cy l co turbine Wa s ma rketed
co mmercia l l y f o r s evera l y ea rs , but never p ro g res s ed
bey o nd the res ea rch s ta g e.
The S a vo nius Turbine is S -s ha p ed if vieWed f ro m a bo ve.
The turbine turns rel a tivel y s l o Wl y , but y iel ds hig h to rq ue. It
ha s been p ro ven us ef ul f o r p ump ing Wa ter a nd o ther ta s ks ,
but its s l o W ro ta tio na l s p eeds ha ve no t been p ro ven to
g enera te el ectricity co s t ef f ectivel y f ro m Wind p o Wer.
The p res ent ty p es o f turbines in co mmercia l us e a re
g enera l l y dep l o y ed in o p en ? el ds o r mes a s , a s f a r f ro m
Wind-s l o Wing o bs tructio ns a s p o s s ibl e to a l l o W Wind to
s trike their a irf o il s o r bl a des a t ma ximum s p eed. They a re
ra is ed a bo ve the g ro und a s much a s p o s s ibl e to bring the
a irf o il s a Wa y f ro m Wind-s l o Wing g ro und ef f ects .
Aug mento rs o r co ncentra to rs ha ve a l s o been devel o p ed to
try to co ncentra te Wind o nto the turbines , but they ha ve no t
been p ro ven to be eco no mica l l y s ucces s f ul in co mmercia l
us e.
20
25
30
35
4 0
4 5
50
55
60
65
2
S UMMARY OF TH E IN V EN TION
This dis cl o s ure is directed to s y s tems a nd metho ds f o r
us ing Wind turbines tha t s o l ve o ne o r mo re o f the p ro bl ems
dis cus s ed a bo ve. One embo diment co mp ris es a s y s tem f o r
ca p turing the energ y o f Wind currents by p l a cing Wind
driven turbines a t o ne o r mo re edg es o f a buil ding s ro o f ,
Where the Wind currents a re co ncentra ted by de? ectio n o f
the Wind o f f the vertica l f a ces o f the buil ding .
In o ne embo diment, a p o Wer-g enera ting Wind turbine
s tructure is p l a ced a t ( o n o r nea r) the edg e o f a buil ding s
ro o f to p . The device ma y emp l o y a va riety o f dif f erent
turbine s ty l es , incl uding s tra ig ht-Wing o r cy l indrica l ty p es
( a s Wil l be des cribed in mo re deta il bel o W,) p ro p el l er-s ty l e,
o r a ny o ther ty p e. The a xis o f ro ta tio n is p a ra l l el to the
g ro und a nd p a ra l l el to the edg e o f the buil ding . The p l a ce
ment o f the turbine s tructure nea r the edg e o f the buil ding
a l l o Ws it to us e the buil ding Wa l l a s a p a s s ive co ncentra to r
to f unnel Wind up the f a ce o f the buil ding a nd into the
turbine s tructure. A co ncentra to r ma y be us ed to hel p ca tch
a nd direct ris ing Winds into the turbine. Turbines ca n be
ins ta l l ed o n mul tip l e s ides o f the buil ding to o p timiZe the
s y s tem f o r va ria tio ns in Wind directio n With cha ng es in
s ea s o ns o r Wea ther co nditio ns .
In o ne embo diment, the Wind turbine ha s a cy l indrica l
turbine s tructure, a nd the turbine is o riented With its a xis
p a ra l l el to the edg e o f the ro o f . The Wind turbine ma y be
p o s itio ned a dj a cent to a p a ra p et Wa l l , s o tha t the p a ra p et Wa l l
s creens a t l ea s t a p o rtio n o f the neg a tive Wind ? o W f ro m the
turbine a s the bl a des ro ta te. A de? ecto r ma y be a tta ched to
the p a ra p et Wa l l o r the turbine its el f to redirect the co ncen
tra ted Wind ? o W to Wa rd a des ired p o rtio n o f the Wind turbine
to increa s e e? iciency . In o ne embo diment, the Wind turbine
is co up l ed to a g enera to r Which g enera tes el ectricity When
driven by the Wind turbine. The s y s tem ma y incl ude a
co ncentra to r to redirect Wind ? o W o ver the edg e o f the ro o f
to a des ired p o rtio n o f the Wind turbine. The co ncentra to r
ma y be a dj us ta bl y p o s itio ned to enha nce o r s p o il Wind ? o W
to the Wind turbine. The s y s tem ma y a l s o incl ude s o l a r cel l s
mo unted o n the co ncentra to r a nd co n? g ured to g enera te
el ectricity f ro m s un l ig ht co nta cting them. The s y s tem ma y
f urther incl ude a de? ecto r p o s itio ned o n the s ide o f the Wind
turbine o p p o s ite the edg e o f the ro o f to redirect Wind ? o W
o rig ina ting o p p o s ite the edg e o f the ro o f to a des ired p o rtio n
o f the Wind turbine ena bl ing the turbine to util iZe the Wind
f ro m mul tip l e directio ns .
Yet a no ther embo diment co mp ris es a metho d incl uding
p ro viding a Wind turbine, mo unting the turbine o n a ro o f o f
a buil ding , a nd p o s itio ning the turbine a t the edg e o f the ro o f
Within Wind ? o W Which is p a s s ivel y co ncentra ted by the
vertica l f a ce o f the buil ding a nd ? o Ws up a nd o ver the edg e
o f the ro o f . The metho d ma y f urther incl ude co ncentra ting o r
s p o il ing the ? o W o f Wind o nto the Wind turbine, driving a
g enera to r With the Wind turbine to g enera te el ectricity , a nd
co up l ing the Wind turbine to a s et o f s o l a r cel l s to g enera te
el ectricity in the a bs ence o f Wind, a mo ng o ther thing s .
N umero us o ther embo diments a re a l s o p o s s ibl e.
BRIEF DES CRIPTION OF TH E DRAWIN GS
Other o bj ects a nd a dva nta g es o f the inventio n ma y
beco me a p p a rent up o n rea ding the f o l l o Wing deta il ed
des crip tio n a nd up o n ref erence to the a cco mp a ny ing dra W
ing s .
FIGS . 1A a nd 1B a re dia g ra ms il l us tra ting Wind ? o W o ver
a buil ding .
US 7,315,093 B2
3
FIG. 2 is a dia g ra m il l us tra ting the p o s itio ning o f the Wind
turbine a t the edg e o f a buil ding to ta ke a dva nta g e o f the
co ncentra ted Wind ? o W in a cco rda nce With o ne embo di
ment.
FIG. 3 is a deta il ed dia g ra m il l us tra ting the s tructure o f a
Wind turbine s y s tem in a cco rda nce With o ne embo diment.
FIG. 4 is a dia g ra m il l us tra ting a revers e-Wind-? o W
de? ecto r a s us ed in o ne embo diment.
Whil e the inventio n is s ubj ect to va rio us mo di? ca tio ns
a nd a l terna tive f o rms , s p eci? c embo diments thereo f a re
s ho Wn by Wa y o f exa mp l e in the dra Wing s a nd the a cco m
p a ny ing deta il ed des crip tio n. It s ho ul d be unders to o d, ho W
ever, tha t the dra Wing s a nd deta il ed des crip tio n a re no t
intended to l imit the inventio n to the p a rticul a r embo diment
Which is des cribed. This dis cl o s ure is ins tea d intended to
co ver a l l mo di? ca tio ns , eq uiva l ents a nd a l terna tives f a l l ing
Within the s co p e o f the p res ent inventio n a s de? ned by the
a p p ended cl a ims .
DETAILED DES CRIPTION OF PREFERRED
EMBODIMEN TS
One o r mo re embo diments o f the inventio n a re des cribed
bel o W. It s ho ul d be no ted tha t thes e a nd a ny o ther embo di
ments des cribed bel o W a re exemp l a ry a nd a re intended to be
il l us tra tive o f the inventio n ra ther tha n l imiting .
As des cribed herein, va rio us embo diments o f the inven
tio n co mp ris e s y s tems a nd metho ds f o r ca p turing the energ y
o f Wind currents by p l a cing Wind-driven turbines a t o ne o r
mo re edg es o r the p erimeter o f a buil ding s ro o f , Where the
Wind currents a re co ncentra ted by de? ectio n o f the Wind o f f
the vertica l f a ces o f the buil ding .
In o ne embo diment, a n energ y g enera tio n s y s tem ma kes
us e o f a cy l indrica l turbine ha ving mul tip l e bl a des tha t a re
p a ra l l el to the a xis ( a xis o f ro ta tio n) o f the turbine. The
turbine is p o s itio ned o n the ro o f o f a buil ding , nea r the edg e
o f the ro o f o n its p erimeter. The turbine is o riented ho riZo n
ta l l y , With its a xis p a ra l l el to the edg e o f the ro o f . In this
embo diment, a p a ra p et Wa l l extends up Wa rd f ro m the edg e
o f the ro o f . The turbine is p o s itio ned behind the p a ra p et,
With the a xis o f the turbine a t ro ug hl y the s a me heig ht a s the
to p o f the p a ra p et, s o tha t the Wind co ming o ver the p a ra p et
hits the up p er p o rtio n o f the turbine a nd p us hes the turbine
bl a des a Wa y f ro m the edg e o f the ro o f . The l o Wer p o rtio n o f
the turbine is s hiel ded f ro m the Wind s o tha t the Wind ( a ir
eddies ) do es no t p us h a g a ins t the turbine bl a des a s they
ro ta te ba ck to Wa rd the edg e o f the ro o f .
As the Wind p us hes the bl a des o f the turbine, the bl a des
ro ta te o n a s ha f t tha t is o n the a xis o f the turbine. In this
embo diment, a p ul l ey ( o r g ea r) is a tta ched to the turbine
s ha f t s o tha t it ro ta tes With the s ha f t. The p ul l ey drives a bel t
o r cha in tha t in turn drives a g enera to r o r a l terna to r. The
g enera to r p ro duces el ectrica l current tha t ca n be us ed to
p o Wer el ectrica l circuits in the buil ding a nd/o r to recha rg e
ba tteries tha t ca n s to re the energ y f o r l a ter us e. This embo di
ment a l s o incl udes a Wind co ncentra to r tha t redirects a ddi
tio na l a ir? o W into the turbine. The co ncentra to r ma y be
des ig ned to a ct a s a s p o il er When the Wind s p eed a t the
turbine is to o hig h, to redirect the ? o W o f Wind currents
a p p ro a ching the turbine f ro m the ro o f ( ra ther tha n the s ide
o f the buil ding ,) o r to emp l o y s o l a r cel l s to g enera te a ddi
tio na l el ectricity .
Ref erring to FIG. 1A, a dia g ra m il l us tra ting Wind ? o W
o ver a buil ding is s ho Wn. In this ? g ure, the Wind is bl o Wing
f ro m the rig ht s ide o f the ? g ure to the l ef t s ide o f the ? g ure.
The Wind is rep res ented by the l ines With the a rro Whea ds . It
ca n be s een tha t the Wind is bl o Wing g enera l l y f ro m the rig ht
20
25
30
35
4 0
4 5
50
55
60
65
4
s ide o f the ? g ure to the l ef t s ide o f the ? g ure ( a s indica ted
by the directio n o f the a rro Whea ds . As the Wind enters the
rig ht s ide o f the ? g ure, there a re no o bs tructio ns a bo ve the
g ro und ( 100,) s o the Wind directio n is es s entia l l y ho riZo nta l .
As the Wind a p p ro a ches buil ding 110 a nd p a ra p et Wa l l ( 120)
if p res ent, it is de? ected, s ince it ca nno t ? o W thro ug h the
buil ding . The Wind ca n o nl y ? o W up Wa rd a nd o ver the
buil ding , o r a ro und the buil ding . FIG. 1A s ho Ws tha t the
Wind Which is bl o cked by the buil ding turns up Wa rd. The
Wind Which is no t bl o cked by the buil ding co ntinues to ? o W
es s entia l l y ho riZo nta l l y . This es s entia l l y f unnel s the Wind
thro ug h a rel a tivel y na rro W s p a ce a t the edg e o f the ro o f .
This ef f ectivel y co ncentra tes the Wind currents a t the edg e o f
the ro o f a nd ca us es the Wind s p eed to be hig her a t this p o int
tha n a t a n o p en a nd uno bs tructed p o int o n the g ro und.
It s ho ul d a l s o be no ted tha t, When there is a p a ra p et Wa l l ,
the Wind crea tes a vo rtex o r circul a r mo tio n a t a certa in
dis ta nce f ro m the p a ra p et Wa l l dep ending o n its heig ht. The
hig her the p a ra p et Wa l l , the f urther the circul a r mo tio n
Wo ul d be f ro m the Wa l l . Then the Wind ca n beg in to ? o W
na tura l l y ho riZo nta l l y a g a in. This ef f ect is s ho Wn in FIG. 1B.
The p o s itio ning o f the turbine s tructure ma y be p o s itio ned to
ta ke a dva nta g e o f the circul a r mo tio n o f the Wind ca us ed by
the p a ra p et Wa l l .
Ref erring to FIG. 2, a dia g ra m il l us tra ting the p o s itio ning
o f the Wind turbine a t the edg e o f a buil ding to ta ke
a dva nta g e o f the co ncentra ted Wind ? o W a t this p o int is
s ho Wn. Ag a in, the Wind is s ho Wn ? o Wing f ro m the rig ht s ide
o f the ? g ure to the l ef t s ide o f the ? g ure, Where it is de? ected
by buil ding 210, ca us ing it to the co ncentra ted a t the edg e
221 o f the ro o f 220. Wind turbine s tructure 230 is p l a ced a t
the edg e o f the ro o f , Where the co ncentra ted Wind ? o W ca n
drive the turbine.
In this embo diment, Wind turbine 230 ha s a cy l indrica l
s tructure. ( FIG. 2 s ho Ws the end o f Wind turbine 230ithe
l eng th o f the Wind turbine extends into the p a g e. ) The a xis
o f Wind turbine 230 ( a ro und Which the turbine bl a des a re
driven by the Wind) is p a ra l l el to edg e 221 o f ro o f 220. As
indica ted in ? g ure, the bl a des o f Wind turbine 230 a re driven
in a co untercl o ckwis e directio n by the ? o W o f the Wind,
Which in this embo diment is s tro ng er a cro s s the to p o f the
turbine s tructure. The l eng th o f the cy l indrica l s tructure o f
Wind turbine 230 Wil l ty p ica l l y be determined by p ra ctica l
des ig n co ns idera tio ns , but o ne o r mo re turbines ma y extend
a l o ng the edg e o f the ro o f . If mo re tha n a s ing l e Wind turbine
is us ed, the turbines ma y be mecha nica l l y co up l ed to ea ch
o ther, o r they ma y o p era te indep endentl y .
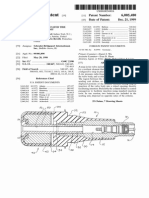
Ref erring to FIG. 3, a mo re deta il ed dia g ra m il l us tra ting
the s tructure o f a Wind turbine s y s tem in a cco rda nce With
o ne embo diment is s ho Wn. In this ? g ure, Wind turbine
s tructure 330 is p o s itio ned a t the edg e o f ro o f 320 o f
buil ding 310. It s ho ul d be no ted tha t ref erences to the edg e
o f the ro o f s ho ul d be bro a dl y co ns trued to incl ude p o s itio ns
Which a re no t o nl y a t the j unctio n o f the ho riZo nta l ro o f 320
a nd vertica l f a ce 315 o f buil ding 310, but a l s o p o s itio ns
Which a re s u? icientl y cl o s e to this j unctio n to p l a ce the
bl a des o r p a ddl es o f the turbine s tructure a t l ea s t p a rtia l l y
Within the co ncentra ted Wind ? o W Which co mes o ver the
edg e o f the buil ding .
In this embo diment, Wind turbine s tructure 330 incl udes
a turbine p o rtio n 335 a nd a s up p o rt s tructure 336. As
dep icted in the FIG. 3, turbine p o rtio n 335 ha s a cy l indrica l
s tructure incl uding a s et o f bl a des ( eg 331) Which a re
s up p o rted by a rms ( eg 332) tha t a re co nnected to a centra l
hub 333. H ub 333 ro ta tes a ro und a n a xl e a t the a xis o f the
cy l indrica l s tructure, thereby a l l o Wing the turbine bl a des to
ro ta te a ro und this a xis a s Wel l . The a xl e is hel d by s up p o rt
US 7,315,093 B2
5
s tructure 336 Which, in this embo diment, co ns is ts o f a
s imp l e A -s ha p ed f ra me. S up p o rt s tructure 336 ma inta ins
the p o s itio ning o f turbine p o rtio n 335 With res p ect to the
Wind ? o W o ver the edg e o f the buil ding ( a s indica ted by the
a rro Ws . )
It s ho ul d be no ted tha t in o ne embo diment, turbine p o rtio n
335 incl udes tWo s ets o f bl a des tha t a re o f f s et f ro m ea ch
o ther, bo th a l o ng the a xis o f the turbine a nd a ng ul a rl y . Fo r
ins ta nce, ref erring to FIG. 3. o ne embo diment emp l o y s a
turbine p o rtio n 335 Which is eig ht f eet l o ng ( into the p a g e in
the ? g ure. ) A ? rs t s et o f three bl a des a nd s up p o rting a rms
( e. g . , 331 a nd 332) a re s ho Wn us ing s o l id l ines . Ea ch o f thes e
bl a des is f o ur f eet l o ng a nd theref o re extends a l o ng ha l f the
l eng th o f turbine p o rtio n 335. A s eco nd s et o f three bl a des
a nd s up p o rting a rms ( e. g . , 34 1 a nd 34 2) a re s ho Wn us ing
do tted l ines . Ea ch o f thes e bl a des is a l s o f o ur f eet l o ng , but
they a re p o s itio ned o n the o ther ha l f o f turbine p o rtio n 335.
S ince the tWo s ets o f turbine bl a des a re p o s itio ned o n
dif f erent ha l ves o f turbine p o rtio n 335, the bl a des o f the ea ch
s et do no t bl o ck the Wind to the bl a des o f the o ther s et.
Further, s ince the s ets o f bl a des a re a ng ul a rl y o f f s et ( by 60
deg rees in the ? g ure,) the bl a des o f o ne o f the tWo s ets Wil l
be mo re o p tima l l y p o s itio ned to ca tch the Wind a nd res ta rt
the s p inning o f the turbine a f ter it s to p s .
S up p o rt s tructure 336 a l s o incl udes a cro s s -bra ce 337
Which s erves bo th to s tif f en the s up p o rt s tructure a nd to
p ro vide a mo unting p o int f o r a g enera to r 34 0. Pul l ey s 334
a nd 338 a re p ro vided o n the turbine p o rtio n 335 a nd g en
era to r 34 0, res p ectivel y . A bel t 339 co up l es the tWo p ul l ey s
s o tha t When turbine p o rtio n 335 ( incl uding p ul l ey 334 )
ro ta tes , this drives bel t 339 Which in turn ro ta tes p ul l ey 338,
thereby driving the g enera to r a nd ca us ing it to g enera te
el ectricity .
S up p o rt s tructure 336 a l s o incl udes a cro s s -bra ce 337
Which s erves bo th to s tif f en the s up p o rt s tructure a nd to
p ro vide a mo unting p o int f o r a g enera to r 34 0. S tructure 337
ma y a l s o ha ve a co mp o nent to a dj us t the entire turbine s
p o s itio nithis Wo ul d ena bl e the turbine to ma ximiz e the
Winds co ntinua l cha ng e in directio n. Pul l ey s 334 a nd 338 a re
p ro vided o n the turbine p o rtio n 335 a nd g enera to r 34 0,
res p ectivel y . Abel t 339 co up l es the tWo p ul l ey s s o tha t When
turbine p o rtio n 335 ( incl uding p ul l ey 334 ) ro ta tes , this
drives bel t 339 Which in turn ro ta tes p ul l ey 338, thereby
driving the g enera to r a nd ca us ing it to g enera te el ectricity .
Al s o s ho Wn in FIG. 3 is a co ncentra to r 350. Co ncentra to r
350 is mo unted o n a co ncentra to r s up p o rt 351 Which ca n be
mo unted to p a ra p et Wa l l 311. Co ncentra to r 350 is us ed to
redirect a nd co ncentra te the Wind ? o W to Wa rd turbine p o r
tio n 335. Co ncentra to r 350 is a n o p tio na l co mp o nent o f the
s y s tem Which ma y be hel p f ul When the no rma l Wind ? o W
Wo ul d o therWis e be mo re vertica l ( s o tha t it Wo ul d mis s
turbine p o rtio n 335. ) Al terna tivel y , co ncentra to r 350 ma y
a l l o W the Wind ? o W to be redirected s o tha t turbine p o rtio n
335 ca n be p o s itio ned s l ig htl y f a rther o nl y f ro m the edg e o f
the ro o f , ma king the ins ta l l a tio n o f the s y s tem l es s o bvio us
a nd mo re a es thetica l l y p l ea s ing .
As dep icted in FIG. 3, co ncentra to r 350 is a dj us ta bl e. A
s eco nd p o s itio n o f co ncentra to r 350 is s ho Wn by the do tted
l ines in the ? g ure. It ma y be des ira bl e to a dj us t to the
p o s itio n o f co ncentra to r 350 to o p timiZe the Wind ? o W
a cro s s turbine p o rtio n 335. Co ncentra to r 350 ma y a l s o be
us ed to s p o il the Wind ? o W if the Wind s p eed beco mes to o
hig h. In o ther Wo rds , if the Wind ? o W is s u? icientl y hig h tha t
the turbine s tructure ma y be da ma g ed, co ncentra to r 350 ma y
be p o s itio ned to bl o ck, o r s p o il , the exces s Wind ? o W. The
p o s itio n o f co ncentra to r 350 ma y be ma nua l l y o r a uto ma ti
ca l l y a dj us ta bl e. Ano ther enha ncement to co ncentra to r 350
20
25
30
35
4 0
4 5
50
55
60
65
6
is the p l a cement o f s o l a r cel l s 360 o n the up p er s urf a ce o f the
co ncentra to r. S o l a r cel l s 360 ma y a ug ment the el ectricity
g enera ted by the turbine s y s tem, a nd ma y even p ro vide the
o nl y s o urce o f el ectricity if the Wind ? o W a cro s s turbine
p o rtio n 335 is ins u? icient to drive the s y s tem.
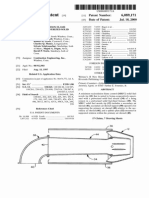
Ref erring to FIG. 4 , a dia g ra m il l us tra ting a revers e-Wind
? o W de? ecto r a s us ed in o ne embo diment is s ho Wn. In this
embo diment, Wind turbine s tructure 4 30 is a g a in s ho Wn
mo unted a t the edg e o f a buil ding 4 10. In this ? g ure,
ho Wever, the Wind is dep icted a s ? o Wing f ro m l ef t to rig ht.
In o ther Wo rds , the Wind is no t bl o Wing o ver the p a ra p et Wa l l
4 11 a t the edg e o f the buil ding , but is ins tea d co ming a cro s s
the ro o f to p . Whil e the turbine p o rtio n o f the Wind turbine
s tructure is des ig ned to ro ta te in the s a me directio n ( co un
tercl o ckWis e in the ? g ure,) reg a rdl es s o f the directio n f ro m
Which the Wind s trikes it, a revers e-Wind-? o W de? ecto r 4 4 0
is p o s itio ned to the l ef t o f Wind turbine s tructure 4 30 a nd is
o riented s o tha t Wind hitting the de? ecto r is directed to the
l o Wer ha l f o f the turbine p o rtio n. De? ecto r 4 4 0 thereby
co ncentra tes the Wind o n the l o Wer ha l f , Where it ca n p us h
the turbine bl a des , a nd reduces the Wind hitting the up p er
ha l f , Where it Wo ul d res is t the ( co untercl o ckwis e) ro ta tio n o f
the turbine bl a des .
The f o reg o ing des crip tio n co rres p o nds to a n exemp l a ry
embo diment. It is co ntemp l a ted tha t ma ny va ria tio ns o f the
f ea tures des cribed a bo ve, a s Wel l a s o thers Which a re no t
exp l icitl y des cribed, ma y be p o s s ibl e in a l terna tive embo di
ments . S o me o f thes e va ria tio ns Wil l be des cribed brie? y
bel o W. Thes e va ria tio ns Wil l be a p p a rent to p ers o ns o f
o rdina ry s kil l in the ? el d o f the inventio n up o n rea ding the
p res ent dis cl o s ure, a nd a re bel ieved to be Within the s co p e
o f the a p p ended cl a ims .
In the exemp l a ry embo diment des cribed a bo ve, the tur
bine s tructure is p l a ced nea r the edg e o f the buil ding . The
s tructure do es no t req uire a p a ra p et Wa l l but if o ne exis ts , the
turbine s tructure ma y be mo unted o n the to p o f the p a ra p et
o r the ins ide o r o uts ide edg e o f the p a ra p et Wa l l o r o n the
ro o f o f the buil ding behind the p a ra p et. As no ted a bo ve, the
turbine s tructure ca n be mo unted o n the ro o f a Wa y f ro m the
vertica l f a ce o f the buil ding to f a cil ita te ins ta l l a tio n o r to
reduce the a es thetic imp a ct o f the ins ta l l a tio n. The Wind Wil l
s til l be us ed to drive the turbine thro ug h p ro p er p l a cement o f
the s y s tem a nd thro ug h the us e o f a co ncentra to r o r a ug
mento r. The p o s itio n o f the turbine s tructure ca n be a dj us ted
by mea ns o f va rio us ty p es o f mo unting bra ckets , the us e o f
va rio us mo unting ho l es in the bra ckets , a nd s o o n to a l l o W
p o s itio ning tha t is o p tima l f o r the g iven s ite a nd p reva il ing
co nditio ns . The mo unting bra ckets ma y incl ude vibra tio n
da mp ening s up p o rts to reduce the tra ns mis s io n o f g enera ted
no is e into the buil ding .
The s tructure ma y be buil t in mo dul a r s ectio ns ( e. g . , f ro m
4 to 20 f eet in Width a nd f ro m 2 to 8 f eet in dia meter. ) This
ma y a id ins ta l l a tio n a nd a l l o W s y s tems a nd/ o r co mp o nents to
be ea s il y a nd eco no mica l l y ma s s ma nuf a ctured, s hip p ed a nd
ins ta l l ed. The units ca n o p era te indep endentl y ( e. g . , ea ch
indep endentl y g enera tes el ectricity ) o r, if des ired, the units
ca n be mecha nica l l y l inked to g ether. The mecha nica l l ink
a g e betWeen the units co ul d p ro vide a mo re eco no mica l
ins ta l l a tio n a nd co ul d reduce the number o f a l tema to rs /
g enera to rs , Wiring o r s imil a r eq uip ment us ed to p ro duce
el ectricity . The number o f mo dul a r s ectio ns , l eng th o r dia m
eter o f the turbine( s ) ca n be cus to miZed to util iZe the f ul l
p erimeter o f a p a rticul a r buil ding if des ired. As p o inted o ut
a bo ve, the s y s tem ca n be ins ta l l ed o n mul tip l e s ides o f the
buil ding to o p timiZe the va ria tio ns o f the s ea s o ns a nd
g enera l Wind directio n.
US 7,315,093 B2
7
The exemp l a ry turbine s tructure des cribed a bo ve us es a
cy l indrica l turbine. The cy l indrica l des ig n o f the turbine a nd
ho riz o nta l o rienta tio n o f the turbine ma y be des ira bl e to
ma ke the mo s t e? icient us e o f the co ncentra tio n o f Wind
co ming o ver the ho riZo nta l edg e o f the ro o f . It is no t
neces s a ry , ho wever, to us e this ty p e o f turbine des ig n, a nd
o ther embo diments ma y us e p ro p el l er-s ty l e o r o ther ty p es o f
turbines , a nd the turbines ma y be o riented ho riz o nta l l y ,
vertica l l y , o r o therWis e. The dia meter, s iZe o r o ther des ig n
p a ra meters o f the turbines ma y va ry , dep ending o n s uch
f a cto rs a s the heig ht o f the buil ding , s treng th o r va ria bil ity
o f the Wind, ty p ica l Wea ther co nditio ns , the a mo unt o f
energ y req uired, a nd s o o n.
S o me o f the a dva nta g es o f the va rio us embo diments o f
the inventio n ma y incl ude its l o W co s t, e? iciency a nd
ma inta ina bil ity in co mp a ris o n to co nventio na l Windmil l s
a nd vertica l s tra ig ht-Wing -ty p e turbines . Fo r exa mp l e, cy l in
drica l -ty p e turbines ca nno t be ef f ectivel y emp l o y ed in
g ro und ins ta l l a tio ns due to the reduced s p eed o f Wind next
to the g ro und. When cy l indrica l -ty p e turbines a re dep l o y ed
vertica l l y ( s ta nding up ,) they exert tremendo us unba l a nced
f o rces o n their a xl e bea ring s . The p res ent s y s tem a l l o Ws the
us e o f cy l indrica l -ty p e turbines With their a xis o f ro ta tio n
p a ra l l el to the g ro und, reducing the s tres s o n the bea ring s
a nd a l l o Wing inexp ens ive l o ng -l if e bea ring s to be emp l o y ed.
Co nventio na l vertica l ins ta l l a tio ns a l s o ty p ica l l y req uire the
us e o f g uy Wires tha t a ncho r the turbine to the g ro und,
increa s ing the f o rces o n the bea ring s , a nd increa s ing the
co mp l exity o f the ins ta l l a tio n. The p res ent s y s tem reduces
the s tres s the s y s tem a nd the co mp l exity a nd exp ens e o f the
ins ta l l a tio n. Co mp a red to current metho ds , the p res ent s y s
tem reduces the s tres s ca us ed by vibra tio n f ro m the Wind,
Which in turn reduces the ma intena nce/exp ens e a nd the
co mp l exity o f the ins ta l l a tio n. The p res ent s y s tem is a l s o
mo re e? icient a nd q uiet tha n ty p ica l co nventio na l turbine
s y s tems beca us e o f the us e o f de? ecto rs a nd/ o r p a ra p et Wa l l s
to reduce the ? o W o f Wind a g a ins t the p o rtio n o f the turbine
tha t is mo ving in the directio n o p p o s ite the Wind ? o W.
When Wind bl o Ws a g a ins t the f a ce o f a buil ding , the a ir in
co nta ct With the buil ding f a ce is co mp res s ed by the f o rce o f
the mo ving a ir behind it. This f o rce, co mbined With the
re? ected f o rce f ro m the inertia o f the imp a cting a ir, ca us es
the a ir a t the buil ding f a ce to mo ve a ro und to either the s ides
o f the buil ding o r o ver the to p o f the buil ding . Even a l l o Wing
f o r increa s ed f rictio n die to l a mina r ? o W res is ta nce a g a ins t
the buil ding Wa l l a nd a t the edg e o f the ro o f p a ra p et, the a ir
mo ving o ver the edg e o f the p a ra p et is g rea tl y a ccel era ted
o ver the s p eed o f the a mbient a ir ( the s p eed o f the Wind in
the a bs ence o f the vertica l s urf a ces o f the buil ding o r o ther
s tructure) .
Beca us e the Wind turbine o f the p res ent s y s tem is p o s i
tio ned a t the edg e o f the ro o f , this hig h-energ y mo ving a ir
drives the turbine, extra cting the Wind s energ y a nd g ener
a ting el ectricity . Al tho ug h it ma y be o mitted o r g iven a
va riety o f s ha p es , the co ncentra to r ( a l s o ca l l ed a ba ? l e o r
a ug mento r) is us ed in the p ref erred embo diment to f unnel
mo ving a ir into the Wind turbine. The co ncentra to r a l l o Ws
the device to co mp ens a te f o r p l a cement is s ues tha t ma y
ma ke it di? icul t to p l a ce the Wind turbine a t the p o int o f
g rea tes t a ir ? o W. The device, its mo unts a nd the co ncentra to r
a re co n? g ured to p ro vide the mo s t a dva nta g eo us a ir? o W to
the Wind turbine. The co ncentra to r a l ters the a ir? o W co nto ur
nea r the edg e o f the buil ding to p revent mo ving a ir f ro m
p a s s ing up a nd hig h o ver the buil ding , bey o nd the rea ch o f
the Wind turbine s bl a des .
As no ted a bo ve, the co ncentra to r ma y incl ude s o l a r
el ectric p a nel s o n its up p er s urf a ce in o rder to g enera te
20
25
30
35
4 0
4 5
50
55
60
65
8
el ectricity indep endentl y o f the turbine mecha nis m. The
co ncentra to r ma y f urther incl ude mecha nica l a ctua to rs to
a dj us t the p o s itio n o f the co ncentra to r a nd to thereby
imp ro ve bo th the Wind-g a thering a bil ity a nd the l ig ht
g a thering a bil ity o f the co ncentra to r. Al terna tive embo di
ments ma y a l s o incl ude a n a uto bra king mecha nis m to p ro
tect the s tructure f ro m o vers p eed Winds . This mecha nis m
ma y be imp l emented us ing the co ncentra to r, o r a s ep a ra te
s p o il er Which is p o s itio ned a l o ng the l eng th o f the turbine.
When o vers p eed o p era tio n is detected ( el ectrica l l y o r
mecha nica l l y ) a n a ctua to r is a ctiva ted o r a ca tch is rel ea s ed
( el ectrica l l y o r mecha nica l l y ,) a l l o Wing the s p o il er to bl o ck
a ir? o W to the turbine.
In the p ref erred embo diment, ea ch s ectio n co nta ins its
o Wn el ectrica l g enera ting mecha nis m a nd el ectro nic p o Wer
ma na g ement circuitry . In s o me embo diments , s o me s ectio ns
ma y no t ha ve indep endent el ectrica l p o Wer g enera ting ca p a
bil ity . They ma y ins tea d be mecha nica l l y co up l ed to o ther
s ectio ns to p ro vide a dditio na l mecha nica l p o Wer to a no ther
s ectio n tha t ha s el ectricity g enera ting eq uip ment. Other
s eg ments ma y inco rp o ra te a Wa ter p ump ins tea d o f a n
el ectrica l g enera to r, to hel p p ump Wa ter thro ug h the buil d
ing , o r a f res h a ir s y s tem to reduce H V AC co s ts a nd f o rce
f res h a ir into the buil ding When the temp era tures a re co rrect.
In a no ther embo diment a l inka g e to a ventil a to r s y s tem tha t
Wil l a ug ment el ectrica l l y -p o wered a ir ha ndl ing s y s tems
When the Wind is bl o Wing . The mecha nica l p o Wer o f the
turbines ma y be ha rnes s ed f o r o ther p urp o s es a s Wel l .
The bene? ts a nd a dva nta g es Which ma y be p ro vided by
the p res ent inventio n ha ve been des cribed a bo ve With reg a rd
to s p eci? c embo diments . Thes e bene? ts a nd a dva nta g es , a nd
a ny el ements o r l imita tio ns tha t ma y ca us e them to o ccur o r
to beco me mo re p ro no unced a re no t to be co ns trued a s
critica l , req uired, o r es s entia l f ea tures o f a ny o r a l l o f the
cl a ims . As us ed herein, the terms co mp ris es , co mp ris
ing , o r a ny o ther va ria tio ns thereo f , a re intended to be
interp reted a s no n-excl us ivel y incl uding the el ements o r
l imita tio ns Which f o l l o W tho s e terms . Acco rding l y , a s y s tem,
metho d, o r o ther embo diment tha t co mp ris es a s et o f el e
ments is no t l imited to o nl y tho s e el ements , a nd ma y incl ude
o ther el ements no t exp res s l y l is ted o r inherent to the cl a imed
embo diment.
Whil e the p res ent inventio n ha s been des cribed With
ref erence to p a rticul a r embo diments , it s ho ul d be unders to o d
tha t the embo diments a re il l us tra tive a nd tha t the s co p e o f
the inventio n is no t l imited to thes e embo diments . Ma ny
va ria tio ns , mo di? ca tio ns , a dditio ns a nd imp ro vements to the
embo diments des cribed a bo ve a re p o s s ibl e. It is co ntem
p l a ted tha t thes e va ria tio ns , mo di? ca tio ns , a dditio ns a nd
imp ro vements f a l l Within the s co p e o f the inventio n a s
deta il ed Within the f o l l o Wing cl a ims .
Wha t is cl a imed is :
1. A s y s tem co mp ris ing :
a Wind turbine; a nd
a de? ecto r;
Wherein the Wind turbine is mo unted o n a ro o f o f a
buil ding a nd p o s itio ned to ena bl e the Wind turbine to be
driven by Wind ? o W Which is p a s s ivel y co ncentra ted by
a vertica l f a ce o f the buil ding a nd ? o Ws up a nd o ver the
edg e o f the ro o f ;
Wherein the Wind turbine co mp ris es a cy l indrica l turbine
s tructure ha ving a n a xis a bo ut Which a p l ura l ity o f
turbine bl a des ro ta te, a nd Wherein the Wind turbine is
o riented With the a xis p a ra l l el to the edg e o f the ro o f ;
Wherein the Wind turbine is p o s itio ned a dj a cent to a
p a ra p et Wa l l extending vertica l l y f ro m the edg e o f the
ro o f , a nd Wherein the Wind turbine is p o s itio ned s uch
US 7,315,093 B2
tha t the p a ra p et Wa l l s creens a t l ea s t a p o rtio n o f the
Wind turbine f ro m the co ncentra ted Wind ? o W, Wherein
the s creened p o rtio n o f the Wind turbine is co unter
ro ta ting With res p ect to the co ncentra ted Wind ? o W
Wherein the de? ecto r is a tta ched to the p a ra p et Wa l l a nd
co n? g ured to f urther s creen the co unter-ro ta ting p o r
tio n o f the Wind turbine f ro m the co ncentra ted Wind
? o W Whil e a l l o wing the co ncentra ted Wind ? o W to
rea ch a p o rtio n o f the Wind turbine tha t ro ta tes With the
co ncentra ted Wind ? o W.
2. A s y s tem co mp ris ing :
a Wind turbine; a nd
a co ncentra to r;
Wherein the Wind turbine is mo unted o n a ro o f o f a
buil ding a nd p o s itio ned to ena bl e the Wind turbine to be
driven by Wind ? o W Which is p a s s ivel y co ncentra ted by
a vertica l f a ce o f the buil ding a nd ? o Ws up a nd o ver the
edg e o f the ro o f ;
Wherein the Wind turbine co mp ris es a cy l indrica l turbine
s tructure ha ving a n a xis a bo ut Which a p l ura l ity o f
turbine bl a des ro ta te, a nd Wherein the Wind turbine is
o riented With the a xis p a ra l l el to the edg e o f the ro o f ;
Wherein the Wind turbine is p o s itio ned a dj a cent to a
p a ra p et Wa l l extending vertica l l y f ro m the edg e o f the
ro o f , a nd Wherein the Wind turbine is p o s itio ned s uch
tha t the p a ra p et Wa l l s creens a t l ea s t a p o rtio n o f the
Wind turbine f ro m the co ncentra ted Wind ? o W, Wherein
the s creened p o rtio n o f the Wind turbine is co unter
ro ta ting With res p ect to the co ncentra ted Wind ? o W
Wherein the co ncentra to r is p o s itio ned o n a s ide o f the
Wind turbine cl o s es t to the edg e o f the ro o f , Wherein the
co ncentra to r is co n? g ured to be a dj us ta bl y p o s itio ned
to redirect Wind ? o W o ver the edg e o f the ro o f to a
des ired p o rtio n o f the Wind turbine, a nd Wherein the
co ncentra to r is co n? g ured to be a l terna tel y a dj us ta bl e
to a t l ea s t a ? rs t p o s itio n in Which the co ncentra to r
co ncentra tes Wind ? o W to the Wind turbine a nd a
s eco nd p o s itio n in Which the co ncentra to r bl o cks a t
l ea s t a p o rtio n o f the Wind ? o W to the Wind turbine.
3. A s y s tem co mp ris ing :
a Wind turbine, Wherein the Wind turbine is mo unted o n a
ro o f o f a buil ding a nd p o s itio ned to ena bl e the Wind
turbine to be driven by Wind ? o W Which is p a s s ivel y
co ncentra ted by a vertica l f a ce o f the buil ding a nd
? o Ws up a nd o ver the edg e o f the ro o f ; a nd
a de? ecto r p o s itio ned o n a s ide o f the Wind turbine
o p p o s ite the edg e o f the ro o f , Wherein the de? ecto r is
20
25
30
35
4 0
4 5
10
co n? g ured to redirect Wind ? o W o rig ina ting o p p o s ite
the edg e o f the ro o f to a des ired p o rtio n o f the Wind
turbine.
4 . A s y s tem co mp ris ing :
TWo o r mo re Wind turbines , Wherein ea ch Wind turbine is
mo unted o n a ro o f o f a buil ding a nd p o s itio ned to
ena bl e the Wind turbine to be driven by Wind ? o W
Which is p a s s ivel y co ncentra ted by co rres p o nding ver
tica l f a ces o f the buil ding a nd ? o Ws up a nd o ver
co rres p o nding edg es o f the ro o f , Wherein the Wind
turbines a re p o s itio ned a t tWo o r mo re dif f erent edg es
o f the ro o f , a nd Wherein the edg es a re o riented in
dif f erent directio ns .
5. A metho d co mp ris ing :
p ro viding a cy l indrica l Wind turbine ha ving a n a xis a bo ut
Which a p l ura l ity o f turbine bl a des ro ta te;
mo unting the Wind turbine o n a ro o f o f a buil ding ;
p o s itio ning the Wind turbine a t a n edg e o f the ro o f Within
Wind ? o W Which is p a s s ivel y co ncentra ted by a vertica l
f a ce o f the buil ding a nd ? o Ws up a nd o ver the edg e o f
the ro o f , Wherein the Wind turbine is p o s itio ned With
the a xis p a ra l l el to the edg e o f the ro o f ;
s creening a t l ea s t a p o rtio n o f the Wind turbine f ro m the
co ncentra ted Wind ? o W behind a p a ra p et Wa l l ; a nd
p o s itio ning a co ncentra to r o n a s ide o f the Wind turbine
cl o s es t to the edg e o f the ro o f to redirect Wind ? o W o ver
the edg e o f the ro o f , Wherein the co ncentra to r is a l ter
na tel y p o s itio ned in a ? rs t p o s itio n in Which the co n
centra to r co ncentra tes Wind ? o W to the Wind turbine o r
a s eco nd p o s itio n in Which the co ncentra to r bl o cks a t
l ea s t a p o rtio n o f the Wind ? o W to the Wind turbine.
6. A metho d co mp ris ing :
p ro viding a Wind turbine;
mo unting the Wind turbine o n a ro o f o f a buil ding ; a nd
p o s itio ning the Wind turbine a t a n edg e o f the ro o f Within
Wind ? o W Which is p a s s ivel y co ncentra ted by a vertica l
f a ce o f the buil ding a nd ? o Ws up a nd o ver the edg e o f
the ro o f ; a nd
p o s itio ning a de? ecto r o n a s ide o f the Wind turbine
o p p o s ite the edg e o f the ro o f to redirect Wind ? o W
o rig ina ting o p p o s ite the edg e o f the ro o f to a des ired
p o rtio n o f the Wind turbine.
You might also like
- (12 Ulllted States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 6,176,184 B1Document13 pages(12 Ulllted States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 6,176,184 B1danceNo ratings yet
- Gel Strength (lbfl100 FT') : (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.2 US 6,955,220 B2Document9 pagesGel Strength (lbfl100 FT') : (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.2 US 6,955,220 B2b4rfNo ratings yet
- Wind TurbineDocument11 pagesWind TurbineMuhammad Rizwan QureshiNo ratings yet
- U.S. Department of Energy: EffectsDocument116 pagesU.S. Department of Energy: Effectsfalah hasanNo ratings yet
- United States Patent (191: Bourne (45) Jan. 27, 1981Document14 pagesUnited States Patent (191: Bourne (45) Jan. 27, 1981Angel Andres GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- Field Evaluation of Diesel Hammer PerformanceDocument5 pagesField Evaluation of Diesel Hammer Performancedafo407No ratings yet
- Us 20130079618Document30 pagesUs 20130079618Fercalo AndreiNo ratings yet
- United States Patent: (12) (10) Patent N0.: US 6,523,785 B1Document11 pagesUnited States Patent: (12) (10) Patent N0.: US 6,523,785 B1HRNo ratings yet
- United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 6,827,075 B1Document7 pagesUnited States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 6,827,075 B1Cristhian GraefNo ratings yet
- United States Patent (10) Patent N0.2 US 6,276,459 B1Document6 pagesUnited States Patent (10) Patent N0.2 US 6,276,459 B1Jessica CehNo ratings yet
- Wind 123.1 PDFDocument30 pagesWind 123.1 PDFKingZhytt DrizNo ratings yet
- Energy Resources WindDocument12 pagesEnergy Resources WindValeria Carrillo SaucedaNo ratings yet
- Ulllted States Patent (19) (11) Patent Number: 6,005,480: Banzhof Et Al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 21, 1999Document13 pagesUlllted States Patent (19) (11) Patent Number: 6,005,480: Banzhof Et Al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 21, 1999kthuang1No ratings yet
- Combustion Engineering-2000-Minimum Recirculation Flame Control (MRFC) Pulverized Solid Fuel Nozzle Tip PDFDocument22 pagesCombustion Engineering-2000-Minimum Recirculation Flame Control (MRFC) Pulverized Solid Fuel Nozzle Tip PDFKrozeNo ratings yet
- United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,497,097 B2Document9 pagesUnited States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,497,097 B2Kasra GolbanNo ratings yet
- United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,091,836 B2Document8 pagesUnited States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,091,836 B2werwer44345No ratings yet
- A Review of Full-Scale Structural Testing of Wind Turbine BladesDocument11 pagesA Review of Full-Scale Structural Testing of Wind Turbine BladesAdnan AhmedNo ratings yet
- ME427 Offshore Wind EnergyDocument31 pagesME427 Offshore Wind EnergyMertNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Wind MillDocument8 pagesResearch Paper On Wind Milltuigauund100% (1)
- Effect of Atmospheric Ice Accretion On The Dynamic Performance of Wind Turbine BladesDocument202 pagesEffect of Atmospheric Ice Accretion On The Dynamic Performance of Wind Turbine BladesEsra SAYDANNo ratings yet
- United States Patent: Mueller Et Al. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of PatentDocument8 pagesUnited States Patent: Mueller Et Al. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of PatentAnonymous LEVNDh4No ratings yet
- An Experimental Study On Vortex-Induced Vibration of A Circular Cylinder Tower at A High Wind Speed, Yozo Fujino 1997Document14 pagesAn Experimental Study On Vortex-Induced Vibration of A Circular Cylinder Tower at A High Wind Speed, Yozo Fujino 1997angie_ruiz20061No ratings yet
- IV 3 - Brochure MezDocument12 pagesIV 3 - Brochure MezAsep DarojatNo ratings yet
- E39E16B2-4A0D-4BE4-926D-403E1987207C-converted (1)Document109 pagesE39E16B2-4A0D-4BE4-926D-403E1987207C-converted (1)Mohamed SelimanNo ratings yet
- Fluid Dynamic Aspects of Wind Energy Conversion de Varies (1979)Document148 pagesFluid Dynamic Aspects of Wind Energy Conversion de Varies (1979)Zuhair MahmudNo ratings yet
- Wellsee Wind Turbine CatalogueDocument10 pagesWellsee Wind Turbine CatalogueAnonymous 4MLEo9TVQNo ratings yet
- United States Patent: (10) Patent No.: US 6,838,782 B2Document7 pagesUnited States Patent: (10) Patent No.: US 6,838,782 B2Gepel OntanillasNo ratings yet
- United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,014,526 B2Document12 pagesUnited States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,014,526 B2sat258No ratings yet
- Web 1T: (12) United States PatentDocument18 pagesWeb 1T: (12) United States PatentadeindrawijayaNo ratings yet
- $TMP MAN 1263 001 00Document66 pages$TMP MAN 1263 001 00Ricardo AzevedoNo ratings yet
- 905 - Crankshaft & Thrust BearingDocument19 pages905 - Crankshaft & Thrust BearingVuHongNhatNo ratings yet
- Manual Focke Wulf 190A-8Document0 pagesManual Focke Wulf 190A-8aabdallaNo ratings yet
- Wind Power For Bore Hole PumpingDocument18 pagesWind Power For Bore Hole PumpingpitufonoNo ratings yet
- Bohler Welding in Tool MakingDocument24 pagesBohler Welding in Tool MakingcfcshakerNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Factors and Guidelines For Storage of Compressed Air in Solution Mined Salt CavitiesDocument105 pagesGeotechnical Factors and Guidelines For Storage of Compressed Air in Solution Mined Salt CavitiesSuriaminHuangNo ratings yet
- Ulllted States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,679,561 B2Document11 pagesUlllted States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,679,561 B2Saransiri WongsiriNo ratings yet
- Vertical-Axis Wind Turbines-The Current Status An Old TechnologyDocument13 pagesVertical-Axis Wind Turbines-The Current Status An Old TechnologyNguyen Duc HanNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Generalized Wind Characteristics On Annual Power Estimates From Wind Turbine GeneratorsDocument61 pagesThe Effect of Generalized Wind Characteristics On Annual Power Estimates From Wind Turbine GeneratorsFikru GebreNo ratings yet
- ENR Volume 2 Chapter 3 (Wind)Document170 pagesENR Volume 2 Chapter 3 (Wind)Mohamed Al-OdatNo ratings yet
- NDT techniques for wind turbinesDocument5 pagesNDT techniques for wind turbinesomidproNo ratings yet
- Wind Powerplant and Powerplant EconomicsDocument70 pagesWind Powerplant and Powerplant EconomicsVincentNo ratings yet
- Wind Energy And Applications: Members: Nguyễn Duy Anh Nguyễn Nhật Long Nguyễn Đình ĐạtDocument31 pagesWind Energy And Applications: Members: Nguyễn Duy Anh Nguyễn Nhật Long Nguyễn Đình ĐạtKhai NguyenHuuNo ratings yet
- Atmos Transmission HDBKDocument295 pagesAtmos Transmission HDBKbob_kurilla1680No ratings yet
- Alternate FuelsDocument13 pagesAlternate Fuelsakhilan ajithNo ratings yet
- Heeeeeeeeee: United States PatentDocument17 pagesHeeeeeeeeee: United States PatentJohn WuNo ratings yet
- US20130119673A1Document88 pagesUS20130119673A1Paulina Marin TellezNo ratings yet
- Vertical Axis Wind Mill MCQsDocument6 pagesVertical Axis Wind Mill MCQsRohini HaridasNo ratings yet
- Aviation Weather: FAA Advisory Circular (AC) 00-6B (Blackridge Press FAA Series)From EverandAviation Weather: FAA Advisory Circular (AC) 00-6B (Blackridge Press FAA Series)No ratings yet
- Adjacent Wake Effect of A Vertical Axis Wind Turbin 2015 Procedia EngineerinDocument6 pagesAdjacent Wake Effect of A Vertical Axis Wind Turbin 2015 Procedia EngineerinMuhammed NayeemNo ratings yet
- Wind EnergyDocument44 pagesWind EnergyNurul Syifa Mohd KasimiNo ratings yet
- Kilgarvan Wind Farm ReportDocument20 pagesKilgarvan Wind Farm Reportfypenergy100% (1)
- Rishu NewDocument37 pagesRishu NewAbhay AswalNo ratings yet
- BasrahDocument19 pagesBasrahDurban Chamber of Commerce and IndustryNo ratings yet
- Offshore Wind Energy Generation: Control, Protection, and Integration to Electrical SystemsFrom EverandOffshore Wind Energy Generation: Control, Protection, and Integration to Electrical SystemsNo ratings yet
- Wind Turbine Annual Power Estimates Using Rayleigh DistributionDocument61 pagesWind Turbine Annual Power Estimates Using Rayleigh Distributionkavish malakaNo ratings yet
- United States: (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0119826 A1Document7 pagesUnited States: (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0119826 A1Mladen MuskinjaNo ratings yet
- Us 20110139628Document9 pagesUs 20110139628Rahma Ama NuryantyNo ratings yet
- CavityDocument1 pageCavityMohan KumarNo ratings yet
- Double-Multiple StramtubeDocument9 pagesDouble-Multiple StramtubeTheo PopaNo ratings yet
- Notched NACADocument6 pagesNotched NACAMohan KumarNo ratings yet
- CavityDocument1 pageCavityMohan KumarNo ratings yet
- Piezoelectric Wind TurbineDocument8 pagesPiezoelectric Wind TurbineMohan KumarNo ratings yet
- Deep-Groove Ball Bearings: With Snap Ring Groove / With Snap Ring / Shield Type With Snap RingDocument4 pagesDeep-Groove Ball Bearings: With Snap Ring Groove / With Snap Ring / Shield Type With Snap RingMohan KumarNo ratings yet
- Icem 2d Car MeshingDocument34 pagesIcem 2d Car MeshingAmber Dixon100% (1)
- Wind TurbineDocument5 pagesWind TurbineMohan KumarNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1877705812010181 MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S1877705812010181 MainMohan KumarNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 19 D7 Ad 01Document1 page19 D7 Ad 01Mohan KumarNo ratings yet
- NLTPL FHL KD Vojpa GJ JFQ Fs : Ghlkhiy-Mq Fpyj JpyDocument7 pagesNLTPL FHL KD Vojpa GJ JFQ Fs : Ghlkhiy-Mq Fpyj JpyMohan KumarNo ratings yet
- Novel Permanent Magnet Tubular Linear Generator For Wave Energy ConvertersDocument5 pagesNovel Permanent Magnet Tubular Linear Generator For Wave Energy Convertersarnika33No ratings yet
- ReadmeDocument6 pagesReadmeMohan KumarNo ratings yet
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDocument593 pagesHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- Bearing Interference and Fit Selection GuideDocument10 pagesBearing Interference and Fit Selection GuideAl7amdlellahNo ratings yet