0% found this document useful (0 votes)
943 views6 pagesAspheric Surfaces and Conic Definitions
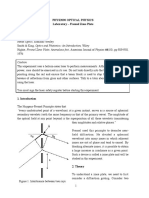
The document discusses aspheric surfaces which are used in optics to correct aberrations and are defined by having curvature that varies with radius from the optic axis. It describes how conic surfaces including paraboloids, ellipsoids and hyperboloids are used and how their shapes are affected by the conic constant. Specific examples of using parabolic mirrors and correcting astigmatism with higher order terms are provided.
Uploaded by
pakofrCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
943 views6 pagesAspheric Surfaces and Conic Definitions
The document discusses aspheric surfaces which are used in optics to correct aberrations and are defined by having curvature that varies with radius from the optic axis. It describes how conic surfaces including paraboloids, ellipsoids and hyperboloids are used and how their shapes are affected by the conic constant. Specific examples of using parabolic mirrors and correcting astigmatism with higher order terms are provided.
Uploaded by
pakofrCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Aspheric Surfaces: Discusses the definition and application of aspheric surfaces and the concept of 'sag' from spherical curvature.
- Conic Surfaces: Explains how conic surfaces are formed, defines different conic types, and presents related surface equations.
- Effect of Conic Constant k: Examines the variations of conic surfaces influenced by different values of constant k and their impacts on optics.
- Mirror and Parabolas: Explores the application of parabolas in designing mirrors for telescopic purposes and correcting optical aberrations.
- Correcting Astigmatism: Details the methods for correcting astigmatism using higher-order terms and adapting surface shapes.
- Aspheric Lens and Design: Highlights the process of designing aspheric lenses with CAD tools and challenges related to manufacturing complexity.