Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Genetics Neuro
Uploaded by
caneman2014Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Genetics Neuro
Uploaded by
caneman2014Copyright:
Available Formats
Genetics Neuro:
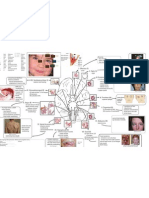
Red ragged muscle fibers are seen in mitochondrial diseases. Muscle fibers have this appearance because
abnormal mitochondria accumulate under the sarcolemma. Mitochondrial diseases show maternal
inheritance.
An increased number of trinucleotide repeats on the HD gene is associated with Huntington disease. The
larger the number of the repeats, the earlier the onset of the disease. Trinucleotide expansion occurs during
paternal transmission, causing a genetic phenomenon called anticipation.
Neurofibromatosis type l is a single-gene autosomal-dominant disorder. It occurs due to mutation of the
NF-1 gene located on the chromosome i 7. Cafe-au-lait spots, multiple neurofibromas, and Lisch nodules
are the most common symptoms.
Early-onset (<60y/o) familial Alzheimer disease is associated with three gene mutations: APP
(chromosome 21), presenilin 1 gene on chromosome 14 and presenilin 2 gene on chromosome 1. Lateonset familial Alzheimer disease is associated with apolipoprotein F4 genotype.
The familial mental retardation gene 1 (FMR1) is located on the long arm of the X chromosome. An
increased number of CGG trinucleotide repeats leads to hyper methetoin of cysteine bases and gene
inactivation. This defect is the cause of fragile X syndrome, which manifests with mental retardation1
facial dysmorphism, and macroorchidism.
Mitochondrial diseases are characterized by exclusively-maternal inheritance. The variable severity of
these diseases is explained by the random distribution of normal and mutated mitochondria between
daughter cells during mitosis; as a result, some cells may have completely healthy mitochondria, while
other cells contain mitochondria affected by genetic mutation (Heteroplasmy). MELAS is a mitochondrial
syndrome.
Alteration of gene expression in Huntington disease is believed to occur due to hyper methylation of
histones. Hypermethylated histones bind DNA and prevent transcription of certain genes. This leads to the
disruption of synthesis of some neutrophic proteins.
Friedreich ataxia is an autosomal recessive condition. The mutated gene on chromosome 9 has an increased
number of trinucleotide repeats. Friedreich ataxia is often associated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy,
diabetes mellitus, kyphoscoliosis, and foot deformities.
Fragile X syndrome is a common cause of inherited mental retardation. The disorder is X-linked and affects
males. Patients have mental retardation, dysmorphic facial features (large jaw large protruding ears) and
macroorchidism.
Fragile X syndrome arises secondary to an increase in the number of trinucleotide repeats within the FMR1
gene on the X chromosome. Typical clinical features of this condition include mental retardation1 facial
deformities, and macroorchidism.
A -amyloid plays an important role in the development of Alzheimer disease. Its precursor protein (APP)
is coded by a gene located on chromosome 21. Patients with trisomy 21 (Down syndrome) are likely to
develop Alzheimer disease after age 40.
Other conditions associated with Down syndrome include:
1. Acute leukemias: both AML and ALL
2. Congenital heart disease: endocardial cusion defect, VSD, ASD
3. GIT defects: duodenal atresia and Hirschsprung disease
You might also like
- Paneer MasalaDocument1 pagePaneer Masalacaneman2014No ratings yet
- Olfactory and Cranial Nerves at a GlanceDocument1 pageOlfactory and Cranial Nerves at a Glancecorreiodesportivo8071No ratings yet
- ScribdDocument1 pageScribdcaneman2014No ratings yet
- (WWW - Usmedbook.tk) EmbryologyDocument21 pages(WWW - Usmedbook.tk) Embryologycaneman2014No ratings yet
- Pancreatic LymphDocument1 pagePancreatic Lymphcaneman2014No ratings yet
- Joe Green: Objective ExperienceDocument1 pageJoe Green: Objective Experiencecaneman2014No ratings yet
- USMLE STEP 1 and STEP 2 Highly Tested Topics Gold CollectionDocument36 pagesUSMLE STEP 1 and STEP 2 Highly Tested Topics Gold CollectionTyler Lawrence CoyeNo ratings yet
- USMLE STEP 1 and STEP 2 Highly Tested Topics Gold CollectionDocument36 pagesUSMLE STEP 1 and STEP 2 Highly Tested Topics Gold CollectionTyler Lawrence CoyeNo ratings yet
- Blood Gases Washed PDFDocument1 pageBlood Gases Washed PDFcaneman2014No ratings yet
- USMLE STEP 1 and STEP 2 Highly Tested Topics Gold CollectionDocument36 pagesUSMLE STEP 1 and STEP 2 Highly Tested Topics Gold CollectionTyler Lawrence CoyeNo ratings yet
- GP Takeout MenuDocument2 pagesGP Takeout Menucaneman2014No ratings yet
- Basic First Aid PDFDocument10 pagesBasic First Aid PDFkeziahmaedavidNo ratings yet
- 2015 USMLE BulletinDocument28 pages2015 USMLE BulletinUSB_90No ratings yet
- Medicine - Picmonics List - List of PicmonicsDocument21 pagesMedicine - Picmonics List - List of Picmonicscaneman2014100% (1)
- Resp PathDocument11 pagesResp Pathcaneman2014No ratings yet
- First Aid Step 1 2012 Errata 130301 FinalDocument29 pagesFirst Aid Step 1 2012 Errata 130301 FinalAbia Izzeldin KamilNo ratings yet
- Behav SC NeuroDocument2 pagesBehav SC Neurocaneman2014No ratings yet
- Goljan - High Yield Questions For USMLEDocument36 pagesGoljan - High Yield Questions For USMLEMustafa MenemNo ratings yet
- Goljan SlidesDocument383 pagesGoljan Slidesusmle196% (23)
- HistologyDocument1 pageHistologycaneman2014No ratings yet
- UsmleDocument1 pageUsmlecaneman2014No ratings yet
- Biochem OtherDocument2 pagesBiochem Othercaneman2014No ratings yet
- EmbryoDocument5 pagesEmbryocaneman2014No ratings yet
- Behav SC OtherDocument3 pagesBehav SC Othercaneman2014No ratings yet
- Biochem MSKDocument2 pagesBiochem MSKcaneman2014No ratings yet
- Biochem OncologyDocument1 pageBiochem Oncologycaneman2014No ratings yet
- Genetics OtherDocument4 pagesGenetics Othercaneman2014No ratings yet
- Biochem NeuroDocument3 pagesBiochem Neurocaneman2014No ratings yet
- Biochem HepatologyDocument2 pagesBiochem Hepatologycaneman2014No ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- OBATALA - Ifa and The Chief of The Spirit of The White ClothDocument5 pagesOBATALA - Ifa and The Chief of The Spirit of The White ClothToyin Adepoju100% (3)
- A Beautiful Day in The Neighborhood Activity GuideDocument13 pagesA Beautiful Day in The Neighborhood Activity GuideQuirk Books100% (8)
- Medium Term Plan On Teaching Scratch in Year 4Document5 pagesMedium Term Plan On Teaching Scratch in Year 4api-272550320No ratings yet
- Patanjali Yoga Sutras IntroductionDocument49 pagesPatanjali Yoga Sutras IntroductiongurusattaNo ratings yet
- Republic Act 1425 (Autosaved)Document36 pagesRepublic Act 1425 (Autosaved)hue sandovalNo ratings yet
- CDC Project Proposal TemplateDocument11 pagesCDC Project Proposal TemplateMirza ArfanNo ratings yet
- Procurement-Lecture 3 Customer Service and Logistics: Abdikarim Mohaidin AhmedDocument33 pagesProcurement-Lecture 3 Customer Service and Logistics: Abdikarim Mohaidin AhmedMA. CHRISTINE BODUANNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 & 2Document18 pagesChapter 1 & 2Bella Monica Montecino100% (3)
- G8DLL Q2W6 LC32-34Document17 pagesG8DLL Q2W6 LC32-34Joemard FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Constitution of India, Law and Engineering QuantumDocument143 pagesConstitution of India, Law and Engineering QuantumKnowledge Factory100% (5)
- Recommended Curriculum: Seven (7) Types of CurriculumDocument1 pageRecommended Curriculum: Seven (7) Types of CurriculummoyesaNo ratings yet
- SHS General Mathematics Q2 M7Document16 pagesSHS General Mathematics Q2 M7Abegail PanangNo ratings yet
- Busn 702Document9 pagesBusn 702Pablo GuzmánNo ratings yet
- Role of education in curbing child labourDocument11 pagesRole of education in curbing child labourA.n. Surya100% (2)
- Buddhism and Psychology - A Working BibliographyDocument44 pagesBuddhism and Psychology - A Working BibliographyAlan Poey100% (1)
- NIH Public Access: Sleep and Women's HealthDocument31 pagesNIH Public Access: Sleep and Women's HealthHusni FaridNo ratings yet
- Reflection On Teaching Practice To YLsDocument3 pagesReflection On Teaching Practice To YLsivannasoledadNo ratings yet
- Asymptotic Notations ExplainedDocument28 pagesAsymptotic Notations ExplainedNarendra Singh PatelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Principles of Laboratory MedicineDocument19 pagesIntroduction To The Principles of Laboratory Medicinedanielle kaye arangoteNo ratings yet
- Summary Covers Exam MaterialDocument30 pagesSummary Covers Exam MaterialWriting ServiceNo ratings yet
- Ankit - KP Horary Software - Prashna Kundali Software - Free KP Astrology SoftwareDocument3 pagesAnkit - KP Horary Software - Prashna Kundali Software - Free KP Astrology SoftwareANKIT SINGHNo ratings yet
- Position and Powers of Karta in Hindu LawDocument11 pagesPosition and Powers of Karta in Hindu LawAniket SachanNo ratings yet
- Radar Engineering, 1/e: Book Information Sheet Book Information SheetDocument2 pagesRadar Engineering, 1/e: Book Information Sheet Book Information SheetLakshmi MounikaNo ratings yet
- BallTank Foundation Design Guide Using AFES 21pDocument51 pagesBallTank Foundation Design Guide Using AFES 21pcgingenieros100% (1)
- Oral Com Module Week 4 Converted From PDF To WordDocument10 pagesOral Com Module Week 4 Converted From PDF To WordRowena Francisco Go VillorenteNo ratings yet
- The AdjectiveDocument3 pagesThe AdjectiveAna DerilNo ratings yet
- Software Configuration ManagementDocument27 pagesSoftware Configuration ManagementJay BorthenNo ratings yet
- Issue Essay For GREDocument1 pageIssue Essay For GREBharath RaghavanNo ratings yet
- Research in Daily Life 2Document166 pagesResearch in Daily Life 2Zianna Marie De RamosNo ratings yet