100% found this document useful (1 vote)
351 views19 pagesIntroduction to Laboratory Medicine
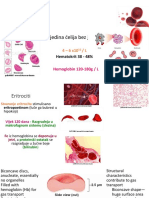
The document provides an introduction to laboratory medicine, discussing how laboratory tests impact patient care through confirmation of clinical diagnoses, guiding treatment decisions, and detecting antibiotic resistance. It notes that laboratory medicine involves pathologists, scientists, and technicians performing hundreds of millions of tests annually in the US, accounting for around 2% of healthcare costs. Key terms discussed include reference laboratories, which perform specialized tests, and point-of-care testing, which provides rapid results at the patient's location to directly influence care. Case studies demonstrate how point-of-care strep tests can support prescribing or withholding antibiotics.
Uploaded by
danielle kaye arangoteCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
351 views19 pagesIntroduction to Laboratory Medicine
The document provides an introduction to laboratory medicine, discussing how laboratory tests impact patient care through confirmation of clinical diagnoses, guiding treatment decisions, and detecting antibiotic resistance. It notes that laboratory medicine involves pathologists, scientists, and technicians performing hundreds of millions of tests annually in the US, accounting for around 2% of healthcare costs. Key terms discussed include reference laboratories, which perform specialized tests, and point-of-care testing, which provides rapid results at the patient's location to directly influence care. Case studies demonstrate how point-of-care strep tests can support prescribing or withholding antibiotics.
Uploaded by
danielle kaye arangoteCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd