Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Psychoactive Drugs
Uploaded by
Phillip WilsonCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Psychoactive Drugs
Uploaded by
Phillip WilsonCopyright:
Available Formats
Odalys Martinez
January 7, 2015
Period 5
Module 9: A Chart of Psychoactive Drugs
a. Alcohol
Research: Historically, alcoholic beverages have served as sources of
needed nutrients and have been widely used for their medicinal, antiseptic
and painkilling properties. There are 13 minerals that are essential for
human life and all of them can be found in alcohol. Many believe that
farming started to produce ingredients for alcohol rather than food
production. Western culture also has some of the strictest laws for alcohol
in the world.
Effects: Alcohol affects every organ in the drinker's body and can damage
a developing fetus. Intoxication can impair brain function and motor skills;
heavy use can increase risk of certain cancers, stroke, and liver disease.
Other effects include reduced inhibitions, slurred speech, motor
impairment, confusion, memory problems, concentration problems, coma,
and breathing problems.
b. Valium
Research: A very popular prescription drug. Its prescribed to treat
sleeplessness, anxiety and muscle spasms. It comes in liquid and pill
forms. It is occasionally used for operations as it helps reduce tension and
anxiety.
Effects: Effects of valium include stomach pain, agitation, anxiety,
blistering or peeling of skin, blurred vision, confusion, chills, cough, dark
urine, lightheadedness, fast heartbeats, irregular breathing, fever,
headache, increased muscle spasms, irritability, lack of appetite, loss of
bladder control, nausea, pale skin, rashes, seizures, and yellow eyes.
c. Xanax
Research: Xanax is used to treat anxiety and panic disorders as well as
tremors. It belongs to a class of medications called benzodiazepines. It
can be found in forms such as tablets, liquid, disintegrating tablets, and
extended release tablets. It acts on the brain and central nervous system,
targeting a natural body chemical that lessens abnormal brain excitement.
Effects: Xanax can cause a person to become forgetful, clumsy, drowsy,
discouraged, irritable, relaxed, and have trouble speaking or
concentrating.
d. Opium
Research: Opium was commonly used a painkiller before morphine was
developed. You can smoke opium or ingest it through tea with alkaline.
However, both forms are dangerous as there can be too much of it used
and the effects can vary depending on how its taken.
Effects: Most opium effects do not need medical attention since the body
can get accustomed to it. Effects include relaxation, reduced anxiety,
emotional detachment, reduced pain and stress, sleepiness, altered mood,
reduced appetite, weight loss, reduced energy, sweating, difficulty
concentrating, and impaired vision.
e. Heroin
Research: Heroin is synthesized from morphine and appears in a white or
brown powder or as a black, sticky substance. In 2011, 4.2 million
American aged 12 or older had used heroin at least once in their lives.
About 23% of users become dependent on it. It can be injected, snorted,
or smoked. The drug reaches then reaches the brain rapidly.
Effects: Many users of heroin reach a high and usually have a dry mouth,
flushing of the skin, or clouded mentality. Long term effects include bad
teeth, inflammation of the gums, constipation, cold sweat, itching, weak
immune system, respiratory illness, muscular weakness or partial
paralysis, menstrual disturbance in women and spontaneous abortion,
loss of memory, depression, loss of appetite, insomnia. Street heroin
especially can cause blood clots and damage vital organs.
f. Codeine
Research: Codeine is a narcotic pain-reliever and cough suppressant
similar to morphine. A small amount of it is converted to morphine in the
body. The precise mechanism of action of codeine is not known but it
binds to receptors in the brain that are important for transmitting the
sensation of pain throughout the body.
Effects: Codeine causes increased tolerance of pain, slow heart rate,
shallow breath, confusion, agitation, feelings of extreme happiness or
sadness, seizures r bladder problems.
g. Caffeine
Research: Caffeine is mostly added to foods, drinks, and medicines. 90%
of people in the world use caffeine and in the U.S., 80% of adults consume
caffeine every. The average adult intakes 200 mg per day, the same
amount found in four cans of soda. It is mostly used to improve mental
alertness or with painkillers. It is also used to treat asthma, gallbladder
disease, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, shortness of breath in
newborns and low blood pressure.
Effects: Caffeine may cause diarrhea, dizziness, fast heartbeat, blurred
vision, dry mouth, flushed dry skin, bad breath, increased urination,
unusual thirst, irritation, and tremors.
h. Nicotine
Research: Nicotine is the primary ingredient in tobacco products. Most
smokers can identify it as harmful and nearly 35 million attempt to quit
each year. Unfortunately, more than 85% of those attempting to quit
relapse within a week. Nicotine increases levels of dopamine and allows
the user to feel more pleasure. The short-term effects last shortly causing
the user to use the drug more frequently.
Effects: Nicotine causes lung disease, asthma symptoms, cancer of
mouth, kidney, esophagus, stomach, pancreas, cervix, and bladder,
increased risk of heart disease, and early menopause in women.
i. Cocaine
Research: Cocaine is a powerfully addictive stimulant that directly affects
the brain. Cocaine was labeled the drug of the 1980s and 1990s because
of its extensive popularity and use during that period. However, cocaine is
not a new drug. In fact, it is one of the oldest known psychoactive
substances. Coca leaves, the source of cocaine, have been chewed and
ingested for thousands of years, and the purified chemical, cocaine
hydrochloride, has been an abused substance for more than 100 years.
Effects: Dilated pupils; increased body temperature, heart rate, and blood
pressure; nausea; increased energy, alertness; euphoria; decreased
appetite and sleep, panic attacks and violent behavior. Long-term effects
include anxiety, paranoia, insomnia, and nasal damage.
j. Crack
Research: Crack cocaine is a freebase form of cocaine that can be
smoked. Crack cocaine effects do not last as long as powder cocaine.
This usually results in the user smoking it again in less than 20 minutes. A
crack user is therefore always in need of the drug and may resort to crime.
Effects: Short-term effects include dilated pupils, dry mouth, disturbed
sleep patterns, nausea, erratic behavior, increased heart rate, blood
pressure, or body temperature, hallucinations, intense euphoria,
depression, intense drug craving, panic attacks, and seizures. Long-term
effects include permanent damage of blood vessels, liver, kidney, or lung
damage, respiratory failure, malnutrition, sever tooth decay, chest pains,
infertility, mood disturbance, and depression.
k. Amphetamine
Research: Amphetamine stimulates the central nervous system by
increasing the amount of certain chemicals in the body. It is used to treat
narcolepsy and attention deficit disorders with hyperactivity. Adderall is a
popular form of prescribed amphetamine.
Effects: Short-term effects include increased heart rate, raised blood
pressure, loss of appetite, euphoria, feeling of control and alertness,
increased concentration, reduce sensation of fatigue, increased
confidence, and more social. Long-term effects include extreme anxiety,
feeling of superiority, insomnia, restlessness, hallucinations, tremors,
weight loss, and aggressive behavior.
l. Methamphetamine
Research: Methamphetamine is a stimulant drug that is chemically similar
to amphetamine. It takes the form of a white, odorless, bitter-tasting
crystalline powder. Methamphetamine is taken orally, smoked, snorted, or
dissolved in water or alcohol and injected. Smoking or injecting the drug
delivers it very quickly to the brain, however the high fades quickly.
Methamphetamine increases the amount of the neurotransmitter
dopamine, leading to high levels of that chemical in the brain. It is rarely
prescribed but can be used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.
Effects: Short-term effects include loss of appetite, increased heart rate,
dilated pupils, disturbed sleep patterns, nausea, violent behavior,
hallucinations, panic attacks, and seizures. Long-term effects include
permanent damage to blood vessels, destruction of tissues in nose if
sniffed, damage to lung, liver, and kidney, severe tooth decay,
disorientation, depression, and damage to the brain similar to alzheimers
disease, epilepsy, and strokes.
m. LSD
Research: LSD (d-lysergic acid diethylamide) is one of the most potent
mood-changing chemicals. It was discovered in 1938 and is manufactured
from lysergic acid, which is found in ergot, a fungus that grows on rye and
other grains. LSD is sold in tablets, capsules, and, occasionally, liquid
form; thus, it is usually taken orally. LSD is often added to absorbent
paper, which is then divided into decorated pieces, each equivalent to one
dose. The experiences, often referred to as trips, are long; typically, they
end after about 12 hours. LSD is not considered an addictive drug since it
does not produce compulsive drug-seeking behavior. However, LSD does
produce tolerance.
Effects: Short-term effects include increased heart rate, blood pressure,
heart failure, rapid or abnormal breathing, lung failure, changed in mood,
confusion, disorientation, suspiciousness, loss of muscle control, irrational
actions, distorted reality, aggressiveness, distorted sense of time and
space, sense of relaxation, nausea, tremors, flushed skinned, dilated
pupils, hallucinations, and panic due to unpredictable trips. Long term
effects include flashbacks, decreased motivation, depression, increased
panic, mental disturbance, and delusion.
n. Ecstasy
Research: Most people who use MDMA take it in a pill, tablet, or capsule.
The popular term Molly (slang for molecular) refers to the pure
crystalline powder form of MDMA, usually sold in capsules. It is dangerous
since it is man made and pills may contain other drugs and the amount
differs. Ecstasy usually takes 15 minutes to enter the bloodstream.
Effects: Short-term effects include anxiety, restlessness, irritability,
sadness, impulsiveness, aggression, sleep disturbance, lack of appetite,
and thirst. Long-term effects include nausea, chills, sweating, involuntary
jaw clenching and teeth grinding, muscle cramps, dehydration, high blood
pressure, and kidney failure.
o. Marijuana
Research: Marijuana is the most common illicit drug used in the United
States. It had a period of decline but use increased after 2007. Marijuana
is usually smoked in hand-rolled cigarettes or in water pipes. Marijuana
smoke has a pungent and distinctive, usually sweet-and-sour, odor.
Effects: Include dizziness, shallow breathing, red eyes and dilated pupils,
dry mouth, increased appetite, sleepiness, and slow reaction time. Longterm effects cause a disrupted menstrual cycle, cause men to be sterile
due to deformed sperm, weak immune system, and inability to understand
things clearly or retain information.
You might also like
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- 07-30487 Notice of JoinderDocument20 pages07-30487 Notice of Joinderkykphilippe91% (11)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Morality and Pedophilia in LolitaDocument5 pagesMorality and Pedophilia in LolitaDiana Alexa0% (1)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- 1st Year Unit 7 Writing A Letter About A CelebrationDocument2 pages1st Year Unit 7 Writing A Letter About A CelebrationmlooooolNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shaft KeywayDocument8 pagesShaft KeywayturboconchNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- 99 Attributes of Allah Al Khaliq (The Creator) Al Bari (The Inventor) Al Musawwir (The Fashioner)Document7 pages99 Attributes of Allah Al Khaliq (The Creator) Al Bari (The Inventor) Al Musawwir (The Fashioner)Abdourahamane GarbaNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Sacred Books of The East Series, Volume 47: Pahlavi Texts, Part FiveDocument334 pagesSacred Books of The East Series, Volume 47: Pahlavi Texts, Part FiveJimmy T.100% (1)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Arts 9 M1 Q3 1Document15 pagesArts 9 M1 Q3 1Gina GalvezNo ratings yet
- R15 Aerodynamics Notes PDFDocument61 pagesR15 Aerodynamics Notes PDFRahil MpNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- LifeSkills - Role PlayDocument7 pagesLifeSkills - Role Playankit boxerNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Azhari, Journal 7 2011Document11 pagesAzhari, Journal 7 2011Khoirunnisa ANo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Antenna and Propagation: Introduction + Basic ConceptsDocument19 pagesAntenna and Propagation: Introduction + Basic Conceptsanon_584636667No ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Karling Aguilera-Fort ResumeDocument4 pagesKarling Aguilera-Fort Resumeapi-3198760590% (1)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Predictor Corrector MethodsDocument5 pagesPredictor Corrector MethodsM2C7r6No ratings yet
- Indian Standard: General Technical Delivery Requirements FOR Steel and Steel ProductsDocument17 pagesIndian Standard: General Technical Delivery Requirements FOR Steel and Steel ProductsPermeshwara Nand Bhatt100% (1)
- Sui Man Hui Chan and Gonzalo CoDocument22 pagesSui Man Hui Chan and Gonzalo CoKatrina Anne Layson YeenNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- 0 - Past Simple TenseDocument84 pages0 - Past Simple Tenseשחר וולפסוןNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Performance AnalyticsDocument193 pagesPerformance AnalyticsGNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Agostinis Et Al-2011-CA - A Cancer Journal For CliniciansDocument32 pagesAgostinis Et Al-2011-CA - A Cancer Journal For CliniciansKauniIsaacNo ratings yet
- Best Resume Template CanadaDocument4 pagesBest Resume Template Canadaafjwdprlzaxewj100% (2)
- Ultimate Power Errata: Ultimate Power Mutants & Masterminds Mutants & Masterminds FAQ Mutants & MastermindsDocument2 pagesUltimate Power Errata: Ultimate Power Mutants & Masterminds Mutants & Masterminds FAQ Mutants & MastermindsYunus Emre AtalayNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- UEFA Stadium Design Guidelines PDFDocument160 pagesUEFA Stadium Design Guidelines PDFAbdullah Hasan100% (1)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- KISS Notes The World CommunicatesDocument30 pagesKISS Notes The World CommunicatesJenniferBackhus100% (4)
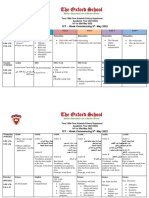
- Term 3 Mid-Term Assessment ScheduleDocument9 pagesTerm 3 Mid-Term Assessment ScheduleRabia MoeedNo ratings yet
- Group No. - Leader: MembersDocument7 pagesGroup No. - Leader: MembersJONATHAN NACHORNo ratings yet
- Dina Iordanova - Women in Balkan Cinema, Surviving On The MarginsDocument17 pagesDina Iordanova - Women in Balkan Cinema, Surviving On The MarginsimparatulverdeNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting and Management Essentials You Always Wanted To Know: 4th EditionDocument21 pagesCost Accounting and Management Essentials You Always Wanted To Know: 4th EditionVibrant Publishers100% (1)
- SVFC BS Accountancy - 2nd Set Online Resources SY20-19 2nd Semester PDFDocument14 pagesSVFC BS Accountancy - 2nd Set Online Resources SY20-19 2nd Semester PDFLorraine TomasNo ratings yet
- Battleship PotemkinDocument7 pagesBattleship PotemkinMariusOdobașa100% (1)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Types of Editorial Texts: Queen Zayra Dela Rosa Francisco DagohoyDocument8 pagesTypes of Editorial Texts: Queen Zayra Dela Rosa Francisco DagohoyAkiro KaitoNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials Lab 1-Zip Tie Tensile TestingDocument7 pagesMechanics of Materials Lab 1-Zip Tie Tensile TestingcoolshavaNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)