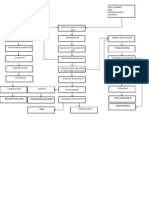
Modifiable
Pathophysiology
Non-modifiable
Alcoholic
Gender: Male
Exposure to other
pathogens
Genes
Workplace
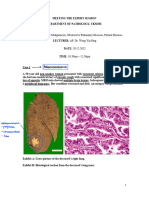
PTB
Homogenous spread of M. tuberculosis
Accumulation of bacteria in vertebrae T10, T11, and T12
Proliferation of bacteria in vertebrae
M. tuberculosis bacilli kills surrounding disk tissues
Vertebral narrowing
Progressive microcellular damage/ injured cells release chemicals
Vertebral collapse
Increased metabolic function of the body
Cytokine interleukin pyrogen release
Redness, heat
Vasodilation of involved blood vessels
Compression of spinal cord
Decreased sensory perception and muscle rating
Increased temp
Increased permeability of surrounding area allowing plasma
to leak from blood stream into extravascular space
Decreased ability to feel
urge and control defecation
and micturation
Decreased
physical
mobility
�Localized edema
Increased pressure on surrounding area
Back pain
Urinary retention
Muscle atrophy
Decreased
metabolism
Constipation
�Tumor growth
Dizziness
Involvement of cerebelum
Changes in emotional
state, behavior,
difficulty in thinking,
speaking, hemiparesis
Involvement of frontal lobe
Compression of other
parts of the brain
Increased ICP
Spread to other parts of the brain
Pain/headache
Inflammation
Irritation of vagal center in the
medulla
Cerebral edema
Vomiting
Compressed
cranial nerves
Skull cannot accommodate
increasing tumor size
Stroke
Increased consumption of
nutrients of tumor cells
Decreased nutrient supply to
normal cells
Apoptosis
Cerebral hypoxia
Weight loss
Cardiac/respiratory arrest
Death
�Increased vulnerability of epithelial
tissue to irritants and carcinogens
Chronic irritation/exposure to
carcinogens
Inhaled carcinogen
lodges in alveoli
Inflammation of the pleura
Altered permeability of
pleural membrane
Interruption of normal cells
Activation of normal cancer cells
Binding of bacterial cell
wall to macrophage
Primary growth of tumor cells in
epithelial tissues
Increased capillary wall
permeability
Spread of bacilli via
lymphatic system to other
parts and lobes of the lungs
Abnormal collection of
fluid in pleural space
Bacilli replicates
Effusion formation
Failure of immune system to
recognize cancer cell as foreign body
Progression of proliferation
of cancer cells
Formation of granuloma
Flattening of diaphragm
Drainage of necrotic material into
tracheobronchial tree
Obstruction of bronchus
due to tumor
Cancer cells detach from
primary tumor
Tumor enlarges through
blood vessels
Migration via lymph nodes or
blood circulation
Restrictive ventilatory defect
Scar formation
Shortness of
breath, difficulty
of breathing
Active infection
Cough, chest pain
Cancer cells established at
secondary sites