1. What is the use of BusinessObjects Data Services?
Answer:
BusinessObjects Data Services provides a graphical interface that allows you to easily
create jobs that extract data fromheterogeneous sources, transform that data to meet
the business requirements of your organization, and load the data into a single
location.
2. Define Data Services components.
Answer:
Data Services includes the following standard components:
Designer
Repository
Job Server
Engines
Access Server
Adapters
Real-time Services
Address Server
Cleansing Packages, Dictionaries, andDirectories
Management Console
3. What are the steps included in Data integration process?
Answer:
Stage data in an operational datastore, data warehouse, or data mart.
� Update staged data in batch or real-time modes.
Create a single environment for developing, testing, and deploying the entire
data integration platform.
Manage a single metadata repository to capture the relationships between
different extraction and access methods and provide integrated lineage and
impact analysis.
4. Define the terms Job, Workflow, and Dataflow
Answer:
A job is the smallest unit of work that you can schedule independently for
execution.
A work flow defines the decision-making process for executing data flows.
Data flows extract, transform, and load data. Everything having to do with data,
including reading sources, transforming data, and loading targets, occurs inside
a data flow.
5. Arrange these objects in order by their hierarchy: Dataflow, Job, Project, and
Workflow.
Answer
Project, Job, Workflow, Dataflow.
6. What are reusable objects in DataServices?
Answer:
Job, Workflow, Dataflow.
7. What is a transform?
Answer:
A transform enables you to control how datasets change in a dataflow.
8. What is a Script?
�Answer:
A script is a single-use object that is used to call functions and assign values in a
workflow.
9. What is a real time Job?
Answer:
Real-time jobs "extract" data from the body of the real time message received and
from any secondary sources used in the job.
10. What is an Embedded Dataflow?
Answer:
An Embedded Dataflow is a dataflow that is called from inside another dataflow.
11. What is the difference between a data store and a database?
Answer:
A datastore is a connection to a database.
12. How many types of datastores are present in Data services?
Answer:
Three.
Database Datastores: provide a simple way to import metadata directly froman
RDBMS.
Application Datastores: let users easily import metadata frommost Enterprise
Resource Planning (ERP) systems.
Adapter Datastores: can provide access to an applications data and metadata or
just metadata.
13. What is the use of Compace repository?
Answer:
�Remove redundant and obsolete objects from the repository tables.
14. What are Memory Datastores?
Answer:
Data Services also allows you to create a database datastore using Memory as the
Database type. Memory Datastores are designed to enhance processing performance
of data flows executing in real-time jobs.
15. What are file formats?
Answer:
A file format is a set of properties describing the structure of a flat file (ASCII). File
formats describe the metadata structure. File format objects can describe files in:
Delimited format Characters such as commas or tabs separate each field.
Fixed width format The column width is specified by the user.
SAP ERP and R/3 format.
16. Which is NOT a datastore type?
Answer:
File Format
17. What is repository? List the types of repositories.
Answer:
The DataServices repository is a set of tables that holds user-created and predefined
system objects, source and target metadata, and transformation rules. There are 3
types of repositories.
A local repository
A central repository
A profiler repository
�18. What is the difference between a Repository and a Datastore?
Answer:
A Repository is a set of tables that hold system objects, source and target metadata,
and transformation rules. A Datastore is an actual connection to a database that holds
data.
19. What is the difference between a Parameter and a Variable?
Answer:
A Parameter is an expression that passes a piece of information to a work flow, data
flow or custom function when it is called in a job. A Variable is a symbolic
placeholder for values.
20. When would you use a global variable instead of a local variable?
Answer:
When the variable will need to be used multiple times within a job.
When you want to reduce the development time required for passing values
between job components.
When you need to create a dependency between job level global variable name
and job components.
21. What is Substitution Parameter?
Answer:
The Value that is constant in one environment, but may change when a job is migrated
to another environment.
22. List some reasons why a job might fail to execute?
Answer:
Incorrect syntax, Job Server not running, port numbers for Designer and Job Server
not matching.
�23. List factors you consider when determining whether to run work flows or
data flows serially or in parallel?
Answer:
Consider the following:
Whether or not the flows are independent of each other
Whether or not the server can handle the processing requirements of flows
running at the same time (in parallel)
24. What does a lookup function do? How do the different variations of the
lookup function differ?
Answer:
All lookup functions return one row for each row in the source. They differ in how
they choose which of several matching rows to return.
'
25. List the three types of input formats accepted by the Address Cleanse
transform.
Answer:
Discrete, multiline, and hybrid.
26. Name the transform that you would use to combine incoming data sets to
produce a single output data set with the same schema as the input data sets.
Answer:
The Merge transform.
27. What are Adapters?
Answer:
Adapters are additional Java-based programs that can be installed on the job server to
provide connectivity to other systems such as Salesforce.com or the
�JavaMessagingQueue. There is also a SoftwareDevelopment Kit (SDK) to allow
customers to create adapters for custom applications.
28. List the data integrator transforms
Answer:
Data_Transfer
Date_Generation
Effective_Date
Hierarchy_Flattening
History_Preserving
Key_Generation
Map_CDC_Operation
Pivot Reverse Pivot
Table_Comparison
XML_Pipeline
29. List the Data Quality Transforms
Answer:
Global_Address_Cleanse
Data_Cleanse
Match
Associate
Country_id
� USA_Regulatory_Address_Cleanse
30. What are Cleansing Packages?
Answer:
These are packages that enhance the ability of Data Cleanse to accurately process
various forms of global data by including language-specific reference data and parsing
rules.
31. What is Data Cleanse?
Answer:
The Data Cleanse transform identifies and isolates specific parts of mixed data, and
standardizes your data based on information stored in the parsing dictionary, business
rules defined in the rule file, and expressions defined in the pattern file.
32. What is the difference between Dictionary and Directory?
Answer:
Directories provide information on addresses from postal authorities. Dictionary files
are used to identify, parse, and standardize data such as names, titles, and firm data.
33. Give some examples of how data can be enhanced through the data cleanse
transform, and describe the benefit of those enhancements.
Answer:
Enhancement Benefit
Determine gender distributions and target
Gender Codes marketing campaigns
Provide fields for improving matching
Match Standards results
�34. A project requires the parsing of names into given and family, validating
address information, and finding duplicates across several systems. Name the
transforms needed and the task they will perform.
Answer:
Data Cleanse: Parse names into given and family.
Address Cleanse: Validate address information.
Match: Find duplicates.
35. Describe when to use the USA Regulatory and Global Address Cleanse
transforms.
Answer:
Use the USA Regulatory transform if USPS certification and/or additional options
such as DPV and Geocode are required. Global Address Cleanse should be utilized
when processing multi-country data.
36. Give two examples of how the Data Cleanse transform can enhance (append)
data.
Answer:
The Data Cleanse transform can generate name match standards and greetings. It can
also assign gender codes and prenames such as Mr. and Mrs.
37. What are name match standards and how are they used?
Answer:
Name match standards illustrate the multiple ways a name can be represented.They
are used in the match process to greatly increase match results.
38. What are the different strategies you can use to avoid duplicate rows of data
when re-loading a job.
Answer:
Using the auto-correct load option in the target table.
� Including the Table Comparison transform in the data flow.
Designing the data flow to completely replace the target table during each
execution.
Including a preload SQL statement to execute before the table loads.
39. What is the use of Auto Correct Load?
Answer:
It does not allow duplicated data entering into the target table.It works like Type 1
Insert else Update the rows based on Non-matching and matching data respectively.
40. What is the use of Array fetch size?
Answer:
Array fetch size indicates the number of rows retrieved in a single request to a source
database. The default value is 1000. Higher numbers reduce requests, lowering
network traffic, and possibly improve performance. The maximum value is 5000
41. What are the difference between Row-by-row select and Cached comparison
table and sorted input in Table Comparison Tranform?
Answer:
Row-by-row select look up the target table using SQL every time it receives
an input row. This option is best if the target table is large.
Cached comparison table To load the comparison table into memory. This
option is best when the table fits into memory and you are comparing the entire
target table
Sorted input To read the comparison table in the order of the primary key
column(s) using sequential read.This option improves performance because
Data Integrator reads the comparison table only once.Add a query between the
source and the Table_Comparison transform. Then, from the querys input
schema, drag the primary key columns into the Order By box of the query.
42. What is the use of using Number of loaders in Target Table?
�Answer:
Number of loaders loading with one loader is known as Single loader Loading.
Loading when the number of loaders is greater than one is known as Parallel
Loading. The default number of loaders is 1. The maximum number of loaders is 5.
43. What is the use of Rows per commit?
Answer:
Specifies the transaction size in number of rows. If set to 1000, Data Integrator sends
a commit to the underlying database every 1000 rows.
44. What is the difference between lookup (), lookup_ext () and lookup_seq ()?
Answer:
lookup() : Briefly, It returns single value based on single condition
lookup_ext(): It returns multiple values based on single/multiple condition(s)
lookup_seq(): It returns multiple values based on sequence number
45. What is the use of History preserving transform?
Answer:
The History_Preserving transform allows you to produce a new row in your target
rather than updating an existing row. You can indicate in which columns the transform
identifies changes to be preserved. If the value of certain columns change, this
transform creates a new row for each row flagged as UPDATE in the input data set.
46. What is the use of Map-Operation Transfrom?
Answer:
The Map_Operation transform allows you to change operation codes on data sets to
produce the desired output. Operation codes: INSERT UPDATE, DELETE,
NORMAL, or DISCARD.
47. What is Heirarchy Flatenning?
Answer:
�Constructs a complete hierarchy from parent/child relationships, and then produces a
description of the hierarchy in vertically or horizontally flattened format.
Parent Column, Child Column
Parent Attributes, Child Attributes.
48. What is the use of Case Transform?
Answer:
Use the Case transform to simplify branch logic in data flows by consolidating case or
decision-making logic into one transform. The transformallows you to split a data set
into smaller sets based on logical branches.
49. What must you define in order to audit a data flow?
Answer:
You must define audit points and audit rules when you want to audit a data flow.
50. List some factors for PERFORMANCE TUNING in data services?
Answer:
The following sections describe ways you can adjust Data Integrator performance
Source-based performance options
Using array fetch size
Caching data
Join ordering
Minimizing extracted data
Target-based performance options
Loading method and rows per commit
Staging tables to speed up auto-correct loads
� Job design performance options
Improving throughput
Maximizing the number of pushed-down operations
Minimizing data type conversion
Minimizing locale conversion
Improving Informix repository performance
Data Services Scenario Questions Part 1
In this tutorial we will discuss some scenario based questions and their solutions using SAP Data Services. This
article is meant mainly for Data Services beginners.
This article is one of the series of articles written to showcase the solutions of different business scenarios in SAP
Data Services. You may browse all the scenarios from the below list.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Cumulative Sum of salaries, department wise
Getting the value from the previous row in the current row
Getting the value from the next row in the current row
Getting total Sum of a value in every row
Cumulative String Concatenation (Aggregation of string)
Cumulative String Aggregation partition by other column
String Aggregation
Consider the following Source data in a flat file:
DEPTNO
SALARY
10
1000
20
2000
30
3000
40
4000
Scenario 1: Lets try to load the Cumulative Sum of salaries of the departments into the target table. The target table
data should look like below:
DEPTNO
SALARY
CUMULATIVE_SALARY
10
1000
1000
�20
2000
3000
30
3000
6000
40
4000
10000
Solution:
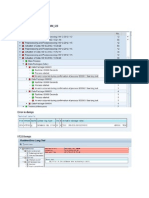
1. Let us first define the Source File Format. This same file format will be reused for the next set of the scenario
questions.
2. Next we create a new Batch Job, say JB_SCENARIO_DS. Within the Job we create a Data Flow, say
DF_SCENARIO_1.
3. At the Data flow level i.e. Context DF_SCENARIO_1, we Insert a new Parameter using the Definitions tab. Lets
name it as $PREV_SAL with Data type decimal(10,2) and Parameter type as Input.
�At the Job level i.e. Context JB_SCENARIO_1, we initialize the Parameter $PREV_SAL using the Calls tab. We set
the Agrument value to 0.00
�4. Next we create a New Custom Function from the Local Object Library. Lets name it CF_CUME_SUM_SAL.
�Within the Custom Function Smart Editor, first we Insert two Parameters, namely $CURR_SAL and $PREV_SAL with
Data type decimal(10,2) with Parameter type as Input and Input/Output respectively.
Also we modify the Return Parameter Data type to decimal(10,2).
5. Next we define the custom function as below and Validate the same.
$PREV_SAL = $CURR_SAL + $PREV_SAL;
Return $PREV_SAL;
�The purpose of defining the Parameter and Custom Function is to perform Parameter Short-circuiting. Here within
the function, we basically set the $PREV_SAL Parameter of type Input/Output to sum of salaries till the current
processing row. Since it is of type Input/Output the calculated sum value or the retained sum of salary is passed back
into the Dataflow Parameter. So by using Custom Function we can modify and pass values to a Dataflow Parameter.
Hence the Parameter defined at Dataflow level is short-circuited with the Input/Output Parameter of the Custom
Function.
6. Lets go back and design the Data flow. First of all we take the File Format defined earlier, from the Local Object
Library as Source.
7. Next we place a Query transform, say QRY_CUME_SUM. First we select the columns DEPTNO and SALARY
from the Schema In of the Query transform and Map to Output.
Next we specify a New Function Call in Schema Out of the Query transform. Choose the Custom Functions from
the Function categories and select the Function name CF_CUME_SUM_SAL.
Next we Define Input Parameters. We specify the inputs as below:
$CURR_SAL = FF_SRC_DEPT.SALARY
$PREV_SAL = $PREV_SAL
Select the Return column as the Output Parameter.
�8. Finally we place a Template Table as Target in the Target Datastore.