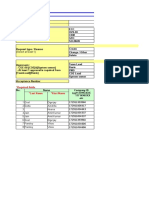
AMRITA VISHWA VIDYAPEETHAM
COURSE PLAN
Academic year: 2013 - 14
Department: Computer Science
Course Code: CA44
Lecturer: Pallavi M S
Lectur
e No(s)
Topics
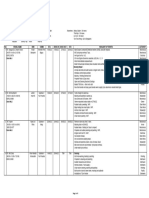
Introduction to software
project management
1-4
Step-wise: an Overview of
project Planning
5-7
810
Step-wise: an Overview of
project Planning
13 - 14
Key-words
Objectives
Remarks
Introduction,. Why SPM, Project,
contract management and techical
management, Activities covered by
SPM,Management,
Problems,
Stakeholders.
Introduction to step wise project
planning, step 0: select project, step
1:identify project scope and objectives,
step
2:
identify
project
infrastructures,step
3: analyse project characteristics,
4.Identify project products and
activities, 5. Estimate effort for each
activity, step 6: identify acivity risks, 7.
Allocate resources
Understand some problems
and concerns of software
project managers, define
usual stages.
Chapter 1 Software Project
Management , By Bob and Mike
Page -1 to Page 17
Approach project planning
in an organised step-by-step
manner
Chapter 2 Software Project
Management , By Bob and Mike
Page -20 to Page 28
See where the techniques
described in other chapters
fit into an overall planning.
Repeat the planning process
in more details for sets of
activities within a project as
the time comes to execute
them.
Chapter 2 Software Project
Management , By Bob and Mike
Page -28 to Page 38
Understand how individual
projects can be grouped into
programmes
Chapter 3 Software Project
Management , By Bob and Mike
Page -41 to Page 46
Understand how the
implementation of
programmes and projects
can be managed so that the
Chapter 3 Software Project
Management , By Bob and Mike
Page -46 to Page 66
Class Test-1
Introduction, Programme management,
Managing the allocation of resources
within programmes, Strategic
programme management, Creating a
programme.
Programme management Aids to programme management,
and project evaluation
Benefits management, evaluation of
individual projects, Technical assement
Programme management
and project evaluation
11 -12
Semester: V
Programme: MCA
Odd/Even: Odd
Course Title: Software Project Management
�Programme management
and project evaluation
15 16
Selection
appropriate
approach
of
an
project
17 18
Selection
appropriate
approach
of
an
project
19 20
Selection
appropriate
approach
of
an
project
Software effort estimation
21-24
Software effort estimation
2527
Activity planning
28-30
30-32
Activity planning
33 -
Risk Management
planned benefits are
achieved.
Cost-benefit analysis, Cash flow Carry out an evaluation and
forecasting, Cost-benefit evaluation select
techniques, Risk evaluation
Introduction, Choosing technologies, Take account of the
Technical plan contents list, Choice of characteristics of the system
process models, structure versus speed to be developed when
of delivery
planning a project
The waterfall model, V-process model, Make best use of process
sprial model, Software prototyping, model
Other ways of categorizing prototypes,
Incremental delivery
Dynamic systems development method, Reduce other risks by
extreme
programming,
managing creation of appropriate
iterative process
prototypes
First Periodicals
Introduction, Where are estimates Understand the range of
done?, Problems with over- and under- estimating methods that can
estimates, The basis for software be used.
estimating, software effort estimation
techniques.
Expert judgement, estimating by Count the function points
analogy, Albrecht function point for a system
analysis, Function points marks II,
COCOMO: a parametric model
Introduction, The objectivesof activity Produce an activity plan for
planning, When to plan, Project a project
schedules, Projects and activities, Estimate the overall
Sequencing and scheduling activities
duration of a project
Network planning models, Formulating Create a critical path and a
a network model, Adding the time precedence network for a
dimension, The forward pass, the project
backward pass, Identifying critical
activities, Activity-on-arroww networks
Class Test-2
Introduction, Risk, Categories of risk, A Identify the factors putting a
Chapter 4 Software Project
Management , By Bob and Mike
Page -68 to Page 74
Chapter 4 Software Project
Management , By Bob and Mike
Page -74 to Page 82
Chapter 4 Software Project
Management , By Bob and Mike
Page -82 to Page 89
Chapter 5 Software Project
Management , By Bob and Mike
Page -92 to Page 98
Chapter 5 Software Project
Management , By Bob and Mike
Page -100 to Page 114
Chapter 6 Software Project
Management , By Bob and Mike
Page -117 to Page 125
Chapter 6 Software Project
Management , By Bob and Mike
Page -125 to Page 137
Chapter 7 Software Project
�36
37
40
41 - 12
Resource allocation
Resource allocation
Monitoring and Control
40-44
Managing Contracts
44-48
49 - 55
Managing people and
organizing teams
56 - 60
Software Quality
framework for dealing with risk, Risk
identification, Risk assessment, Risk
planning, Risk Management, Evaluating
risks to schedule,Applying the PERT
technique
Introduction, The nature of resources,
Identifying resource requirements,
Scheduling, resources, Creating critical
paths
project at risk
Categorize and prioritize
actions for risks elimination
or containment
Management , By Bob and Mike
Page -146 to Page 168
Identify the resources
required for a project, Make
the demand for resources
more even throughout the
life of a project
Produce a work plan and
resource schedule
Chapter 8 Software Project
Management , By Bob and Mike
Page -174 to Page 182
Counting the cost, Being specific,
Publishing the reource schedule, cost
schedules, the scheduling sequence
Second Periodicals
Introduction, Creating the framework, Monitor the progress of
Collecting
the
data, Visualizing projects
progress, Cost monitoring, Earned value Assess the risk, Visualize
analysis,
Prioritizing
monitoring, and sasses the state of a
Getting the project back to target, project
Change control
Chapter 8 Software Project
Management , By Bob and Mike
Page -183 to Page 189
Introduction, The ISO 12207 approach
to the acquisition and supply of
software, the supply process, Types of
contract placement, typical terms of a
contract,
Contract
management,
Acceptance
Introduction, Understanding behaviour,
Organizational behaviour:a background,
Slecting the right person for the job,
Instruction in the best methods,
motivation.
Working
in
groups,
becoming a team, Decision making,
leadership, Organizational structures,
Introduction, the place of software
quality in project planning, The
importance of software quality, The
importance of software quality, Deging
Follow the stages needed to
acquire software from an
external supplier, Plan the
evaluation of a proposal of
product
Chapter 10 Software Project
Management , By Bob and Mike
Page -212 to Page 230
Identify some of the factors
that influence peoples
behavior in a project
Increase staff motivation
Chapter 11 Software Project
Management , By Bob and Mike
Page -232 to Page 230
Importance of software
quality, Define the qualities
of goog software
Chapter 12 Software Project
Management , By Bob and Mike
Page -258 to Page 282
Chapter 9 Software Project
Management , By Bob and Mike
Page -190 to Page 207
�software quality, ISO 9126,
End Semester Examination
Text Books/References:
1. Software Project Management, fourth edition by Bob Hughes & Mike Cotterell.
Evaluation Pattern:
Internal Assessment:
Periodicals:
Two periodicals of 50 Marks each conducted in 6th & 11th week of 15 working weeks.
Question Paper Format
o 5 questions of 2 marks each = 10 marks
o 5 questions of 6 marks each = 30 marks
o 1 question of 10 marks each = 10 marks
o Total = 10 + 30 + 10 =50 marks
Duration of the test is one & an half hour.
Each periodicals is scale down to 15 marks
Total : 15(P1) + 15(P2) = 30 marks
Continuous Assessment:
Class Test 1 before First Periodicals 5 Marks ( Paper for 10 marks, Scale down to 5 marks)
Class Test 2 before First Periodicals 5 Marks ( Paper for 10 marks, Scale down to 5 marks)
Seminar / Paper presentation/ Assignments 5 Marks
Attendance, Behaviour, Attitude -- 5 Marks
Total : (5 + 5 + 5 + 5) = 20 Marks
�Total Internal Assessment Marks : 30 + 20 = 50 Marks
End semester examination:
Maximum marks : 100 marks (scale down to 50 marks)
Duration : 3 hrs
Question paper format :
o 10 questions of 2 marks each = 20 marks
o 5 questions of 16 marks each = 80 marks(section may contain 2 or 3 sub questions)
Total Marks = 50 (internals) + 50 (end semester examination) = 100 Marks
Faculty Details
Name: Pallavi M S
Mobile: 8495956468
Email:ms_pallavi@asas.mysore.amrita.edu