Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sistem Selcoperm
Uploaded by
GROIIMCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sistem Selcoperm
Uploaded by
GROIIMCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrochlorination
Electrochlorination
Overview
Electrochlorination
Why electrochlorination?
Chlorine as disinfectant is often used
Depot effect
Effectivity
Regulations and standards
Low-cost disinfection agent
Risks of chlorine gas
Chlorine discharge by wrong handling or technical failure
Safety thinking especially in dense populated regions
Local regulations for transportation
Electrochlorination
Why electrochlorination?
No handling with dangerous chemicals
Common salt is harmless and can be stored without problems
Always fresh hypochlorite available
no decomposition compared to commercial hypochlorite solution
few generation of by-products (chlorate)
Cost saving production
Chemicals and energy less than 1 per kg chlorine with common salt electrolysis
Electrochlorination
Method of electrolytic chlorine production
Anode (+)
Chlorine
Salt + Water
Sodium
hydroxide +
Hydrogen
Cathode (-)
Sodium hypochlorite + Hydrogen + Salt
+ Water
Anode (+)
Cl2
2 NaCl
2 H2O
NaClO + H2 + NaCl + H2O
2NaOH + H2
Cathode (-)
Electrochlorination
Disinfection effect of electrolytic chlorine
Electrolytical chlorine production
e2 NaCl + 2 H20 2 NaOH + Cl2 + H2
2 NaOH + Cl2 NaCl + NaClO + H20
Reaction with water
NaClO + H20 NaOH + HClO
HClO + H20 H30+ + ClOHClO is the disinfectant,
not Cl2 or ClO- !
High pH dependancy
Electrochlorination
pH effect on hypochlorite effectiveness
pH range with 90% HClO content
Electrochlorination
Disinfection effect with hypochlorite
Microbicidal effect
irreversible oxidation (plus chlorination) of cell components,
structure proteins, enzymes, DNA
Characteristics
extensive application spectrum at pH 5 to 7
sensitive against organic load
corrosive at application temperatures > 40C and pH < 7
strong product influence taste / smell
AOX (adsorbent organic halogens) contribution
Electrochlorination
Types of electrolytic chlorine production
Chlorine
Electrolysis
Membrane divided
Undivided cell
cell
Diluted
brine
Natural brine
(ocean water)
Chloride
containing water
Saturated
brine
Diluted
hydrochloric
acid
Electrochlorination
Undivided cells with NaCl
H2
NaCl +
H2O
Cathode
NaClO
NaClO
NaOH
H+
Na+
Cl2
H2O
OH-
NaCl
Cl-
solution
+
Anode
Electrochlorination
Function principle undivided cell electrolysis
5
NaClO
NaCl + H2O, saturated
H2O, softened
H2O, supply
H2
Air
1
7
2
1 Water softener
2 Brine tank
3 Undivided cell
4 Degassing tank H2
5 Ventilation
6 Storage tank
7 Dosing pump
Electrochlorination
Membrane cells with NaCl
NaClO + NaCl + H2O
NaOH
H2
Cathode
NaCl+
H2O
Cl2
Na+ + OH= NaOH
Anode
Na+
H2O
NaCl+
H2 O
Electrochlorination
Function principle, membrane standard method
Cl2
NaClO
Saturated Brine
Rest brine
Rest brine + Chlorine gas
H2O, softened
H2O, supply
9
H2
8
10
NaOH
7
NaOH +H2
Air
1
2
1 Softener
2 Brine tank
3 Membrane cell
4 Degassing tank Cl2
5 Reaction tower
6 Degassing tank H2
7 Dosing pump
8 Mixing tank
9 pH measurement
10 Dosing pump
Electrochlorination
Function principle, hydrochloric acid electrolysis
H2 to the air
ca. 0,3 g/l Chlorine solution
Flow meter with
min. monitoring
Anode (+)
(2 Cl- Cl2+2 e-)
Operation water
80 - 100 l/h
Cathode (-)
(2 H+ +2e- => H2)
Acid drain
ca. 1% HCl
pH 1-2
Electrochlorination
Comparison of electrolytic methods
Undivided cell
Raw material
Membrane divided cells
Diluted brine
Saturated brine
Diluted hydrochloric acid
Undivided flow-through cell
Membrane divided cell
Membrane divided cell
Salt consumption per kg Cl2
3,0 3,5 kg
1,7 2,0 kg
Acid consupmtion per kg Cl2
1,2 kg at 100 % conc.
4,0 4,5 kWh
4,5 5,0 kWh
4,0 4,5 kWh
Hypochlorite solution 6-8 g/l
Hypochlorite solution 25 g/l
Chlorine solution 0,5 - 1 g/l
0,80 1,00
0,60 0,80
6,00 8,00
Simple
Robust
Reliable
No salt carry-over
High product concentration
Low operation costs *)
Simple
Robust
Reliable
High salt consumption
Salt carry-over in product
Only high purity salt suitable
Complex, susceptible to
malfunction
High spare parts costs
High operation costs
Low product concentration
Drinking water applications
Very suitable for export
business
Public baths
Also drinking water
Not suitable for export business
Small, private swimming pools
No drinking water plants
Cell construction
Power consumption per kg Cl2
Product
Operation costs per kg Cl2
Advantages
Disadvantages
Preferred application
*) without maintanance (high spare parts costs)
Electrochlorination
Cost calculation, comparison of methods
Chemical cost comparison for an average swimming pool
(1000 kg chlorine per year)
Method
Qty. chemicals
per year
Chemical
costs
Power costs per
kg Chlorine *)
Operation
costs / year
Liquid chlorine
1.000 kg
1,30 / kg
1.300
Hypochlorite solution
6.667 kg
0,58 / kg
3.866
Chlorine granulate /
tablets
1.540 kg
4,00 / kg
6.160
Membrane elektrolysis
1.700 kg
0,18 / kg
= 306
0,55
= 550
856
Undivided electrochlorination
3.200 kg
0,12 / kg
= 384
0,50
= 500
884
*) without dosing equipment
Invest costs must be calculated separately dependant on the system dimensioning.
All dosing systems for chemicals must follow certain local legal regulations concerning installation place
and maintenance. So a total cost comparison can only be done individually.
Electrochlorination
Grundfos Alldos Electrochlorination Systems
Product family name: Selcoperm
Capacities:
125 / 250 / 500 / 1000 / 2000 g/h
System:
Complete plug-and-play systems:
electrochlorination system +
storage tanks for brine and product solutions
Typical disinfection tasks:
Drinking water treatment
Municipal waste water treatment
Swimming pool water treatment
Industrial waste water treatment
Electrochlorination
Electrochlorination System Selcoperm
Installation scheme:
Ventilation
system
Electrolysis
system
Brine tank
Dosing
pumps
Product
tank
Electrochlorination
Electrochlorination System Selcoperm
Example for installation in drinking water plant
Ventilation
system
Electrolysis
system
Chlorine
measurement
Brine tank
Product
tank
Dosing
pump
Electrochlorination
Electrochlorination System Selcoperm
Components:
Front view
Control
unit
Main
switch
Power and signal
supply lines
Display for air
flow rate
Ventilation
motor
Electrochlorination
Electrochlorination System Selcoperm
Components:
Left side view
Water flow
meter and
switch
Dosing pump
for brine
In- and Outlet for water
and brine
Water cooling
for electronics
Sample valves for water,
brine and product
Water softener
Electrochlorination
Electrochlorination System Selcoperm
Components:
Right side view
Hydrogen outlet
Control
unit
Connection to
product storage tank
Degassing column
Electrochlorination cell
Ventilation
system
Electrochlorination
Electrochlorination System Selcoperm
Details electrolysis cell
Electrodes in transparent PVC tube with five years warranty
Voltage between electrodes 26 to 28 V
Dual containment between electrolyser chamber and vent pipework
Brine concentration entering the electrolyser is between 20 and 30 g/l
Concentration sodium hypochlorite leaving the electrolyser< 8 g/l
Product temperature is kept below 35 C which is monitored
The product is kept at a consistent composition via the control panel
monitoring and adjusting :
Water flow
Amperage
Voltage
Temperature
Electrochlorination
Electrochlorination System Selcoperm
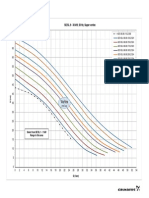
Dimensioning of the systems
Water flow
(log)
Selection sheet for electrolyser system
Tm/d
240
m3/h
10000
120
5000
60
48
2500
2000
30
24
15
1250
1000
Selcoperm 2000
Corresponding
chlorine gas qty.
48kg/d
2000g/h
12
625
500
Selcoperm 1000
1000g/h
24kg/d
6,0
250
Selcoperm 500
500g/h
12kg/d
3,0
2,4
125
100
Selcoperm 250
250g/h
6kg/d
1,5
63
Selcoperm 125
125g/h
3kg/d
Larger capacities
available on request
Smaller capacities
available on request
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9 1.0 1.1 1.2
Dosing quantity mg/l
1.3
1.4
1.5
1.6
1.7
1.8
1.9
2.0
Electrochlorination
Electrochlorination System Selcoperm
System requirements
Inlet water:
- Good quality filtered water (particles < 100 m)
- Low fluoride (< 2 mg/l), iron (< 200 mg/m) and manganese content
(< 20 mg/m)
- Between 125 and 140 litres of water is required to produce 1 kg chlorine.
Salt:
- Food quality grade salt is recommended
- 3 to 3,5 kg salt is required to produce 1 kg chlorine
Power supply:
-4,5 to 5 kW is required to produce 1 kg chlorine
Electrochlorination
Electrochlorination System Selcoperm
End product sodium hypochlorite solution
Typical specifications:
Total chlorine content
0,8 % ( 8 g per litre)
pH
8 - 8,5
Specific density
~ 1,014 g/cm
Product storage time
nearly unlimited at 25 C
Freezing point
-1,1 C
Product concentration and pH value are lower than in commercial
sodium hypochlorite solutions (concentration ~ 15 %, pH ~ 10)
Higher long-term stability, no pH correction with sulphur acid
necessary
Electrochlorination
Electrochlorination System Selcoperm
Hydrogen as By-product
Potential hazards minimized through engineering:
Vertical electrolyser in difference to some competitors, therefore no
hydrogen accumulation in the electrolyser
Hydrogen separation in clear degassing column before outlet to
product tank
Dual contained electrolyser, degassing column and vent pipework
Quantifiable air flow through the dual containment
No source of ignition
Never more than one litre hydrogen (0,09 g) in the system at a time
Electrochlorination
Electrochlorination System Selcoperm
Safety in use of the process
Selcoperm will fail safe in the event of following conditions:
Incorrect water flow
High / low amperage
Over temperature in electronics, electrolyser cell or product outlet
Ventilation failure
Extra high or extra low product tank level
Leakage in hydraulic / electrolyser chamber or in product tank
System inhibit via any site alarm
The system is designed so that no electrical equipment is sited in a
potentially explosive environment.
Electrochlorination
Electrochlorination System Selcoperm
User advantages
Low operator involvement
Low maintenance (inspection once a year)
Safe handling and simple storage of salt as raw material
No separate plant room as for chlorine gas necessary
Low operation costs
Efficient production of disinfectant
Long term stable product storage
Low investment costs
No hazardous products
Electrochlorination
Electrochlorination System Selcoperm
Applications
Treatment of swimming pool water
Electrochlorination
Electrochlorination System Selcoperm
Applications
Treatment of swimming pool water
Example: Installation of
Selcoperm 500 in Sllingen
(Germany) as replacement of
hypochlorite dosing
Electrochlorination
Electrochlorination System Selcoperm
Applications
Treatment of swimming pool water
Example: Installation of Selcoperm
1000 in Heidelsheim (Germany) as
replacement of chlorine gas dosing
Electrochlorination
Electrochlorination System Selcoperm
Applications
A
Drinking water treatment:
A) Raw water treatment
B) Final disinfection
Electrochlorination
Electrochlorination System Selcoperm
Applications
Drinking water treatment
Example: Installation of
Selcoperm 250 in water plant
Alconbury (UK) as alternative to
chlorine gas system
Electrochlorination
Electrochlorination System Selcoperm
Applications
Waste water treatment
Example: Installation of a Selcoperm
with 10.5 kg/h for waste water
treatment in Larnaca (Cyprus)
Electrochlorination
Electrochlorination System Selcoperm
Remote Installations
Electrochlorination
Electrochlorination System Selcoperm
Salt saturator tank - 10 tons
Electrochlorination
Electrochlorination System Selcoperm
Delivery program Selcoperm
Selcoperm electrochlorinators
Type
Capacity g Cl2 / h
Capacity kg Cl2 / day
SES-125
125
SES-250
250
SES-500
500
12
SES-1000
1000
24
SES-2000
2000
48
Dimensions (W x D x H) / mm: 700 x 900 x 1800
Weight: ca. 100 kg
Variants: voltage/frequency and connections on unit (metric/imperial)
Electrochlorination
Electrochlorination System Selcoperm
Delivery program Selcoperm accessories
Brine tanks
Type
Capacity / kg
Diameter (mm)
Height (mm)
SET-150-S
150
550
644
SET-300-S
300
556
930
SET-500-S
500
790
1035
SET-1250-S
1250
1019
1157
Product storage tanks
Type
Capacity / L
Width (mm)
Depth (mm)
Height (mm)
SET-350-P
350
1024
724
1200
SET-501-P
500
1184
864
1250
SET-700-P
700 (2x350)
1804
784
1250
SET-991-P
1000
1474
1074
1500
SET-1001-P
1000 (2x500)
2084
924
1300
SET-2000-P
2000
1350
1800
SET-3000-P
3000
1535
2000
SET-5000-P
5000
1950
2400
SET-10000-P
10000
2000
3800
PWS T1000 test kit for measuring salinity and product concentration
Electrochlorination
Electrochlorination System Selcoperm
Market situation electrochlorination
Most important competitors
Competitor
Prominent
W&T
Severn Trent
System
a) Dulco Zon MCEa
b) CHLORINSITU II
OSEC-B
MCT 12/24/36
Disadvantage
a) membrane system:
higher maintenance
costs, minor lifetime
b) non-divided cell:
only 3-phase power
supply, 3.8kg salt/kg
Cl2, >7kWh/kg Cl2
ca. 15 % less yield
less secure H2
Elimination
higher investment
costs
horizontal
electrolyser cell
no dual containment
H2 dilution fan only
as option
In addition many local manufacturers with simple systems in low price segment are
existing, for example Ekran (RU), Titanor (Ind.), Water Eng. (AUS), Salchlor (AUS).
You might also like
- Headway User Manual 2.6.5.0 - DianellaDocument189 pagesHeadway User Manual 2.6.5.0 - Dianellamotor tankerNo ratings yet
- ChillerDocument3 pagesChillerRomie CubalNo ratings yet
- On Site Sea Water Electrochlorination SystemDocument2 pagesOn Site Sea Water Electrochlorination SystemRaja Prathap SinghNo ratings yet
- SRS (Sulphate Removal System) - Brine Electrolysis - ThyssenKrupp Uhde Chlorine Engineers (Japan) LTDDocument2 pagesSRS (Sulphate Removal System) - Brine Electrolysis - ThyssenKrupp Uhde Chlorine Engineers (Japan) LTDpetros222No ratings yet
- 31 New Interesting Applications For CCP - SW TES SeminarDocument48 pages31 New Interesting Applications For CCP - SW TES SeminarAlfonso José García LagunaNo ratings yet
- Brian Windsor Troubleshooting1Document35 pagesBrian Windsor Troubleshooting1brandlabBDNo ratings yet
- Shortcut Nitrogen Removal-Nitrite Shunt and DeammonificationFrom EverandShortcut Nitrogen Removal-Nitrite Shunt and DeammonificationNo ratings yet
- ElectrochlorinationDocument14 pagesElectrochlorinationManas Mohan BaralNo ratings yet
- Continuous Production Electrochlorinator Sea - Water - Based PDFDocument4 pagesContinuous Production Electrochlorinator Sea - Water - Based PDFdubaisrinivasuluNo ratings yet
- Span TS 3001Document31 pagesSpan TS 3001Muhamad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Cyanide Treatment TechnologiesDocument3 pagesCyanide Treatment Technologiesdei_sandeep7994No ratings yet
- Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP) - Process Flow DiagramDocument4 pagesEffluent Treatment Plant (ETP) - Process Flow DiagramshimanthNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 Arvia Water TreatmentDocument24 pagesExperiment 3 Arvia Water TreatmentBrendaNo ratings yet
- Ballast Water Treatment NaOCl Active Ingredient Hydrogen Management Discussion Document Rev DDocument23 pagesBallast Water Treatment NaOCl Active Ingredient Hydrogen Management Discussion Document Rev DIanPerrettNo ratings yet
- Today'S Topic "Cooling Water Treatement" "Condenser Leak Detection" "Chlorination Plant" AND "Effluent Treatment"Document57 pagesToday'S Topic "Cooling Water Treatement" "Condenser Leak Detection" "Chlorination Plant" AND "Effluent Treatment"saravan1891No ratings yet
- Final-Pulse Chlorination Qatargas 2012 PAPER FinalDocument9 pagesFinal-Pulse Chlorination Qatargas 2012 PAPER FinalMohamed ZaghloulNo ratings yet
- Coagulant (Pac) and Flocculant (Pam)Document2 pagesCoagulant (Pac) and Flocculant (Pam)udit singhNo ratings yet
- Silica Removal During Lime Softening in Water Treatment PlantDocument10 pagesSilica Removal During Lime Softening in Water Treatment PlantLouay MansourNo ratings yet
- Multi Stage Flash Desalination Plant With Brine-Feed Mixing and CoolingDocument8 pagesMulti Stage Flash Desalination Plant With Brine-Feed Mixing and CoolingMuhammadEhtishamSiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Sodium HypochloriteDocument7 pagesSodium HypochloriteEdison Cheong100% (1)
- Briefs - Chlor AlkaliDocument14 pagesBriefs - Chlor AlkaliNuno Formiga100% (1)
- Water Treatment PlantDocument28 pagesWater Treatment PlantVuthpalachaitanya Krishna0% (1)
- 07 - Lime SofteningDocument4 pages07 - Lime SofteningRAJ_1978No ratings yet
- PCB Disposal Facility at Bhilai Steel PlantDocument22 pagesPCB Disposal Facility at Bhilai Steel PlantK.praveenNo ratings yet
- 19 I Lewatit FO 36 Presentation For Customers ShortDocument31 pages19 I Lewatit FO 36 Presentation For Customers ShortAlfonso José García LagunaNo ratings yet
- Etp Process - RefineryDocument3 pagesEtp Process - Refinerysumit gulatiNo ratings yet
- Mod04 Lec06 Electro Deionization (EDI)Document43 pagesMod04 Lec06 Electro Deionization (EDI)Mario Antonio Araya MorosoNo ratings yet
- Electrodialysis Processes With Bipolar Membranes (EDBM) in Environmental Protection - A ReviewDocument22 pagesElectrodialysis Processes With Bipolar Membranes (EDBM) in Environmental Protection - A Reviewandreas.exaNo ratings yet
- Harga Bahan KimiaDocument2 pagesHarga Bahan KimiaAndre Gazali Malik100% (1)
- Pre TreatmentDocument65 pagesPre TreatmentSagar SewlaniNo ratings yet
- Desalination Plant of TobrukDocument21 pagesDesalination Plant of TobrukMotaz ZgogoNo ratings yet
- Bacteriological and Residual Chlorine TestingDocument24 pagesBacteriological and Residual Chlorine TestingunnipraNo ratings yet
- Process Wastewater CharacteristicsDocument12 pagesProcess Wastewater CharacteristicsYeAsin AraFatNo ratings yet
- SUEZ Hand Book For Industrial Water TreatmentDocument1 pageSUEZ Hand Book For Industrial Water TreatmentJahidul IslamNo ratings yet
- INDION Multigrade Filter PDFDocument1 pageINDION Multigrade Filter PDFSandeep K Tiwari100% (1)
- Saltworks Zero Liquid Discharge InfographicDocument2 pagesSaltworks Zero Liquid Discharge InfographicSameer HussainNo ratings yet
- Reverse Osmosis ReportDocument25 pagesReverse Osmosis ReportMuhammad Ishfaq100% (1)
- Scale Remover PresentationDocument18 pagesScale Remover PresentationRaja Pathamuthu.G100% (1)
- Textile WastewaterDocument43 pagesTextile Wastewatersujal jhaNo ratings yet
- 4-MCran Membrane CleaningDocument41 pages4-MCran Membrane CleaningKhalid AbdelRahimNo ratings yet
- Recovery of Salt From Aqueous Solution by Eutectic Freeze CrystallizationDocument39 pagesRecovery of Salt From Aqueous Solution by Eutectic Freeze CrystallizationApurva PatelNo ratings yet
- Demineralized Water Plant SystemDocument4 pagesDemineralized Water Plant SystemrohitkushNo ratings yet
- ChlorineDocument20 pagesChlorineBanamali Mohanta100% (1)
- WWTP ChemicalsDocument34 pagesWWTP ChemicalsHRK65No ratings yet
- Semiconductor Wastewater Treatment Using Tapioca Starch As A Natural CoagulantDocument9 pagesSemiconductor Wastewater Treatment Using Tapioca Starch As A Natural Coagulanthuonggiangnguyen3011No ratings yet
- Report On Multi Effect DistillationDocument6 pagesReport On Multi Effect DistillationMohammadAsifNo ratings yet
- Ide Progreen BrochureDocument4 pagesIde Progreen Brochurelifemillion2847No ratings yet
- Cooling Tower Water Treatment MIOX Superior DisinfectionDocument21 pagesCooling Tower Water Treatment MIOX Superior Disinfectioncarlos0% (1)
- Pde ReportDocument10 pagesPde ReportChellam Siva Chellam SivaNo ratings yet
- CDB Engineering S.P.A. Experience - : Sodium Hypoclorite Plant PresentationDocument17 pagesCDB Engineering S.P.A. Experience - : Sodium Hypoclorite Plant PresentationEby OkvaleyNo ratings yet
- Spiral Wound Forward Osmosis Membrane ModuleDocument12 pagesSpiral Wound Forward Osmosis Membrane Modulejigar patelNo ratings yet
- DesalinationDocument14 pagesDesalinationapi-368121935No ratings yet
- 2010 SMR ClarifierDocument60 pages2010 SMR ClarifierRohan KakdeNo ratings yet
- Lime Softening PDFDocument16 pagesLime Softening PDFBiljana TausanovicNo ratings yet
- Water Softening MethodsDocument34 pagesWater Softening MethodsAjitsingh Jagtap100% (1)
- Design and Operation of Emergency Chlorine Absorption SystemsDocument18 pagesDesign and Operation of Emergency Chlorine Absorption Systemsahmed aliNo ratings yet
- FuMATech AcidMembranes EinzelDocument6 pagesFuMATech AcidMembranes Einzeldow2008No ratings yet
- Desalination EngineeringDocument8 pagesDesalination EngineeringShafayet A SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Cleaning Procedure-GeneralDocument2 pagesCleaning Procedure-Generalmunawar786100% (1)
- Systematic Methods of Water Quality Parameters Analysis: Analytical MethodsFrom EverandSystematic Methods of Water Quality Parameters Analysis: Analytical MethodsNo ratings yet
- Liquid Membranes: Principles and Applications in Chemical Separations and Wastewater TreatmentFrom EverandLiquid Membranes: Principles and Applications in Chemical Separations and Wastewater TreatmentNo ratings yet
- HAPPY WEEK - List of Products - March 2015Document30 pagesHAPPY WEEK - List of Products - March 2015GROIIMNo ratings yet
- HAPPY WEEK - List of Products - March 2015Document30 pagesHAPPY WEEK - List of Products - March 2015GROIIMNo ratings yet
- DMX PumpsDocument33 pagesDMX PumpsGROIIMNo ratings yet
- DMH PumpsDocument23 pagesDMH PumpsGROIIMNo ratings yet
- GSL - PN On Stock - LowDocument2 pagesGSL - PN On Stock - LowGROIIMNo ratings yet
- GCR - PN On Stock - LowDocument2 pagesGCR - PN On Stock - LowGROIIMNo ratings yet
- List of Products On Happy Week Offer - Jan. 2015Document15 pagesList of Products On Happy Week Offer - Jan. 2015GROIIMNo ratings yet
- Pump Selection Guide - SE - SL 9 - 30 KWDocument6 pagesPump Selection Guide - SE - SL 9 - 30 KWGROIIMNo ratings yet
- Bleaching AgentDocument5 pagesBleaching AgentgtarasanNo ratings yet
- Brdy 6ed Ch17 AcidBaseEquilibriaDocument189 pagesBrdy 6ed Ch17 AcidBaseEquilibriaAchmad Rochliadi100% (1)
- Denture Disinfectants Used in Prosthodontics - A ReviewDocument4 pagesDenture Disinfectants Used in Prosthodontics - A ReviewMostafa FayadNo ratings yet
- Update On Endodontic Irrigating Solutions: Bettina Basrani & Markus HaapasaloDocument29 pagesUpdate On Endodontic Irrigating Solutions: Bettina Basrani & Markus HaapasaloSofeaNo ratings yet
- Disinfection by Sodium Hypochlorite. Dialysis Applications (2007)Document168 pagesDisinfection by Sodium Hypochlorite. Dialysis Applications (2007)Popoviciu SimonaNo ratings yet
- 11 3 Umit+Sezgi MANUSCRIPTDocument13 pages11 3 Umit+Sezgi MANUSCRIPTRockhy SyahrialNo ratings yet
- Irrigation in EndodonticsDocument5 pagesIrrigation in EndodonticshunarsandhuNo ratings yet
- Water Part2Document49 pagesWater Part2Madathiparambil ManuNo ratings yet
- YOKOGAWA Exa Fc400g (Ing)Document91 pagesYOKOGAWA Exa Fc400g (Ing)biotech666No ratings yet
- Purification of Water: On Large ScaleDocument71 pagesPurification of Water: On Large ScaleHarshal Sabane100% (5)
- UNIT III AntimicrobialsDocument8 pagesUNIT III AntimicrobialstihomihoNo ratings yet
- Grundfosliterature 3279106Document20 pagesGrundfosliterature 3279106Riski SuhardinataNo ratings yet
- 08 - Chapter 1Document48 pages08 - Chapter 1danfm97No ratings yet
- The Toxicology of Chlorine: School of Safety Science, University of New South Wales, Sydney NSW 2052, AustraliaDocument10 pagesThe Toxicology of Chlorine: School of Safety Science, University of New South Wales, Sydney NSW 2052, AustraliaAswar MakrufNo ratings yet
- Boiler Journal - Sodium ChemicalsDocument9 pagesBoiler Journal - Sodium ChemicalsabdoelandhakimNo ratings yet
- Study Material - Engineering Chemistry MODULE 5-MODULE - 550Document12 pagesStudy Material - Engineering Chemistry MODULE 5-MODULE - 550ChanduNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment Slides ORIGINALDocument44 pagesWater Treatment Slides ORIGINALMarvin SironNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower Water Treatment ChemistryDocument4 pagesCooling Tower Water Treatment ChemistryMuhammad UmairNo ratings yet
- The Treatment of Cooling Water With Chlorine Dioxide PDFDocument10 pagesThe Treatment of Cooling Water With Chlorine Dioxide PDFMumtaz Ahmed GhummanNo ratings yet
- Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate (Nadcc - Anhydrous and Dihydrate)Document8 pagesSodium Dichloroisocyanurate (Nadcc - Anhydrous and Dihydrate)Tarek AlmahdyNo ratings yet
- Group 17 Elements: General Characteristics and Group TrendsDocument9 pagesGroup 17 Elements: General Characteristics and Group TrendsHarsh VyasNo ratings yet
- ECA WaterDocument5 pagesECA WaterAleem AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chlorination PDFDocument21 pagesChlorination PDFKanchanNo ratings yet
- BAR Catalogo Chimico 2016 en - ExportDocument82 pagesBAR Catalogo Chimico 2016 en - ExportdobleNo ratings yet
- Feedback Disinfection QsDocument11 pagesFeedback Disinfection Qshumza bhattiNo ratings yet
- Chlorinated Water Effects To Human HealthDocument53 pagesChlorinated Water Effects To Human HealthNayu Nur Annisa100% (1)
- Macrofouling-Problem & PreventionDocument15 pagesMacrofouling-Problem & PreventionReka ErdantoNo ratings yet
- Patterns in Period 3 ElementsDocument18 pagesPatterns in Period 3 ElementsDania Dobbs100% (2)