Cefotetan (Injection Route)
US Brand Names
Cefotan
Description
Cefotetan injection is used to treat bacterial infections in many different parts of the body.
This medicine is also given before certain types of surgery to prevent infections.
Cefotetan injection belongs to the class of medicines known as cephalosporin antibiotics. It
works by killing bacteria or preventing their growth. However, this medicine will not work
for colds, flu, or other virus infections.
This medicine is available only with your doctor's prescription
Before Using
In deciding to use a medicine, the risks of taking the medicine must be weighed against the
good it will do. This is a decision you and your doctor will make. For this medicine, the
following should be considered:
Allergies
Tell your doctor if you have ever had any unusual or allergic reaction to this medicine or any
other medicines. Also tell your health care professional if you have any other types of
allergies, such as to foods, dyes, preservatives, or animals. For non-prescription products,
read the label or package ingredients carefully.
Pediatric
Appropriate studies have not been performed on the relationship of age to the effects of
cefotetan injection in the pediatric population. Safety and efficacy have not been established.
Geriatric
Appropriate studies performed to date have not demonstrated geriatric-specific problems that
would limit the usefulness of cefotetan injection in the elderly. However, elderly patients are
more likely to have age-related kidney problems, which may require caution and an
adjustment in the dose for patients receiving cefotetan injection.
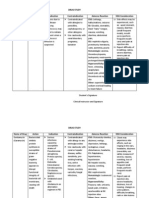
Pregnancy
�Pregnan
cy
Category
All
Trimeste B
rs
Explanation
Animal studies have revealed no evidence of harm to the
fetus, however, there are no adequate studies in pregnant
women OR animal studies have shown an adverse effect,
but adequate studies in pregnant women have failed to
demonstrate a risk to the fetus.
Breastfeeding
There are no adequate studies in women for determining infant risk when using this
medication during breastfeeding. Weigh the potential benefits against the potential risks
before taking this medication while breastfeeding.
Drug Interactions
Although certain medicines should not be used together at all, in other cases two different
medicines may be used together even if an interaction might occur. In these cases, your
doctor may want to change the dose, or other precautions may be necessary. Tell your
healthcare professional if you are taking any other prescription or nonprescription (over-thecounter [OTC]) medicine.
Other Interactions
Certain medicines should not be used at or around the time of eating food or eating certain
types of food since interactions may occur. Using alcohol or tobacco with certain medicines
may also cause interactions to occur. The following interactions have been selected on the
basis of their potential significance and are not necessarily all-inclusive.
Using this medicine with any of the following is usually not recommended, but may be
unavoidable in some cases. If used together, your doctor may change the dose or how often
you use this medicine, or give you special instructions about the use of food, alcohol, or
tobacco.
Ethanol
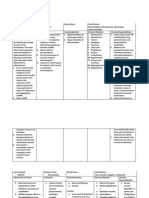
Other Medical Problems
The presence of other medical problems may affect the use of this medicine. Make sure you
tell your doctor if you have any other medical problems, especially:
Colitis (inflammation in gut), history of or
Diarrhea, severe, history of or
Hemolytic anemia or
SeizuresUse with caution. May make these conditions worse.
Kidney diseaseUse with caution. Effects may be increased because of
slower removal of the medicine from the body
Proper Use
A nurse or other trained health professional will give you this medicine. This medicine is
given as a shot into one of your muscles, or through a needle placed in one of your veins.
Precautions
If your symptoms do not improve within a few days, or if they become worse, check with
your doctor.
Hemolytic anemia may occur while you are using this medicine. Stop using this medicine and
check with your doctor right away if you have back, leg, or stomach pains; bleeding gums;
chills; dark urine; difficulty with breathing; fever; general body swelling; headache; loss of
appetite; nausea or vomiting; nosebleeds; pale skin; sore throat; unusual tiredness or
weakness; or yellowing of the eyes or skin.
Cefotetan injection may cause diarrhea, and in some cases it can be severe. Do not take any
medicine to treat diarrhea without first checking with your doctor. Diarrhea medicines may
make the diarrhea worse or make it last longer. If you have any questions about this or if mild
diarrhea continues or gets worse, check with your doctor.
Do not drink alcohol while you are receiving cefotetan injection and for 3 days (72 hours)
after your last dose. Drinking alcohol during this period may cause flushing; headache;
sweating; and fast, pounding, or irregular heartbeat.
Before you have any medical tests, tell the medical doctor in charge that you are receiving
this medicine. The results of some tests may be affected by this medicine.
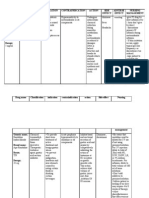
Side Effects
Along with its needed effects, a medicine may cause some unwanted effects. Although not all
of these side effects may occur, if they do occur they may need medical attention.
Check with your doctor or nurse immediately if any of the following side effects occur:
Less common
Abdominal or stomach cramps or tenderness
Back, leg, or stomach pains
Black, tarry stools
Bleeding gums
Bloating
Chest pain
Chills
Cough
Dark urine
Diarrhea
Diarrhea, watery and severe, which may also be bloody
Difficulty with breathing
Fever
General body swelling
Headache
Increased thirst
Loss of appetite
Nausea or vomiting
Nosebleeds
Pain
Painful or difficult urination
Pale skin
Shortness of breath
Sore throat
Sores, ulcers, or white spots on the lips or in the mouth
Swollen glands
Unusual bleeding or bruising
Unusual tiredness or weakness
Unusual weight loss
Yellowing of the eyes or skin
Rare
Blood in the urine
Bluish color
Change in frequency of urination or amount of urine
Changes in skin color
Drowsiness
Increased thirst
Swelling of the feet or lower legs
Tenderness
Weakness
Incidence not known
Blistering, peeling, or loosening of the skin
Cough or hoarseness
Coughing up blood
Difficulty with swallowing
Dizziness
Fast heartbeat
Fever with or without chills
General feeling of tiredness or weakness
High fever
Increased menstrual flow or vaginal bleeding
Itching
Itching of the vagina or genital area
Joint or muscle pain
Lower back or side pain
Nosebleeds
Pain during sexual intercourse
Paralysis
Pinpoint red spots on the skin
Prolonged bleeding from cuts
Puffiness or swelling of the eyelids or around the eyes, face, lips, or tongue
Rash
Red or black, tarry stools
Red or dark brown urine
Red skin lesions, often with a purple center
Red, irritated eyes
Seizures
Skin rash
Sudden decrease in the amount of urine
Swollen or painful glands
Thick, white vaginal discharge with no odor or with a mild odor
Tightness in the chest
Unpleasant breath odor
Vomiting of blood
Wheezing