Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Health Promotion Is About Raising The Health Status of Individuals and Communities
Uploaded by
Monique Mavronicolas0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views3 pagesInfo - borrowed
Original Title
Health Promotion is About Raising the Health Status of Individuals and Communities
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentInfo - borrowed
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views3 pagesHealth Promotion Is About Raising The Health Status of Individuals and Communities
Uploaded by
Monique MavronicolasInfo - borrowed
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Health promotion is about raising the health status of individuals and
communities.
Health promotion is an umbrella term for the range of activities carried out in
various settings, with various groups which tackle causing ill-health
Decline in infectious disease rates, and the emergence diseases linked to
unhealthy lifestyles such as coronary heart disease and cancer, also
supported this change in public health focus.
Increasingly, chronic diseases were viewed as being created in parted by the
individual behavior and life style choices, and subsequently efforts to
encourage individuals to make lifestyle changes became a key focus of public
health work.
Health education - defined as planned learning experiences to facilitate
voluntary change in behaviour to develop consciously pursued health-directed
behaviour.
Emerged as a discipline within public health movement during the late 1800s,
early 1900s - primary aim concerned with encouraging behavioural change.
The emergence of health education is often linked to the rise of the
temperance movement in the UK.
Mass health education programme to deal with 1st World War soldiers
returning home with some form of venereal disease (20%).
Views and values held health and health determinants influences health
professionals and politicians decisions about which health promotion
strategies or approaches should be used.
Health promotion is characterised by the use of diverse approaches, and all
have strengths and limitations.
No single approach is or has been responsible for improvements in the health
status of individuals and/or populations.
Prerequisites for health
Peace
Shelter
Education
Food
Income
A stable eco-system
Sustainable resources
Social justice and equity
5 approaches to health promotion
1. Medical or preventive - To prevent disease
2. Behaviour change - To ensure people are well informed and able to make
healthy choices
3. Educational - To help people to acquire the skills and
4. Empowerment - confidence to take greater control over their health
5. Social change - To change policies and environments in order to facilitate
healthy choices
Strengths of Health Promotion Campaigns may include
Help to raise awareness of health issues
Generate discussion
To motivate people to make changes
Highlight a problem
Inform people
Explain consequence of undesirable behaviour
Can reduce incidence of illness and disease morbidity rate
Can reduce mortality rates
Meet health targets as set by the government
Provide support e.g. Free phone numbers for smokers to quit.
Weaknesses of Health Promotion Campaigns may include
Can result in groups becoming immune to health messages and so they may
be ineffective
People do not like being told what to do
People can become confused with the conflicting messages from various
campaigns/organisations
Can be difficult to get the information across to the target audience
People can simply ignore campaigns
People refuse to believe that they could be affected
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Advanced Practice Nurses: Promoting Evidence Based Practice and Capturing Impact: Lessons From Two UK StudiesDocument34 pagesAdvanced Practice Nurses: Promoting Evidence Based Practice and Capturing Impact: Lessons From Two UK StudiesMonique MavronicolasNo ratings yet
- Monique Mavronicolas - Research ProjectDocument44 pagesMonique Mavronicolas - Research ProjectMonique MavronicolasNo ratings yet
- Dissemination Project WritingDocument9 pagesDissemination Project WritingMonique MavronicolasNo ratings yet
- Research Project ReflectionDocument2 pagesResearch Project ReflectionMonique MavronicolasNo ratings yet
- Monique Mavronicolas - Research Project ProposalDocument3 pagesMonique Mavronicolas - Research Project ProposalMonique MavronicolasNo ratings yet
- Building Resilience, Promoting WellbeingDocument35 pagesBuilding Resilience, Promoting WellbeingMonique MavronicolasNo ratings yet
- Carl Ransom RogersDocument8 pagesCarl Ransom RogersMonique MavronicolasNo ratings yet
- Mental Health PPPDocument6 pagesMental Health PPPMonique MavronicolasNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Campaign ToolkitDocument11 pagesMental Health Campaign ToolkitMonique MavronicolasNo ratings yet
- Personality and HealthDocument6 pagesPersonality and HealthMonique MavronicolasNo ratings yet
- Pass or Fail: Mark - Please Circle The ResultDocument1 pagePass or Fail: Mark - Please Circle The ResultMonique MavronicolasNo ratings yet
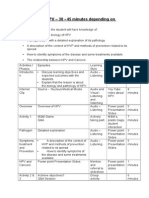
- HPV Lesson Plan PDFDocument25 pagesHPV Lesson Plan PDFMonique MavronicolasNo ratings yet
- Psychosomatic DisordersDocument11 pagesPsychosomatic DisordersJasmin Jacob100% (3)
- Depression PDFDocument2 pagesDepression PDFMonique MavronicolasNo ratings yet
- Human Papilloma Virus: by Monique MavronicolasDocument13 pagesHuman Papilloma Virus: by Monique MavronicolasMonique MavronicolasNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - HPVDocument6 pagesLesson Plan - HPVMonique MavronicolasNo ratings yet
- Self Harm PDFDocument2 pagesSelf Harm PDFMonique MavronicolasNo ratings yet
- Preventing Illness and Living With Ill HealthDocument11 pagesPreventing Illness and Living With Ill HealthMonique MavronicolasNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- PQC-POL002 Qualification Guide For CertOH and iCertOH v1.0Document25 pagesPQC-POL002 Qualification Guide For CertOH and iCertOH v1.0Nathan MwewaNo ratings yet
- BrochureDocument6 pagesBrochureRahul ShettyNo ratings yet
- 10 - The Generics Act of 1988Document22 pages10 - The Generics Act of 1988rhydelNo ratings yet
- Pacific CrossDocument27 pagesPacific Crossanon_873405382No ratings yet
- A Study To Assess The Effectiveness of Selected Teaching Strategies Knowledge Regarding Drug Calculation Among B.Sc. N Students in Selected College at ChennaiDocument3 pagesA Study To Assess The Effectiveness of Selected Teaching Strategies Knowledge Regarding Drug Calculation Among B.Sc. N Students in Selected College at ChennaiEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- PHIL 125: Practical Logic: University of Alberta Sam Hillier, Fall 2013Document12 pagesPHIL 125: Practical Logic: University of Alberta Sam Hillier, Fall 2013Harry WeiNo ratings yet
- NT90004212Document58 pagesNT90004212Jelena ĆukNo ratings yet
- DSM 5Document33 pagesDSM 5Grace Marie100% (2)
- Soy Estrogen Myth False - DR Mercola Caught by Federal Authorities Spreading False Health Info - (Soy Found Not To Contain Estrogen, Soy Does Not Lower Men's Testosterone, Fraudulent Claims)Document10 pagesSoy Estrogen Myth False - DR Mercola Caught by Federal Authorities Spreading False Health Info - (Soy Found Not To Contain Estrogen, Soy Does Not Lower Men's Testosterone, Fraudulent Claims)FRAUDWATCHCOMMISSIONNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Davao Oriental State College of Science and TechnologyDocument4 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Davao Oriental State College of Science and Technologydinheadnursing09No ratings yet
- Risk Assessment - Lifting OperationsDocument6 pagesRisk Assessment - Lifting OperationsJishad Nalakath83% (87)
- Name: Reymark Mutia Narrative Reporting (Doctool) - Edong Permites Chapter - 1 To Start, Type in The Local Server Url Inside The BrowserDocument65 pagesName: Reymark Mutia Narrative Reporting (Doctool) - Edong Permites Chapter - 1 To Start, Type in The Local Server Url Inside The BrowserReymark MutiaNo ratings yet
- Mapeh 2ND QDocument5 pagesMapeh 2ND QMaxicris SlowerNo ratings yet
- Dunkin DonutsDocument2 pagesDunkin DonutszerpthederpNo ratings yet
- When Workers Rate The BossDocument3 pagesWhen Workers Rate The BossSHIVANGI MAHAJAN PGP 2021-23 BatchNo ratings yet
- Resume 3Document2 pagesResume 3api-458753728No ratings yet
- Stacey Waters CVDocument5 pagesStacey Waters CVapi-479651018No ratings yet
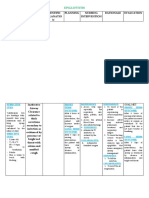
- Epiglottitis: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanatio N Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesEpiglottitis: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanatio N Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationfifiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process Patients With DiabetesDocument14 pagesNursing Process Patients With DiabetesJelly Jia100% (2)
- 1PE 4 Q3 Answer Sheet March 2024Document3 pages1PE 4 Q3 Answer Sheet March 2024Chid CabanesasNo ratings yet
- Invenia ABUS USA Brochure Feb2016Document14 pagesInvenia ABUS USA Brochure Feb2016Asim AliNo ratings yet
- Diet's CardDocument8 pagesDiet's CardJORGE ATRIANONo ratings yet
- Counseling: Counseling Is A Wonderful Twentieth-Century Invention. We Live in A Complex, BusyDocument21 pagesCounseling: Counseling Is A Wonderful Twentieth-Century Invention. We Live in A Complex, BusyAnitha KarthikNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Safety and Health at WorkDocument42 pagesModule 5 Safety and Health at Workdoidoi80% (5)
- Clinic by Alissa QuartDocument4 pagesClinic by Alissa QuartOnPointRadioNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Asli PBL 3 Blok 9Document6 pagesJurnal Asli PBL 3 Blok 9Annisa FadilasariNo ratings yet
- Agri SBA (Broiler)Document20 pagesAgri SBA (Broiler)Shanti KissoondyalNo ratings yet
- Eular References For Website 2015Document240 pagesEular References For Website 2015Antonio BernalNo ratings yet
- Sacred Heart Diocesan School: Student's Learning Activity in PHYSICAL EDUCATION 9Document8 pagesSacred Heart Diocesan School: Student's Learning Activity in PHYSICAL EDUCATION 9KC Tolentino CahanapNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial ResistanceDocument46 pagesAntimicrobial ResistanceEmil CotenescuNo ratings yet