Values at IBM :
Making A Difference
SELUSI conference 2011
Ir. Mia Vanstraelen
Mia.vanstraelen@be.ibm.com
Oct 7th, 2011
�Agenda
IBM at a glance
IBMs Values
Development of IBMs values
Impact on IBMs Business and the world
�IBM at a glance
IBM is a values-based enterprise of individuals, who create and apply
technology to make the world work better.
Today, about 400,000 IBMers around the world
invent and integrate hardware, software and services
to help forward-thinking enterprises, institutions and
people everywhere succeed in building a smarter planet.
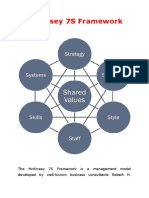
�IBM Values
Dedication to every clients success
Innovation that matters for our company and
for the world
Trust and personal responsibility in all
relationships
�Background: The IBM Perspective
IBMs top management has consistently mandated
commitment to values and the highest ethical standards
- Any great organization owes its resiliency, not to its
form of organization or its administrative skills, but to the
power of what we call beliefs and the appeal these beliefs
have for its people. T.J. Watson, Jr.
- Ethical behavior is good for business because it fosters
one of our greatest assets customer loyalty. L.V.
Gerstner
- Remember that a strong value system based on integrity
and accountability has always been at the core of IBMs
existence. We do not pay lip service to ethics; it is part of
our DNA. S.J. Palmisano
�IBM has reinvented itself many times. But through it all, its DNA, its soul
remained intact. Thats because of something that was part of this
company since its inception.
IBMs most important innovation wasnt a technology or management system. Its
revolutionary idea was to define and run a company by a set of strongly held beliefs
beliefs that would transcend economic cycles, geopolitical shifts, and generations
of products, technologies, employees and leaders
IBMs most important
innovation was the IBMer
�IBM Business Leadership Model
Leadership
Strategy
Execution
Marketplace
Insight
Strategic
Intent
Talent
Business
Design
Critical Tasks
Interdependencies
Innovation
Focus
Climate &
Culture
Market
Results
Formal
Organization
Gap
Performance
Opportunity
IBM Values
IBM Values are foundational to Strategy and Execution which are interdependent on,
and essential to, IBM Business Leadership.
Note: IBM's approach to strategic execution is adapted from Tushman, Michael L. & Charles A.
O'Reilly III. Winning through Innovation. Harvard Business School Press, Boston, MA. 1997.
�In 2003, IBMers participated in
the first values Jam WW
�Development of IBM Values
How IBM
has used Jams
IBM all
company Jams
��IBM Transformation IBMs Approach to Transformation
IBMs Transformation Framework is guided by the IBM Strategy,
grounded in IBM Values and enabled by Transformation Platforms
Guided by the IBM
Strategy and grounded
in our Values
IBM Strategy
IBM Values
Transformation Framework
Business
Process
Excellence
Enable transformation
at the intersection of
business process,
technology and culture
Value-based
Culture
Information
Technology
Enablement
Transformation Platforms
Enable Growth
Capture higher value
Enable Productivity
Invest for growth
Enable Culture Change
Apply shared values
Drive productivity
Sustain our strength in
the global marketplace
by focusing on areas
that enable growth,
productivity, and
culture change
�IBMers can find essential ingredients for growing their careers, and building
and sustaining a company of experts, in our three-tier Career Model
Expertise
Capabilities
Leadership
Job Role Expertise:
Career Capabilities:
IBM Competencies:
Develop deep skills and
expertise specific to a
particular job
Build a broad set of
capabilities to advance a
career
Demonstrate the
leadership that
distinguishes IBM-ers
Employees use a tool to
assess their skills and
close gaps between
current skill levels and
their targets
Employees use the Career
Framework to develop
client-valued capabilities,
document their progress,
and apply for progression
in the framework
Employees grow and
document their progress
in unique leadership
competencies and
behaviors, based on
IBMs values, that are
differentiators for IBM
�Emotional Intelligence Competencies are
Aligned with IBMs existing competency work
Any measurable characteristic of a person that differentiates
level of performance in a given job, role, organization, or
culture
Skills
Knowledge
Social Role, Values
Self-Image
Trait
Motive
Necessary for
top performance
but not sufficient
Characteristic
s
that lead to
longer-term
success
�Values and motivational characteristics vary by generation
Connecting with our people
Workaholics
Sceptical
A contract
Freedom
Title Recognition
Do it your way
You are needed
Source: FDU Magazine
�As an IBMer you will find alignment between the Emotional Intelligence
Competencies and the IBM Values and Leadership Competencies
Managing Yourself
Empathy
Self Control
Self Confidence
Managing Your
Team
Developing Others
Holding People Accountable
Team Leadership
Managing the Work
Results Orientation
Initiative
Problem Solving
Managing
Collaboratively
Influencing Others
Fostering Teamwork
�And employees develop competencies that reflect our
core IBM Values
How and when?
By using the IBM Competencies Learning
Suites to deepen their understanding of the
competencies
Leadership
Capabilities
By making sure to include competency
growth in their career development plan
IBM Competencies:
By using the Career Framework to
document their competency progression
By living our IBM values and demonstrating
leadership in all they do at IBM
Employees demonstrate
the leadership that
distinguishes IBM
�IBM Transformation Underlying Platforms Enabling Culture Change
Defined common values and performance mgmt align employees with
the decisions and strategic priorities of the management teams
Established and periodically refreshed a core set of
leadership competencies for all IBMers
Transformational Leadership
Values-based Culture
Collaborative Innovation
Global IBMer
Defined a new Leadership Framework that
emphasizes business results and the employees
experience
Engaged employees globally in Values Jam to refresh
our Values
Enabled collaborative innovation by making intranet
sophisticated social networking platform
Impact
Established a global innovation agenda that spans
multiple dimensions (e.g., products, services, people)
IBMs Values are integral in our performance, recognition and talent management systems
Tens of thousands of IBM employees actively participate in advancing our Values-based culture via
collaborative technologies
Business Week named IBM one of Twenty Best Companies for Leadership
IBM Research #1 on the US patent list for 17 years
�Business Resilience Services
Why a focus on Climate & Culture?
The Integral Linkage Research Model*
Leadership Practices
Conclusions from nine years of IBM Linkage Research:
IBMers attitudes measured by the Global Pulse
Survey
are leading indicators of future client satisfaction,
revenue growth, and market share
START here:
Walk the talk
Formal change project:
Integral approach
Fit for the Future
Employee development
Acknowledge fear
Business Performance
Employee Results
+ Sales Growth
Work climate
+ Market Share
Professional teamwork
+ Productivity
Employee satisfaction
+ Long term profitability
Employee retention
Customer Results
+ Responsive service
+ Product quality
Elapsed Time
Integral Linkage Research Model, 2005
Customer satisfaction
+ Customer retention
Elapsed time
Work Characteristics
Work characteristics
*Adapted from: (1) The Handbook of Organizational Culture & Climate, chapter 11, by J.W. Wiley & S.M. Brooks. (2) Peter M. Senge and Katrin H. Kufer, Communities of
Leaders or No Leadership at All, ABRIDGED for publication in Cutting Edge: Leadership 2000 by Barbara Kellerman, Larraine R.Matusak. (3) IBM Workforce Research
1997 2005. (4) BC&RS Fit for the Future project 2004 - 2005. (5) Richard Barret, A Whole Systems Approach to Cultural Transformation: Building a Values Driven
Organization, 2005 2006.
IBM Business Consulting Services
BC&RS Fit for the Future | Do not copy or email | IBM Confidential
2005 IBM Corporation
Obstacles to innovation
The IBM Global CEO Study 2006 reveals that 35% of CEOs see
an unsupportive culture and climate as a major obstacle for
innovation
Unsupportive culture and climate
Limited funding for investment
Government and other legal restrictions
Workforce issues arising internally
Process immaturity
Economic uncertainty
Inadequate enabling technologies
Inflexible physical and information technology
infrastructure
Insufficient access to necessary information and
data
Workforce issues arising externally
Other
0%
10%
20%
30%
40%
% of Respondents
For IBM Internal Use Only
59
Leadership competenties and managerial styles (skills and behaviour
of manager) influence up to 70% the climate in a team (Hay Consultants)
Copyright IBM Corporation 2006
Global Business Services
And Leadership Styles make a Difference
Coercive
Authoritative
Affiliative
Democratic
Pace-setting
Coaching
Leaders
Modus
Operandi
Demands
immediate
compliance
Mobilizes
people toward a
vision
Creates
harmony and
builds emotional
bonds
Forges
consensus
through
participation
Sets high
standards for
performance
Develops
people for the
future
In one
sentence
Do what I
tell you
Come with me
People come
first
What do you
think?
Do as I do,
now
Try this
Style
working
Crisis, kickstart
turnaround
When changes
require a new
vision, or clear
direction is
needed
To motivate
people during
stressful
circumstances
To get buy-in or
consensus or
input from
employees
To get quick
results from a
highly
motivated and
competent
team
To help an
employee
improve
performance or
develop LT
strengths
.34
-.25
.42
best
Overall
Impact on
Climate
- .26
.54
.46
Daniel Goleman: Harvard Business Review OnPoint Summer 2006
Daniel Goleman: Harvard Business Review OnPoint Summer 2006
16
September 2006
An integral look at Innovation
Copyright IBM Corporation 2006
The impact of climate on financial results, such as return on sales, revenue
growth, efficiency and profitability has a direct correlation with leadership styles
(next to market conditions and competitive dynamics) and a direct influence on the
bottom line (HBR OnPoint/Summer 2006) and accounts for nearly 1/3 of results.
�IBM Solutions is Leading to Think and Act in New
Ways: Economically, Socially and Technically
Smarter
Roads
Smarter Oil
& Gas
Smarter
Food
Smarter
Healthcare
Smarter
Utilities
Smarter
Retail
Smarter
Telco
Smarter
Supply
Chains
Smarter
Public
Safety
Smarter
Money
Smarter
Transportation
Smarter
Cities
��Our Values at Work outlines the meaning of Trust and
personal responsibility in all relationships
Trust and personal responsibility in all
relationships means:
IBMers actively build relationships with all
the constituencies of our business
including clients, partners, communities,
investors and fellow IBMers.
IBMers build trust by listening, following
through and keeping their word.
IBMers rely on our colleagues to do the right
thing.
IBMers preserve trust even when formal
relationships end.
Inside IBM, weve never been more matrixed, more global, more virtual, more
dependent on people who dont sit next to us and dont report to us. Nonetheless
(or, rather, especially), we must come through for our colleaguesor be clear
about why we cannot. Ambiguity, uncertainty and passing the buck are the
surest ways to kill both productivity and relationships
�Sam Palmisano continues to articulate his expectations
for Trust and personal responsibility in all relationships
At IBM, we've set off down the path of empowering and enabling our people to make
decisions and to act. We have been working to lower the center of gravity' of the
company, as I put itthat is, to trust IBMers and push decision-making authority
out and downThis will require a whole new kind of humility for enterprises and their
leaders. And it will also require a new level of ownership and personal responsibility
among individuals. Both of those shifts will involve major culture change.
Sam Palmisano,
The Globally Integrated Enterprise
April 2007
"This shift of control and decision-making to the IBMer
represents a very new relationship between
enterprises and individuals and that involves a
certain degree of risk. Sharing power always does. But if
you trust your strategy, your capabilities and your
people and if you are confident that all are grounded
in a set of shared values then this is the kind of
innovation you pursue.
Sam Palmisano,
Letter to IBM Shareholders
March 2008
��Back Up
�IBM Strategy to optimize value for our clients
Focus on open technologies and high-value solutions
Deliver integration and innovation to clients
Become the premier Globally Integrated Enterprise
�End of the crisis? ... Which is the next one ?
� 3. Embed corporate values into all leadership initiatives.
Shared values are the underpinning of a corporate-wide culture. They help
unite employees across the globe, as well as enabling fast, independent
decision making consistent with the company's philosophy. As well as
embedding corporate values, be sure to establish the important role of the
leader as a global ambassador; one who not only communicates and
reinforces corporate values, but who embodies them in everyday behaviours
and decisions.
�Growth through Trust Personal Responsability.
The modelCore Customer Business = IBM Business
IBM Value to customer
Overall Value of IBM
�Our Journey
2004
2010
�IBM Transformation Underlying Platforms Enabling Culture Change
Defined common values and performance mgmt align employees with
the decisions and strategic priorities of the management teams
Established and periodically refreshed a core set of
leadership competencies for all IBMers
Transformational Leadership
Values-based Culture
Collaborative Innovation
Global IBMer
Defined a new Leadership Framework that
emphasizes business results and the employees
experience
Engaged employees globally in Values Jam to refresh
our Values
Enabled collaborative innovation by making intranet
sophisticated social networking platform
Impact
Established a global innovation agenda that spans
multiple dimensions (e.g., products, services, people)
IBMs Values are integral in our performance, recognition and talent management systems
Tens of thousands of IBM employees actively participate in advancing our Values-based culture via
collaborative technologies
Business Week named IBM one of Twenty Best Companies for Leadership
IBM Research #1 on the US patent list for 17 years
�Prise de conscience et
comprhension
Communications aux
employs
Kickoff meetings
Communications des
Executives
Programmes des
Partenaires dAffaires
Communications aux
actionnaires
w3.ibm.com/ibm/values
��It Doesnt Happen Overnight It requires integrated,
incremental learning
Improving and sustaining Emotional Intelligence takes a concerted
effort over several months.
Individual
Development
In-house
Training
Minimal
results
Some
behavioral
results
Sustained
individual
performance
improvement
Integrated
Initiatives
with Coaching
and Measurement
Critical mass
for sustained
group
performance
improvement
Organizational
Interventions
Sustained
organizational
improvement
��Emotional Intelligence as a pre-requisite
Daniel Goleman
�Academic experts confirm the importance of Trust and personal
responsibility in all relationships, and the role of leaders in enabling it
The essential ingredient of collaborative effort is trust. High performance teams
are characterized by high mutual trust among members. Leaders succeed in
bringing about change because they are trusted by constituents to reflect their
values and aspirations. An organizational climate of trust enables employees to
surface their ideas and feelings, use each other as resources, and learn together.
Costigan
Key imperatives in building high-trust organizations and teams are:
- Achieving results Following though on business commitments
- Acting with integrity Behaving in a consistent manner
- Demonstrating concern Respecting the well-being of others Shaw
Trust is not something one changes with pronouncements or good intentions.
Seeking to improve trust directly, in fact, can result in higher levels of suspicion if
the process is not managed effectivelyTrust is the outcome of doing a number of
fundamental things right. Those who are successful at building trust usually
dont talk about it; they live it. Shaw
�Discussion: How can strengthening the
Dimensions of Trust help enable achievement
of our business objectives?
The reality is that Trust is a hardedged economic driverbecause
Trust always affects two
outcomes: speed and cost. The
economics of trust are simple: When
trust goes down, speed goes down
and cost goes up When trust goes
up, speed goes up and cost goes
down If we have a low-trust
organization, we can rest assured
we are paying a tax. While these
taxes may not show up on the
income statement as trust taxes,
theyre still there, disguised as other
problems such as redundancy,
bureaucracy, politics,
disengagement, turnover, churn and
fraud. Covey
Character Trust
Competence Trust
Positional Trust
Organizational Trust
�Actions you can take as an IBM leader to strengthen
Trust and personal responsibility in all relationships
Reflect on the leadership role you play in advancing the four dimensions of
trust and be a role model by ensuring your actions, decisions and behaviors
are consistent with this Value
Ensure your teams are clear on their roles, responsibilities and
accountabilities
In communications with your team, cite examples and acknowledge
situations and team members where this Value was demonstrated
Reach out to a leader in an organization where you and/or your team have a
strained relationship, to openly discuss issues and figure out a better way of
working together
Invest in the skills and capabilities of your team
Ensure that expectations with clients are set properly so they can be
delivered on
Engage your teams in a discussion to:
- Review the four dimensions of Trust and personal responsibility
- Identify inhibitors that get in the way of this Value
- Agree on actions you can take locally