Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lichen P
Uploaded by
Nurul AfiahOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lichen P
Uploaded by
Nurul AfiahCopyright:
Available Formats
www.hcvadvocate.
org
a series of fact sheets written by experts in the field of liver disease
HCSP FACT SHEET
EXTRAHEPATIC MANIFESTATION OF HCV
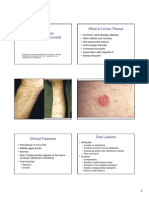
Lichen Planus
Written by: Alan Franciscus, Editor-in-Chief
Foreword
Lichen planus is a fairly common skin disorder that lasts for months to
years. Lichen planus affects about 1 to 2% of the U.S. population and
usually affects people between the ages of 30 and 70 years old and is
slightly more prevalent in women than in men. The exact cause of lichen
planus is unknown, but it seems to be triggered by stress, genetics,
allergic reactions to medicines, and by viral infections such as hepatitis
C. The onset may be gradual or quick. There have been studies that have
found a prevalence of HCV in people with lichen planus from 3.5% to 60%.
For this reason, it has been recommended that people with lichen planus
(especially with elevated liver enzymes) should be tested for HCV.
Lichen planus typically affects the skin, nails, vulva, penis, and mucous
membranes including the mouth. The symptoms appear as purple
or plaque- like shiny flat-topped itchy bumps. Lichen planus is not an
infectious disease so it can not be transmitted to others. There is no cure
for lichen planus, but treatment is effective in alleviating the symptoms
(itching of the skin lesions) and improves the appearance of the rashes. In
addition certain treatments can resolve some of the symptoms associated
with lichen planus and some symptoms will naturally resolve, However,
since lichen planus cannot be cured, the condition may return.
Mouth
Oral lichen planus is an inflammatory condition that affects the lining of the
mouth, usually on the inside of the cheeks, but it can also affect the gums,
tongue and inner cheeks of the mouth. Although rare it can also affect the
throat or esophagus.
Symptoms: The symptoms appear as white, interconnecting lines which
resemble and are named after the lichen plant, but lichen planus is NOT
related in any way to the plant. Severe cases may involve painful sores and
HCSP VERSION 5.2 March 2014
HCSP FACT SHEET
A publication of the
Hepatitis C Support Project
EXECUTIVE DIRECTOR,
EDITOR-IN-CHIEF,
HCSP PUBLICATIONS
Alan Franciscus
DESIGN
Leslie Hoex,
Blue Kangaroo Design
PRODUCTION
C.D. Mazoff, PhD
CONTACT
INFORMATION
Hepatitis C Support Project
PO Box 15144
Sacramento, CA 95813
alanfranciscus@hcvadvocate.org
The information in this fact sheet is
designed to help you understand and
manage HCV and is not intended as
medical advice. All persons with HCV
should consult a medical practitioner
for diagnosis and treatment of HCV.
This information is provided
by the Hepatitis C Support Project a
nonprofit organization for
HCV education, support and advocacy
Reprint permission is
granted and encouraged
with credit to the
Hepatitis C Support Project.
2014 Hepatitis C Support Project
HCSP FACT SHEET
EXTRAHEPATIC MANIFESTATION OF HCV
a series of fact sheets written by experts in the field of liver disease
HCV Lichen Planus
ulcers of the mouth. Very severe cases of lichen
planus of the mouth can slightly increase the risk of
oral cancer.
Lichen planus that affects the mouth is generally
found by a dentist or dental hygienist. The diagnosis
may be confirmed by a biopsy. Yeast infections are
commonly found in association with lichen planus or
can be triggered by topical steroids used to treat it.
Treatment of the yeast infection sometimes improves
the symptoms of oral lichen
planus.
Management: It is
important to control the
disease with medications,
good oral hygiene, and
regular physical exams
to monitor any changes.
Alcohol, tobacco, spicy
foods, peppermint, cinnamon,
citrus type foods and stressful situations trigger the
symptoms and should be avoided if possible.
Management: Strategies to reduce the symptoms
include the use of oatmeal baths (Aveeno), cool
compresses to the affected area of the skin, and antiitch topical creams.
Treatment: The most common treatments include
topical steroids and antihistamines used to relieve
the itching. Severe cases may require the use of
oral corticosteroids such as cortisone or prednisone.
Extreme cases may require photo chemotherapy light
treatment and prescription
drugs to help control and
alleviate the symptoms.
Hair
Lichen planus can affect the
scalp and hair.
Symptoms: Hair thinning,
redness of the scalp and
hair loss can occur. If left
untreated it can cause permanent scarring and
inflammation of hair follicles leading to permanent
hair loss (alopecia).
Treatment: Oral lichen planus treatment includes
the use of topical steroids as well as controlling the
triggers. Regular dental exams are recommended to
look for any tissue changes. Teeth cleaning and good
personal oral hygiene will improve the symptoms.
Treatment: To prevent permanent damage, oral
steroids, plus topical steroids as well as prescribed
oral medications should be taken as soon as possible
to prevent permanent damage.
Skin
Nails
Lichen planus most commonly affects the skin
including the genitals.
Lichen planus can also affect the nails leading to
damage of the nail root.
Symptoms: Bumps can appear on any skin surface,
but are most often found on the inside of the wrists
and ankles, the lower legs, back, and genital regions.
In severe cases, the bumps can be extremely itchy
and painful. When the lesions heal the skin may
become discolored. The skin discoloration usually
fades but may cause scarring especially when the
scalp is involved.
Symptoms: Nail splitting, grooving of the surface
of the nail and the nails can become thin and brittle
and possible nail loss. In severe cases the nail loss
can result in permanent nail root damage.
Treatment: severe cases are treated with
a combination of approaches that include
immuosuppressive drugs.
HCSP VERSION 5.2 March 2014
2014 Hepatitis C Support Project
HCSP FACT SHEET
EXTRAHEPATIC MANIFESTATION OF HCV
a series of fact sheets written by experts in the field of liver disease
HCV Lichen Planus
Check out the following publications:
An Overview of Extrahepatic Manifestations
www.hcvadvocate.org/hepatitis/factsheets_pdf/Extrahepatic.pdf
Essential Cryoglobulinemic Vasculitis
www.hcvadvocate.org/hepatitis/factsheets_pdf/vasculitis.pdf
Skin Conditions
www.hcvadvocate.org/hepatitis/factsheets_pdf/Skin_Conditions_Scatena.pdf
For more information
American Academy of
Dermatology
www.aad.org/skin-conditions/
dermatology-a-to-z/lichen-planus
Mayo Clinic
www.mayoclinic.com
Pubmed Health
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
pubmedhealth/PMH0001870/
Visit our websites to learn more about
viral hepatitis:
www.hcvadvocate.org www.hbvadvocate.org
www.hepatitistattoos.org
Glossary of Terms
ANTIHISTAMINES:
Medications that work by blocking the
effects of the bodys release of histamine
to counter an allergic reaction.
DENTAL HYGIENIST:
A licensed dental professional who
specializes in preventative oral health.
INFLAMMATION:
The bodys response to tissue injury
or infection, typically characterized by
redness, swelling, heat, and pain.
PHOTO CHEMOTHERAPY:
A treatment that consists of a
photosensitizing drug that is followed by
exposure to sunlight or ultraviolet radiation.
STEROID:
A family of substances that share a similar
chemical structure, including certain
hormones (e.g., testosterone) and various
drugs. Topical steroids are applied to the
skin.
YEAST INFECTION:
An overgrowth of certain fungi that can
result in infections of the esophagus,
mouth, digestive tract, skin, esophagus,
vagina and other parts of the body.
HCSP VERSION 5.2 March 2014
2014 Hepatitis C Support Project
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- What is Lichen Planus and Lichenoid MucositisDocument7 pagesWhat is Lichen Planus and Lichenoid MucositisNurul AfiahNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Anaphylactic Shock LectureDocument32 pagesAnaphylactic Shock LectureIchal 'petta' Malebbi100% (1)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- J 1365-4632 2007 03309 XDocument3 pagesJ 1365-4632 2007 03309 XNurul AfiahNo ratings yet
- Ro0409 HandbookDocument63 pagesRo0409 HandbookmeutiaayudilaNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Pedal Interdigital Condylomata Lata A Rare Sign.11Document3 pagesPedal Interdigital Condylomata Lata A Rare Sign.11Nurul AfiahNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- What is Lichen Planus and Lichenoid MucositisDocument7 pagesWhat is Lichen Planus and Lichenoid MucositisNurul AfiahNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Comparative Bacteriology of Acute and Chronic DacryocystitisDocument8 pagesComparative Bacteriology of Acute and Chronic DacryocystitisNurul AfiahNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Syphilis ColorDocument36 pagesSyphilis ColorNurul AfiahNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Tissue Healing Process - DADocument59 pagesTissue Healing Process - DANurul AfiahNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Stevens-Johnson Syndrome: Review of The Literature: Stitt CarolinaDocument4 pagesStevens-Johnson Syndrome: Review of The Literature: Stitt CarolinaNurul AfiahNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Tissue Regeneration Repair GuideDocument50 pagesTissue Regeneration Repair GuideNurul AfiahNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Changes From DSM IV TR To DSM 5Document19 pagesChanges From DSM IV TR To DSM 5David S. Kozin100% (1)
- Tissue Healing Process - DADocument59 pagesTissue Healing Process - DANurul AfiahNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- 1.a.infeksi VirusDocument45 pages1.a.infeksi VirusMutiah MuftihaturrahmahNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Chronic Inflammation - DADocument14 pagesChronic Inflammation - DANurul AfiahNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- 1.a.infeksi VirusDocument45 pages1.a.infeksi VirusMutiah MuftihaturrahmahNo ratings yet
- DSM-V PTSD Diagnostic Criteria309-5Document4 pagesDSM-V PTSD Diagnostic Criteria309-5Nurul AfiahNo ratings yet
- Allopathic Drug Manufacturers (Medex - Com.bd)Document10 pagesAllopathic Drug Manufacturers (Medex - Com.bd)মোঃ এমদাদুল হকNo ratings yet
- Report - Resource Based Conflicts and HR Violations in Protected AreasDocument83 pagesReport - Resource Based Conflicts and HR Violations in Protected AreasMagelah Peter GwayakaNo ratings yet
- Salmodil Syrup: What Is in This LeafletDocument2 pagesSalmodil Syrup: What Is in This LeafletNadia SalwaniNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Munjir Abdullah - Project On PBH101Document4 pagesMunjir Abdullah - Project On PBH101Munjir Abdullah 2112217030No ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- HBEL GuidelineDocument4 pagesHBEL GuidelineRenuka KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Simplified Version of Kisumu County CIDPDocument29 pagesSimplified Version of Kisumu County CIDPGolden AshNo ratings yet
- Measuring Hospital Information System Readiness for E-Health Implementation Using HOT Fit MethodDocument5 pagesMeasuring Hospital Information System Readiness for E-Health Implementation Using HOT Fit Methodrm donorojoNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Mere WaliDocument7 pagesMere WaliMaliCk TaimoorNo ratings yet
- NYCOSH Letter To DOB Re: OSHA Card Arrests 10262015Document2 pagesNYCOSH Letter To DOB Re: OSHA Card Arrests 10262015Monica NovoaNo ratings yet
- Medical Nursing I MCQs .Document7 pagesMedical Nursing I MCQs .naa Adel 01No ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- No Article Title Time of Publication Authors Journal Name Received Date Revised Date Accepted DateDocument4 pagesNo Article Title Time of Publication Authors Journal Name Received Date Revised Date Accepted DateAnin Kalma MartadinataNo ratings yet
- Barangay Nutrition Scholar ProgramDocument4 pagesBarangay Nutrition Scholar ProgramLenz BautistaNo ratings yet
- In vitro dissolution study of Metformin brandsDocument3 pagesIn vitro dissolution study of Metformin brandsrmahbub12No ratings yet
- EJMHR Ezunu Et Al V1Document10 pagesEJMHR Ezunu Et Al V1ngoziestherezunu74No ratings yet
- Small Spaces Need Smart Solutions - Kristoffer ThøgersenDocument12 pagesSmall Spaces Need Smart Solutions - Kristoffer ThøgersenTuan Huy Le100% (1)
- Chapter-14-Pathogenesis-of-Infectious-DiseasesDocument18 pagesChapter-14-Pathogenesis-of-Infectious-DiseasesedemcantosumjiNo ratings yet
- Peme Invitation 2021Document18 pagesPeme Invitation 2021hernie w. vergel de dios jrNo ratings yet
- I. Essay Questions: (2 X 20 40) : M.D. (Homeopathy) Degree Examination - October 2013Document2 pagesI. Essay Questions: (2 X 20 40) : M.D. (Homeopathy) Degree Examination - October 2013amareshscribdNo ratings yet
- UW Water Resources and Innovation Conference 2015Document61 pagesUW Water Resources and Innovation Conference 2015LungisaniNo ratings yet
- Breech BirthDocument10 pagesBreech Birthcirlce:twoworldsconnectedNo ratings yet
- The Psychosocial Impact of Extreme Gaming On Indian Pubg Gamers: The Case of Pubg (Playerunknown'S Battlegrounds)Document8 pagesThe Psychosocial Impact of Extreme Gaming On Indian Pubg Gamers: The Case of Pubg (Playerunknown'S Battlegrounds)qhdpjqofoexsdfbsygNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Đề Thi Thử Thptqg Môn Tiếng AnhDocument8 pagesĐề Thi Thử Thptqg Môn Tiếng AnhHổCápNo ratings yet
- Immunization Monitoring FormDocument4 pagesImmunization Monitoring FormDiler Singh100% (2)
- Case 034: ConstipationDocument7 pagesCase 034: ConstipationZauza100% (1)
- General Tonic Monograph and Pharmacology Shi Quan Da Bu WanDocument8 pagesGeneral Tonic Monograph and Pharmacology Shi Quan Da Bu WanrikiNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal On Fast FoodDocument8 pagesResearch Proposal On Fast FoodManish Ravat100% (5)
- Nursing Care Plan Cesarean DeliveryDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Cesarean DeliveryLei Ortega50% (4)
- Tutorial: MODULE: Musculoskeletal System IIDocument3 pagesTutorial: MODULE: Musculoskeletal System IIrishit20% (5)
- My Courses: Home UGRD-PHYED6101-2113T Week 2: Health-Related Fitness Components Prelim Quiz 1Document4 pagesMy Courses: Home UGRD-PHYED6101-2113T Week 2: Health-Related Fitness Components Prelim Quiz 1Miguel Angelo GarciaNo ratings yet
- Rare blistering skin condition linked to gluten intoleranceDocument2 pagesRare blistering skin condition linked to gluten intoleranceCharticha PatrisindryNo ratings yet
- Breaking the Habit of Being YourselfFrom EverandBreaking the Habit of Being YourselfRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1457)