0% found this document useful (0 votes)
694 views2 pagesWound Dressing Materials Overview
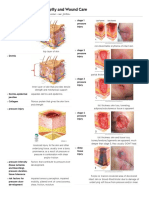
The document provides information on various types of wound dressings, including their uses, materials, and mechanisms of action. It describes dressings for ulcers, wounds, burns, and post-operative sites. Film dressings act as barriers over areas experiencing friction or forces to protect superficial wounds or sites producing minimal exudate. Island dressings are used over sutures to absorb any oozing in the first 24 hours post-op. Non-adherent dressings are coated to not stick to wounds and can be left in place for several days. Alginate dressings absorb exudate to form a gel covering, while hydrofiber dressings made of sodium carboxymethylcellulose absorb fluids and transform into a soft
Uploaded by
rufftuffcookieCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
694 views2 pagesWound Dressing Materials Overview
The document provides information on various types of wound dressings, including their uses, materials, and mechanisms of action. It describes dressings for ulcers, wounds, burns, and post-operative sites. Film dressings act as barriers over areas experiencing friction or forces to protect superficial wounds or sites producing minimal exudate. Island dressings are used over sutures to absorb any oozing in the first 24 hours post-op. Non-adherent dressings are coated to not stick to wounds and can be left in place for several days. Alginate dressings absorb exudate to form a gel covering, while hydrofiber dressings made of sodium carboxymethylcellulose absorb fluids and transform into a soft
Uploaded by
rufftuffcookieCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd