Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Questions: D N Y DD NN YY
Uploaded by
Everton CollingOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Questions: D N Y DD NN YY
Uploaded by
Everton CollingCopyright:
Available Formats
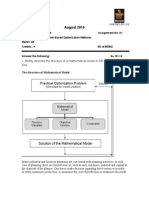
Process Optimization
Tutorial 0
Summer Semester 2012
Department of Chemical Engineering
Malte Behrens, Sergio Lucia
Chair of Process Dynamics and Operations
Prof. Sebastian Engell
1. Questions
a) List the three basic elements that define an optimization problem.
An objective function, f(x), that shall be maximized or minimized
Decision variables, x, that can be chosen
Equality constraints ,h(x) = 0, and/or inequality constraints g(x) 0
b) Assign these three elements to the corresponding aspects of the following example
problems:
1. Weight the different ways with cost factors wi (in /kg); define for each
way a variable xi (in kg). The objective function is than:
f (x) = w i x i
The constraints on the demands Da and Db lead to equality constraints:
Da= x1 + x3
Db= x2 + x4
The constraints on the stored amount SA and SB lead to inequality
constraints:
SA x 1 + x 2
SB x3 + x4
No negative values are allowed for x:
xi 0
w1
Storage A
Customer a
w2
w3
Storage B
w4
Customer b
This is a linear program (LP) since f(x), g(x) and h(x) are linear and xi is an
element of R ( x R )
2. The additional products can only be transported in packages of 5 kg. The
variables zi for these products are integers ( z i R ). The optimization
problem is a Mixed Integer Linear Programm (MILP).
1/3
Process Optimization
Tutorial 0
3. The objective function is the sum of the differences between the measured
values i, at different temperatures Ti and the calculated values m,i given
by the model output y(Ti, ,)= m,i. To avoid +/- cancelation in the sum,
the differences should be squared:
f (x) = f (, ) =
m,i (, ))
The constraints are:
g(x) 0
c) Which graphical representation could qualitatively belong to which problem? Label
the figures.
x2
Lines of iso
costs
Equality
constraints
Inequality
constraint
x1
Optimum
This figure could belong to problem 1
Lines of iso
costs
z2
Inequality
constraint
Equality
constraints
z1
Integer values z
This figure could belong to problem 2
2/3
Process Optimization
Non linear
inequality
constraint
Tutorial 0
Linear
inequality
constraint
x2
Optimum
Lines of iso
costs
x1
This figure could belong to problem 3
d) The definition of convexity can be found in the lecture slides. Figure 3 shows a non
convex problem, because a line between two feasible points which leaves the feasible
region can be drawn:
x2
x1
e) Which definition belongs to which problem?
minn c x
xR
s.t. Ax b = 0
minn c x + 0.5 x Bx
T
xR
s.t. g ( x) 0
xR
zZ m
s.t. h( x, z ) = 0
g ( x, z ) 0
Cx d 0
Problem 1
minn f ( x, z )
Problem 3
Problem 2
3/3
You might also like
- PO SS2012 Tutorial00 AdditionalExerciseDocument2 pagesPO SS2012 Tutorial00 AdditionalExerciseEverton CollingNo ratings yet
- Vanessa-Linear ProgrammingDocument13 pagesVanessa-Linear ProgrammingVanessa PallarNo ratings yet
- MATLAB - Manual (Engineering Mathematics-IV)Document25 pagesMATLAB - Manual (Engineering Mathematics-IV)Advaith ShettyNo ratings yet
- FHMM1314 MBI Topic 3 Student Version 202301Document58 pagesFHMM1314 MBI Topic 3 Student Version 202301Rhinndhi SakthyvelNo ratings yet
- MC0079Document38 pagesMC0079verma_rittika1987100% (1)
- LPDocument49 pagesLPAlefiahMNo ratings yet
- SampleFINAL KEY 205 TaylorDocument9 pagesSampleFINAL KEY 205 Tayloraskar_cbaNo ratings yet
- (Classes 1 & 2) 2 Var Regression-For UploadDocument99 pages(Classes 1 & 2) 2 Var Regression-For UploadNoor AfzalNo ratings yet
- (I-SEMESTER, 2014-2015) Lecturer: Harish Kumar Tutorial 1Document2 pages(I-SEMESTER, 2014-2015) Lecturer: Harish Kumar Tutorial 1Avijeet Singh JaswalNo ratings yet
- Algorithms Chapter 10 Exercises and SolutionsDocument43 pagesAlgorithms Chapter 10 Exercises and Solutionsc_noneNo ratings yet
- Linear ProgrammingDocument68 pagesLinear ProgrammingMy ANo ratings yet
- (II-SEMESTER, 2016-2017) Lecturer: Harish Kumar Tutorial 1Document2 pages(II-SEMESTER, 2016-2017) Lecturer: Harish Kumar Tutorial 1vamgaduNo ratings yet
- What Is Linear Programming?Document5 pagesWhat Is Linear Programming?RenukaSaxenaNo ratings yet
- sn1 BDocument8 pagessn1 BJose Aris SholehuddinNo ratings yet
- SampleFINAL KEY 205Document7 pagesSampleFINAL KEY 205askar_cbaNo ratings yet
- Linear Programming For OptimizationDocument9 pagesLinear Programming For Optimizationاحمد محمد ساهيNo ratings yet
- Operation Research Lecture NotesDocument119 pagesOperation Research Lecture NotesCerebro King100% (1)
- NP Tel ProblemsDocument18 pagesNP Tel ProblemsSreedevi KrishnakumarNo ratings yet
- Op Tim IzationDocument21 pagesOp Tim IzationJane-Josanin ElizanNo ratings yet
- 2 Homework Set No. 2: Problem 1Document3 pages2 Homework Set No. 2: Problem 1kelbmutsNo ratings yet
- SE ES Shamel 2022Document95 pagesSE ES Shamel 2022Sw1 AliswiNo ratings yet
- Power System OptimizationDocument49 pagesPower System OptimizationTesfahun GirmaNo ratings yet
- Linear Programming ModelDocument23 pagesLinear Programming ModelShayan AbagnaleNo ratings yet
- CH 19Document23 pagesCH 19radislamy100% (1)
- EKC 244 Lecture 03Document156 pagesEKC 244 Lecture 03Syamsul Rizal Abd ShukorNo ratings yet
- Part A: Texas A&M University MEEN 683 Multidisciplinary System Design Optimization (MSADO) Spring 2021 Assignment 2Document5 pagesPart A: Texas A&M University MEEN 683 Multidisciplinary System Design Optimization (MSADO) Spring 2021 Assignment 2BobaNo ratings yet
- Aima SVMDocument5 pagesAima SVMgdvngkrishnaNo ratings yet
- ACCT-4103 Mid PreparationDocument16 pagesACCT-4103 Mid PreparationShimul HossainNo ratings yet
- Math 5610 Fall 2018 Notes of 09/25-26/18 Linear ProgrammingDocument14 pagesMath 5610 Fall 2018 Notes of 09/25-26/18 Linear Programmingbb sparrowNo ratings yet
- An Improved Bilevel Evolutionary Algorithm Based On Quadratic ApproximationsDocument15 pagesAn Improved Bilevel Evolutionary Algorithm Based On Quadratic ApproximationsDilan SahinNo ratings yet
- 8 Chapter 3 Graphical MethodDocument11 pages8 Chapter 3 Graphical MethoddureNo ratings yet
- Business Maths Chapter 4Document23 pagesBusiness Maths Chapter 4鄭仲抗No ratings yet
- ch19 PDFDocument23 pagesch19 PDFDonita BinayNo ratings yet
- Lectures PDFDocument167 pagesLectures PDFPriyadi Widodo100% (1)
- Texas A&M MSADO Assignment 4 Optimization AlgorithmsDocument3 pagesTexas A&M MSADO Assignment 4 Optimization AlgorithmsBobaNo ratings yet
- OPTIMIZATION TECHNIQUES EXPLAINEDDocument32 pagesOPTIMIZATION TECHNIQUES EXPLAINEDdileep bangadNo ratings yet
- NaDocument67 pagesNaarulmuruguNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 ADocument7 pagesTutorial 5 AlolkaNo ratings yet
- IX Optimizaci N en La Planificaci N MineraDocument30 pagesIX Optimizaci N en La Planificaci N MineraFabian JadueNo ratings yet
- Constrained OptimizationDocument19 pagesConstrained OptimizationVikram SharmaNo ratings yet
- Model Solutions For Homework Assignment 1 CS798: 1 NoteDocument7 pagesModel Solutions For Homework Assignment 1 CS798: 1 NoteAbhishek ParmarNo ratings yet
- regression exercisesDocument2 pagesregression exercisestmonrealNo ratings yet
- Graphical LP: Solving linear programs graphicallyDocument11 pagesGraphical LP: Solving linear programs graphicallyIndah RiyadiNo ratings yet
- Quntiative Techniques 2 SonuDocument11 pagesQuntiative Techniques 2 SonuSonu KumarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Maths (M.SC.)Document6 pagesWorksheet Maths (M.SC.)shireenNo ratings yet
- Optimization Methods: Introduction to Objective Functions and ConstraintsDocument10 pagesOptimization Methods: Introduction to Objective Functions and Constraintspathi7777No ratings yet
- Optimization Model FormulationDocument10 pagesOptimization Model FormulationKhuram MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- Another Introduction SVMDocument4 pagesAnother Introduction SVMisma_shadyNo ratings yet
- Econ 200 Problem SetsDocument9 pagesEcon 200 Problem SetsSylvester BotelhoNo ratings yet
- Operation Management (MB0048)Document7 pagesOperation Management (MB0048)Sagar TankNo ratings yet
- MC0079 - Computer Based Optimization MethodsDocument10 pagesMC0079 - Computer Based Optimization MethodsHarvinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Linear Programme-Simplex and Graphical PDFDocument34 pagesLinear Programme-Simplex and Graphical PDFRayan Rodrigues100% (1)
- Computer Vision MCQ's For InterviewDocument12 pagesComputer Vision MCQ's For InterviewMallikarjun patilNo ratings yet
- Econometrics III - Home Assignment 1 Endogeneity Simulations, Specification and Data ProblemsDocument2 pagesEconometrics III - Home Assignment 1 Endogeneity Simulations, Specification and Data ProblemsSolomiya PikhNo ratings yet
- Integer Optimization and its Computation in Emergency ManagementFrom EverandInteger Optimization and its Computation in Emergency ManagementNo ratings yet
- 12 - Sampled Data ControlDocument16 pages12 - Sampled Data ControlEverton CollingNo ratings yet
- EMSO: A New Environment For Modelling, Simulation and OptimisationDocument6 pagesEMSO: A New Environment For Modelling, Simulation and OptimisationEverton CollingNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Simulation PDE ModelDocument25 pagesDynamic Simulation PDE ModelEverton CollingNo ratings yet
- 13 - Digital Controller DesignDocument22 pages13 - Digital Controller DesignEverton CollingNo ratings yet
- OPT MatlabDocument19 pagesOPT MatlabPraveen KrsNo ratings yet
- Igcc UnitsDocument40 pagesIgcc UnitsEverton CollingNo ratings yet
- Binary and Ternary Mixture of Polar CompoundsDocument6 pagesBinary and Ternary Mixture of Polar CompoundsEverton CollingNo ratings yet
- Exam ExercisesDocument8 pagesExam ExercisesEverton CollingNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Questions: D N Y DD NN YYDocument4 pages1.1 Questions: D N Y DD NN YYEverton CollingNo ratings yet
- 1.1. Questions: D N Y DD NN YYDocument2 pages1.1. Questions: D N Y DD NN YYEverton CollingNo ratings yet
- PO SS2011 05.1 DynamicOptimization p11Document11 pagesPO SS2011 05.1 DynamicOptimization p11Everton CollingNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Scheduling KP 110512bDocument16 pagesLecture 4 - Scheduling KP 110512bEverton CollingNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Flowsheeting in GPROMSDocument18 pagesLecture 3 - Flowsheeting in GPROMSEverton CollingNo ratings yet
- Lecture3-PO SS2011 04.1 MultidimensionalOptimizationUnconstrained p9Document9 pagesLecture3-PO SS2011 04.1 MultidimensionalOptimizationUnconstrained p9Everton CollingNo ratings yet
- Lecture5-PO SS2011 05 EvolutionaryAlgorithm p51Document50 pagesLecture5-PO SS2011 05 EvolutionaryAlgorithm p51Everton CollingNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Problems With Inequality Constraints: General FormDocument6 pages4.3 Problems With Inequality Constraints: General FormEverton CollingNo ratings yet
- OptimizationExample Finkler FinalDocument32 pagesOptimizationExample Finkler FinalEverton CollingNo ratings yet
- Lecture1-PO SS2011 01 Introduction p26Document26 pagesLecture1-PO SS2011 01 Introduction p26Everton CollingNo ratings yet
- Lecture4-PO SS2011 04.2 MultidimensionalOptimizationEqualityConstraint p5Document5 pagesLecture4-PO SS2011 04.2 MultidimensionalOptimizationEqualityConstraint p5Everton CollingNo ratings yet
- Lecture1-PO SS2011 02 ScalarOptimization p8Document8 pagesLecture1-PO SS2011 02 ScalarOptimization p8Everton CollingNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger Performance PDFDocument18 pagesHeat Exchanger Performance PDFcynaiduNo ratings yet
- Tratamento GLPDocument30 pagesTratamento GLPEverton CollingNo ratings yet
- Refinery BasicsDocument43 pagesRefinery BasicsSalim ChohanNo ratings yet