Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Parallelogram
Parallelogram
Uploaded by
Choki Wangmo100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
119 views2 pagesThis experiment aims to find the weight of an unknown body using the parallelogram law of vectors. Weights are attached to two hangers and balanced by a third weight suspended from the middle hanger. The positions of the weights are marked and lines are drawn to form a parallelogram, allowing the resultant force to be determined. This resultant force is equal and opposite to the unknown weight. The experiment is repeated with different known weights to calculate the unknown weight through the parallelogram law of vectors.
Original Description:
Original Title
Parallelogram.doc
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis experiment aims to find the weight of an unknown body using the parallelogram law of vectors. Weights are attached to two hangers and balanced by a third weight suspended from the middle hanger. The positions of the weights are marked and lines are drawn to form a parallelogram, allowing the resultant force to be determined. This resultant force is equal and opposite to the unknown weight. The experiment is repeated with different known weights to calculate the unknown weight through the parallelogram law of vectors.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
119 views2 pagesParallelogram
Parallelogram
Uploaded by
Choki WangmoThis experiment aims to find the weight of an unknown body using the parallelogram law of vectors. Weights are attached to two hangers and balanced by a third weight suspended from the middle hanger. The positions of the weights are marked and lines are drawn to form a parallelogram, allowing the resultant force to be determined. This resultant force is equal and opposite to the unknown weight. The experiment is repeated with different known weights to calculate the unknown weight through the parallelogram law of vectors.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
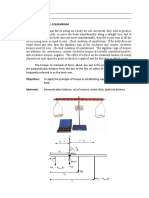
EXPERIMENT NO : 4
PARALLELOGRAM LAW OF VECTORS
Aim:
To find the weight of a given body using parallelogram law of vector addition.
Apparatus: GUDYHVDQGV apparatus, three hangers, weights, thin strong thread, white drawing paper sheet,
mirror strip, sharp pencil, half metre scale, set squares, protactor.
Theory:
If the body of unknown weight W suspended from middle hanger, balances weights P
and Q suspended from other two hangers, then P + Q + W = 0
Or
W = - (P + Q)
W = |R| (R resultant vector)
The unknown weight must have a magnitude equal to the resultant of the other two known
weights.
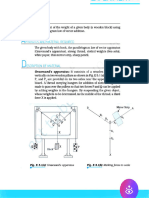
Procedure:
1. SHW XS WKH GUDYHVDQGV DSSDUDWXV ZLWK LWV ERDUG YHUWLFDO.
2. Fix the white drawing paper sheet on the board.
3. Put a thread over the rims of the pulleys and attach some weights P and Q at its ends.
4. Tie another thread at the middle of the thread passing over the pulleys and attach a known weight S in
such a way that the knot is nearly in the middle.
5. Mark the position of the junction as O.
6. Keeping mirror strip length wise under each thread, mark the position of the ends the image of thread
in the mirror, covering the image by the thread ( this removes parallax error ).The positions are P 1, P 2
for thread of weight P, Q 1and Q for
2 the thread of weight Q and S , S
1 for
2 thread of weight S.
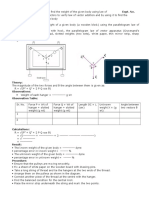
7. Remove paper from the board.
8. Draw lines through points P1and P to
2 represent P, through points Q and
1 Q to 2represent Q and
through points S1and S to
represent
S.
These
lines
must
meet
at
point
O.
2
9. Taking a suitable scale ( say, 1 cm = 10 gwt. ) ,represent P and Q .
10. Complete parallelogram OACB and join OC. It represents R.
11. Calculate the magnitude of the resultant vector
12. Calculate the weight of the body.
13. Repeat the experiment with unequal weights on both sides.
Result : The weight of the given body = ____________________ g wt.
Precautions:
1. The board should be stable and vertical
2. The pulleys should be frictionless.
3. The weights should not touch the board but hang freely.
4. Points should be marked with sharp pencil.
5. Junction O should be at the middle of the paper
Sources of error:
1. Pulleys may have friction
2. Weights may not be accurate
3. Points may not be marked correctly
Eby P Kurien
eby@selltheshell.com
Observation and calculation:
For equal weights :
Scale : 1cm = _____ g wt.
Force
Sr.
P
Q
No.
(g wt)
(g wt)
Sides
OA
(cm)
OB
(cm)
OC
(cm)
Resultant
Force R
(g wt)
Weight
W
(g wt)
OC
(cm)
Resultant
Force R
(g wt)
Weight
W
(g wt)
1.
2.
For unequal weights :
Scale : 1cm = _____ g wt.
Force
Sr.
P
Q
No.
(g wt)
(g wt)
1.
2.
Eby P Kurien
eby@selltheshell.com
Sides
OA
(cm)
OB
(cm)
You might also like
- Vectors in Two and Three DimentionsDocument48 pagesVectors in Two and Three Dimentionsuzlifatul jannahNo ratings yet
- Origami and MathsDocument2 pagesOrigami and MathsSowjanya GudimetlaNo ratings yet
- Physics Project Parallelogram Law of Vector AdditionDocument7 pagesPhysics Project Parallelogram Law of Vector Additionaakash sharma60% (5)
- Elementary Vectors: Pergamon International LibraryFrom EverandElementary Vectors: Pergamon International LibraryRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Expt Moment of Force EquilibriumDocument8 pagesExpt Moment of Force EquilibriumAbegail MacatangayNo ratings yet
- ENGR 245 Past FinalDocument13 pagesENGR 245 Past FinalIbrahim AbdullahNo ratings yet
- ApparatusDocument5 pagesApparatusDenzel MusaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1 Vectors PracticalsDocument4 pagesLab Report 1 Vectors PracticalsShaurya AlapatiNo ratings yet
- Phy ProjectDocument13 pagesPhy ProjectPari AgarwalNo ratings yet
- AimDocument2 pagesAimysNo ratings yet
- AMBRISHDocument13 pagesAMBRISHambrishNo ratings yet
- Dhairya Phy Investigatory PDFDocument7 pagesDhairya Phy Investigatory PDFDeepal ShahNo ratings yet
- Parallelogram of Vectors-1Document4 pagesParallelogram of Vectors-1arhammoeed2810No ratings yet
- Vidit Phy Investigatory PDFDocument7 pagesVidit Phy Investigatory PDFDeepal ShahNo ratings yet
- Practicals DAE APPLIED MECHANICSDocument3 pagesPracticals DAE APPLIED MECHANICSSyed Wajih Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument15 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectShine Roseline100% (1)
- APSIDocument19 pagesAPSIdishantbvaghela1818No ratings yet
- Investigatory ProjectDocument18 pagesInvestigatory ProjectDishant VaghelaNo ratings yet
- PracticalsDocument3 pagesPracticalsSyed Wajih Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- Parallelogram Law of VectorsDocument4 pagesParallelogram Law of Vectorspiyushdua01No ratings yet
- To Find The Weight of A Given Body Using Parallelogram Law of VectorsDocument5 pagesTo Find The Weight of A Given Body Using Parallelogram Law of VectorsBaskaran JNo ratings yet
- Concurrent Forces in Equilibrium, Lab ManualDocument4 pagesConcurrent Forces in Equilibrium, Lab Manualsharavan desaiNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Parallelogram PracticalDocument5 pagesClass 11 Parallelogram Practicalpratyushpradhan929No ratings yet
- Physics Practical Class 11Document9 pagesPhysics Practical Class 11Surbhi DwivediNo ratings yet
- Law of ParallelogramDocument2 pagesLaw of ParallelogramstutikapoorNo ratings yet
- Triangle of Forces Board Student Worksheet: TheoryDocument4 pagesTriangle of Forces Board Student Worksheet: TheoryUttam ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Parallelogram Law of VectorsDocument3 pagesParallelogram Law of VectorsKoushiik KumarNo ratings yet
- Maths Project 8Document4 pagesMaths Project 8Debjeet DeyNo ratings yet
- Sample Investigatory Project - Class-11Document12 pagesSample Investigatory Project - Class-11Dishant VaghelaNo ratings yet
- Physics Journal Edited-1Document13 pagesPhysics Journal Edited-1bye363607No ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument10 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectTarun Kumar100% (1)
- Physics Investigative Project1 (Final)Document10 pagesPhysics Investigative Project1 (Final)tbf06720No ratings yet
- Experiment - 1 AIM: To Determine The Reduced Level of An Object When Base Is Instruments Used: Theodolite, Tape, Leveling Staff, Ranging RodDocument12 pagesExperiment - 1 AIM: To Determine The Reduced Level of An Object When Base Is Instruments Used: Theodolite, Tape, Leveling Staff, Ranging RodSakthi Murugan100% (1)
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced LevelDocument4 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced LevelHubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- El 2 20 04 2024Document3 pagesEl 2 20 04 2024hattorininja1986No ratings yet
- Parallelogram Law of ForceDocument3 pagesParallelogram Law of Forcebluewingstechnologies25No ratings yet
- Lamis Theorem App.Document3 pagesLamis Theorem App.Service MMINo ratings yet
- On The Theory of Elastic Wires. by A. B.: - Quart. Journ. SF Math., Vol. Iv., P. 12Document23 pagesOn The Theory of Elastic Wires. by A. B.: - Quart. Journ. SF Math., Vol. Iv., P. 12FilippinNo ratings yet
- Smiths Prize ExamDocument8 pagesSmiths Prize ExamMalai DuraiNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelDocument4 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelHubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- Lab Activities Class 12 Term 2sDocument6 pagesLab Activities Class 12 Term 2sdasdaNo ratings yet
- Physics Practical ExperimentDocument18 pagesPhysics Practical ExperimentThanveer PutchakayalaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Lab ManualDocument16 pagesEngineering Mechanics Lab Manualprathameshbhat88100% (2)
- 0a.specimen M3Document4 pages0a.specimen M3Margarita SatrakiNo ratings yet
- Electricity & MagnetismDocument39 pagesElectricity & MagnetismAditya KumarNo ratings yet
- Practical 6 Use of Metre Scale As A Levermass of Metre Rule Using Principle of MomentsDocument2 pagesPractical 6 Use of Metre Scale As A Levermass of Metre Rule Using Principle of Momentsaiyo rammaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 (Moment of Force)Document2 pagesAssignment 1 (Moment of Force)Priyanka DubeyNo ratings yet
- Application, Its Magnitude, and Its DirectionDocument12 pagesApplication, Its Magnitude, and Its DirectionJohn Laurence Gonzaga AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Division of An Angle Into Equal Parts and Construction of Regular Polygons by Multi-Fold OrigamiDocument8 pagesDivision of An Angle Into Equal Parts and Construction of Regular Polygons by Multi-Fold OrigamiDũng Nguyễn TiếnNo ratings yet
- Activities Py 11Document22 pagesActivities Py 11Suraj SahooNo ratings yet
- Chapter 09Document9 pagesChapter 09tranhuukhoaNo ratings yet
- Wopho 13 Prob7-Final PDFDocument3 pagesWopho 13 Prob7-Final PDFPeter JonesNo ratings yet
- Conservation Laws PDFDocument4 pagesConservation Laws PDFApoorv SrivastavNo ratings yet
- 2008 Paper IDocument8 pages2008 Paper IhmphryNo ratings yet
- Lab Report On Measuring Gravitational AccelerationDocument14 pagesLab Report On Measuring Gravitational Accelerationkpasindu70% (10)
- Name - Class Sec - Roll Subject - Session: Saikat Das XI A 27 Physics 20 - 20Document6 pagesName - Class Sec - Roll Subject - Session: Saikat Das XI A 27 Physics 20 - 20SAIKAT DASNo ratings yet
- DownloadDocument8 pagesDownloadDivya HMNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigative Project (Final)Document11 pagesPhysics Investigative Project (Final)tbf06720No ratings yet