Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hemical Quilibrium: (A) Characterstics of Irreversible Reaction
Hemical Quilibrium: (A) Characterstics of Irreversible Reaction
Uploaded by
dheerajpradeepOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hemical Quilibrium: (A) Characterstics of Irreversible Reaction
Hemical Quilibrium: (A) Characterstics of Irreversible Reaction
Uploaded by
dheerajpradeepCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemical Equilibrium
1.
IRREVERSIBLE REACTION
Reactions which proceed in such a way that reactants are completely converted (i. e. 100%) in to products are
called irreversible reaction.
(A) Characterstics of Irreversible Reaction :
(i)
Reactions moves in one direction i.e. in forward direction only i.e. from left to right.
(ii)
Products do not react together to produce reactants again i.e. no backward reaction.
(iii) Always carried out in open vessel.
(iv) In such reactions arrow () is placed between reactant and product which shows direction of chemical
change. [Reactant Products]
(B) Examples of Irrevessible Reaction :
(i)
Thermal decomposition reaction :
Example :
(ii)
2
2KCl(s) + 3O2(g)
2 KClO3(s)
Heat
MnO
(decomposition of potassium chlorate)
Precipitation reaction :
Example :
AgNO3(aq) + NaCl(aq) AgCl(s) + NaNO3 (aq)
white ppt.
(iii) Neutralisation reaction : Reaction between strong acid and a strong base to give salt and
water is called neutralisation reactions.
Example :
H2SO4
Strong Acid
+ 2NaOH
Strong Base
Na2SO4 + 2H2O
Salt
Water
(iv) Redox and combustion reactions :
Example :
SnCl2 + 2FeCl3 SnCl4 + 2FeCl2
2Mg + O2 2MgO
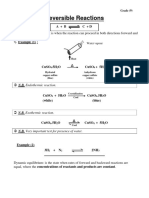
2. REVERSIBLE REACTION
The chemical reactions which take place in both directions i.e. in the forward direction as well as in backward
direction under similar conditions are called reversible reactions.
Forward direction
Left to right
Backward direction
Right to left
Or
Reactions which proceed in both the directions and does not reach to completion are called reversible reactions.
You might also like
- Chemical Equilibria RevisedDocument56 pagesChemical Equilibria RevisedKINOBE MARKNo ratings yet
- 1st GENERAL CHEMISTRY 2 2nd QuarterDocument2 pages1st GENERAL CHEMISTRY 2 2nd QuarterSid Eleazar R. Gaffud100% (2)
- SheetDocument36 pagesSheetmurugan NishanthNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument23 pagesChemical EquilibriumArihant BedagkarNo ratings yet
- 02 - Chemical Equilibrium (Theory) Module-3-1Document18 pages02 - Chemical Equilibrium (Theory) Module-3-1Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- T10 - Equilibria IDocument17 pagesT10 - Equilibria I5jonjacNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Classification of ReactionDocument3 pagesChemistry Classification of ReactionMohammad RussellNo ratings yet
- 1648-Crash Course-Chemical Equilibrium EnglishDocument15 pages1648-Crash Course-Chemical Equilibrium EnglishAlok GuptaNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical ReactionsDocument26 pagesTypes of Chemical ReactionsAshanna DouglasNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Dynamic Equilibrium 1718Document13 pages6.1 Dynamic Equilibrium 1718Ainaa NajwaaNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between A Physical Change and A Chemical Reaction?Document49 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between A Physical Change and A Chemical Reaction?nkznghidsnidvNo ratings yet
- Final Study Materials of Chapter Chemical Equilibrium 1Document23 pagesFinal Study Materials of Chapter Chemical Equilibrium 1bashantsahani060No ratings yet
- Equilibrium Meaning in ChemistryDocument16 pagesEquilibrium Meaning in Chemistryosmanmahdy19No ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document200 pagesChapter 6Hafizszul FeyzulNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument36 pagesChemical EquilibriumTasawar Hussain DayoNo ratings yet
- CH - 10 Reversible ReactionDocument7 pagesCH - 10 Reversible ReactionAhmedNo ratings yet
- Topic 6-L4-5-Chemical Equilibrium-KadyDocument58 pagesTopic 6-L4-5-Chemical Equilibrium-Kadyhaotongxu14No ratings yet
- 10th Chemistry English #KLS-1 PDFDocument17 pages10th Chemistry English #KLS-1 PDFSumair Khan Masood100% (1)
- Part X Chemical EquilibriumDocument14 pagesPart X Chemical Equilibriumyana LAUNo ratings yet
- Chemister Class 10 Chapter 1Document6 pagesChemister Class 10 Chapter 1Zohaib ZahidNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Dynamic EquilibriumDocument26 pages7.1 Dynamic EquilibriumScotrraaj GopalNo ratings yet
- JB CI 7.1 Chemical EquilibriumDocument9 pagesJB CI 7.1 Chemical EquilibriumOCRChemistrySaltersNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument43 pagesChemical EquilibriumSultan ParvezNo ratings yet
- Hand Written NotesDocument12 pagesHand Written NotesOne phase 23No ratings yet
- Focus Coaching Centre Cet - Neet-Crash Course: Subject: Chemistry Unit 7-Eqilibrium Resource Person: Priyanka RajaramDocument13 pagesFocus Coaching Centre Cet - Neet-Crash Course: Subject: Chemistry Unit 7-Eqilibrium Resource Person: Priyanka RajaramPriyankaNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument49 pagesChemical EquilibriumPhoemela SangumayNo ratings yet
- 10th Chemistry Ch9 Extra MCQsDocument6 pages10th Chemistry Ch9 Extra MCQszubairNo ratings yet
- IB CHEM SL Equilibrium Note CardsDocument21 pagesIB CHEM SL Equilibrium Note Cards陳定均No ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument23 pagesChemical EquilibriumFrankieNgNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry: Target: Jee Main and Advanced 2022Document64 pagesPhysical Chemistry: Target: Jee Main and Advanced 2022sarvesh goyalNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Chemical Reactions: Summary QuestionsDocument2 pagesUnit 9 Chemical Reactions: Summary QuestionsLei YinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 CHEMISTRYDocument4 pagesChapter 1 CHEMISTRYAmit Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- L13 PDFDocument26 pagesL13 PDFJoshua RomeaNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument44 pagesChemical Equilibriumtarsem jiNo ratings yet
- 7.1 (A-1.1) EquilibriaDocument4 pages7.1 (A-1.1) Equilibriagreedy AsunaNo ratings yet
- CH-8 O.KDocument26 pagesCH-8 O.KRana Hassan TariqNo ratings yet
- Form III NotesDocument96 pagesForm III NotesYahya MhandoNo ratings yet
- 10th Class Chemistry English Medium NotesDocument35 pages10th Class Chemistry English Medium Notesمحمّد نعیمNo ratings yet
- Physical, Chemical Equilibrium, Equilibrium Constant .Document7 pagesPhysical, Chemical Equilibrium, Equilibrium Constant .Rajesh Kumar ParidaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document4 pagesChapter 52B VILORIA, Kristine Joyce D.No ratings yet
- Reversible Reactions PDFDocument5 pagesReversible Reactions PDFYusra RasoolNo ratings yet
- HOMEWORK For Chapter 13: Chemical Equilibrium: 13.5 Le Châtelier's PrincipleDocument8 pagesHOMEWORK For Chapter 13: Chemical Equilibrium: 13.5 Le Châtelier's PrincipleALEJA MNo ratings yet
- Reversible ReactionsDocument6 pagesReversible ReactionsabdulrehmanNo ratings yet
- 6.2 Reversible Reactions & EquilibriumDocument18 pages6.2 Reversible Reactions & EquilibriumMuhammad Musa HaiderNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Chemical EquilibriumDocument35 pagesChapter 3 Chemical EquilibriumSuraj BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument4 pagesChemical EquilibriumEian InganNo ratings yet
- CH-1 ChemistryDocument4 pagesCH-1 ChemistryMISHKA KHANDELWALNo ratings yet
- Long-Test 2 - Gen Chem 2 - 4th QuarterDocument5 pagesLong-Test 2 - Gen Chem 2 - 4th QuarterCrizalyn CaboNo ratings yet
- Class X Chemistry For Term IDocument74 pagesClass X Chemistry For Term Iphanikumar5100% (1)
- Classification of Chemical Reactions and Substances PDFDocument43 pagesClassification of Chemical Reactions and Substances PDFDaniel YordanovNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Reversible Reactions MCQ Questions Copy Aoudi 2023Document9 pagesTopic 6 Reversible Reactions MCQ Questions Copy Aoudi 2023yamanfortnaimatNo ratings yet
- Reversible ReactionsDocument39 pagesReversible ReactionsUsmaanNo ratings yet
- Reversible Reactions and EquilibriumDocument8 pagesReversible Reactions and Equilibriummahika gaurNo ratings yet
- G-9 Unit 9Document10 pagesG-9 Unit 9Rokeya Alfi MahiNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument51 pagesChemical EquilibriumP NigadeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Test DanielDocument3 pagesChemistry Test Danieldaniel baloch3No ratings yet
- Phase Transfer Catalysis: Principles and TechniquesFrom EverandPhase Transfer Catalysis: Principles and TechniquesCharles LiottaRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Pericyclic Reactions: Organic Chemistry: A Series of Monographs, Vol. 35.2From EverandPericyclic Reactions: Organic Chemistry: A Series of Monographs, Vol. 35.2No ratings yet