Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Project On Full Wave Bridge Rectifier
Uploaded by
samOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Project On Full Wave Bridge Rectifier
Uploaded by
samCopyright:
Available Formats
Project on Full Wave Bridge Rectifier
Introduction:
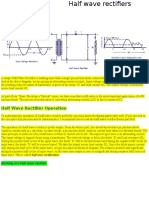
A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC), which
periodically reverses direction, to direct current (DC), which flows in only one
direction. The process is known as rectification. When a single rectifier unit is placed
in series with the load across an ac supply, it converts alternating voltage into unidirectional pulsating voltage, using one half cycles of the applied voltage, the other
half cycles being suppressed because it conducts only in one direction. This is called
half-wave rectification. The basic principle of rectifier is based on the fact that the
resistance of p-n junction diode becomes low when forward biased and become high
when reverse biased. In rectifier when ac current is passed through diode then it
obstructs half of wave i.e. it only allow half wave from their output. The rectifier
removes either negative or positive cycle depends upon connection of diode. This
means rectifier changes ac voltage to dc voltage with corresponding change in
current. Or we can say rectifier converts alternating voltage into unidirectional
pulsating voltage.
diode is an electronic device consisting of two elements known as cathode and
anode. Since in a diode electrons can flow in one direction only i.e. from cathode to
anode so the diode provides the unilateral conduction necessary for rectification. This
is true for diodes of all types-vacuum, gas-filled, crystal or semiconductor, metallic
(copper oxide and selenium types) diodes. Semiconductor diodes, because of their
inherent advantages are usually used as a rectifying device. However, for very high
voltages, vacuum diodes may be employed.
A p-n junction diode can be used as a rectifier in many ways i.e.
c.)
a.)
half-wave rectifier
b.)
full-wave rectifier
Full-wave bridge rectifier
You might also like
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Aircraft Electronics, Microprocessor & ApplicationDocument78 pagesAircraft Electronics, Microprocessor & ApplicationJigar Soni100% (1)
- BC-119 BC-121 Service ManualDocument19 pagesBC-119 BC-121 Service Manualjadi purwonoNo ratings yet
- Jasleen - Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument17 pagesJasleen - Physics Investigatory ProjectDaily Meme DOSENo ratings yet
- Service Bulletin Trucks: Special Tools, Group 2Document46 pagesService Bulletin Trucks: Special Tools, Group 2mattkidoNo ratings yet
- Rectifier - 1 Half-Wave Rectification - 2 Full-Wave Rectification - Peak Loss - The Full-Wave Bridge - RectifierDocument9 pagesRectifier - 1 Half-Wave Rectification - 2 Full-Wave Rectification - Peak Loss - The Full-Wave Bridge - Rectifierysn_usmaniNo ratings yet
- Half Wave Rectifier PDFDocument23 pagesHalf Wave Rectifier PDFArjun SinghNo ratings yet
- Project Report On RectifierDocument10 pagesProject Report On RectifierHArsh90% (10)
- GE Gas Turbine Generator Frame 6 Spare PartsDocument2 pagesGE Gas Turbine Generator Frame 6 Spare PartsAxelrose04100% (1)
- CRS3200Document9 pagesCRS3200Simona Romitan100% (1)
- University of Tun Hussien Onn MalaysiaDocument32 pagesUniversity of Tun Hussien Onn Malaysiaarcalamia100% (3)
- Half and Full Wave RectifierDocument12 pagesHalf and Full Wave Rectifierlucy lucy50% (2)
- Power Diodes and RectifiersDocument5 pagesPower Diodes and Rectifiersmansoor.ahmed100No ratings yet
- Half Wave and Full Wave RectifiersDocument8 pagesHalf Wave and Full Wave RectifiersRavindra SinghNo ratings yet
- Jenbacher Type 9 Flextra Engine 2 PDFDocument8 pagesJenbacher Type 9 Flextra Engine 2 PDFChristian Celeste100% (1)
- Metal DetectorDocument27 pagesMetal Detectorpgetson7128100% (5)
- 02 Water Supply Engineering-Lecture 2-Quantity of Water 2019-2020 PDFDocument14 pages02 Water Supply Engineering-Lecture 2-Quantity of Water 2019-2020 PDFSeashells Do ImpossibleNo ratings yet
- RectifierDocument4 pagesRectifierAngellicaNo ratings yet
- Reid Vapor PressureDocument5 pagesReid Vapor Pressurefumerojr5164100% (1)
- EPF FW Demand Calculation NoteDocument14 pagesEPF FW Demand Calculation NoteEmamokeNo ratings yet
- Bhagvender Singh XII-A Physics Project PDFDocument15 pagesBhagvender Singh XII-A Physics Project PDFvoid50% (4)
- Half Wave RectDocument5 pagesHalf Wave RectVinay JainNo ratings yet
- Rectifier: Under Art Integrated LearningDocument7 pagesRectifier: Under Art Integrated LearningAnshuman TiwariNo ratings yet
- Originalproectphysicsmsword Converted 191225064922Document12 pagesOriginalproectphysicsmsword Converted 191225064922GOKULNo ratings yet
- Analog ElectronicsDocument29 pagesAnalog ElectronicsGarrido González Roberto LeonardoNo ratings yet
- Power Diodes and RectifiersDocument4 pagesPower Diodes and RectifiersKeshav JhaNo ratings yet
- Physics Practical Class 12 Full Wave Rectifier With GraphicsDocument13 pagesPhysics Practical Class 12 Full Wave Rectifier With GraphicsSuraj Official100% (4)
- Rectifiers and It'S TypesDocument6 pagesRectifiers and It'S TypesPrem KumarNo ratings yet
- Physics Project: Xii-ADocument32 pagesPhysics Project: Xii-AneharNo ratings yet
- Department of Electronic Communication: "Rectifier"Document19 pagesDepartment of Electronic Communication: "Rectifier"Bhupendra PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- NAME - Saurav Gupta Roll No - 19ME3FP14: ApparatusDocument26 pagesNAME - Saurav Gupta Roll No - 19ME3FP14: Apparatussaurav guptaNo ratings yet
- A Rectifier Is An Electrical Device That Converts Alternating CurrentDocument7 pagesA Rectifier Is An Electrical Device That Converts Alternating CurrentUmiKalsomNo ratings yet
- RectifiersDocument10 pagesRectifiersjipaglinawanNo ratings yet
- Rectifier ReportDocument9 pagesRectifier ReportMogambo DonNo ratings yet
- Assignment MEDocument3 pagesAssignment MESaad AliKhanNo ratings yet
- 5 (A) - Half Wave Rectifier - Docx - 20231127 - 143415 - 0000Document4 pages5 (A) - Half Wave Rectifier - Docx - 20231127 - 143415 - 0000smrtyfaizan786No ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument12 pagesUntitled Documentaadietya11129No ratings yet
- 5 - Power Diodes and RectifiersDocument5 pages5 - Power Diodes and RectifiersAdel RaweaNo ratings yet
- Practical 12thDocument7 pagesPractical 12thkumarnareshNo ratings yet
- Rectifier: PrincipleDocument3 pagesRectifier: PrincipleRishi ThakurNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument15 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectAjeetNo ratings yet
- RectifiersDocument13 pagesRectifiersInfidragon GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Half Wave RectifiersDocument3 pagesHalf Wave RectifiersSaurabhYadav100% (1)
- DiodeDocument31 pagesDiodenassoro waziriNo ratings yet
- Physics Class 12 Full Wave Rectifier Project FileDocument16 pagesPhysics Class 12 Full Wave Rectifier Project FileNavneet Nigam0% (2)
- Rectifier 1rectifier Investigatory ProjectDocument4 pagesRectifier 1rectifier Investigatory ProjectcapvermaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 03 - Diode Applications (Rectification)Document16 pagesLecture 03 - Diode Applications (Rectification)Joseph NgowiNo ratings yet
- Project Report On RectifierDocument3 pagesProject Report On RectifierAnshulNo ratings yet
- LEARNING GUIDE 02 AC DC RectifierDocument27 pagesLEARNING GUIDE 02 AC DC Rectifiermeseret sisayNo ratings yet
- Abstract:: RectificationDocument11 pagesAbstract:: RectificationFatima Azam ChatthaNo ratings yet
- Half Wave RectifierDocument3 pagesHalf Wave Rectifiertkarpagam6No ratings yet
- EEE Theory PDFDocument3 pagesEEE Theory PDFMd Sabbir Ahmed EkhonNo ratings yet
- Topic: Diodes: By: Uzma AnsariDocument18 pagesTopic: Diodes: By: Uzma AnsariuzmaNo ratings yet
- Physics Project On Full Wave RectifierDocument6 pagesPhysics Project On Full Wave RectifierRijil R Sugathan100% (2)
- Full Wave Rectifier Circuit With Working TheoryDocument7 pagesFull Wave Rectifier Circuit With Working Theorysuraj vishnoiNo ratings yet
- EC-II-NOL Regulation 2008Document131 pagesEC-II-NOL Regulation 2008vishnu.kvlvNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument14 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentSURAJ GAUTAMNo ratings yet
- What Is Analog ElectronicsDocument15 pagesWhat Is Analog ElectronicsAtharv BhedaNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument3 pagesUntitled DocumentJohn Andrei AvilaNo ratings yet
- 03 Rectifiers PRPDocument21 pages03 Rectifiers PRPVarsha PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Exer 8 RephrasedDocument3 pagesExer 8 RephrasedNeil JanasNo ratings yet
- Full Wave RectifierDocument25 pagesFull Wave RectifierSandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- RectifierDocument26 pagesRectifierhemnphysic91No ratings yet
- Full Wave Bridge RectifierDocument4 pagesFull Wave Bridge RectifierSachit KumarNo ratings yet
- New Rich Text DocumentDocument10 pagesNew Rich Text DocumentMALIK HASEEB UR REHMAN AWANNo ratings yet
- INDEXDocument12 pagesINDEXMAYIL SHANKARI PNo ratings yet
- RECTIFIERSDocument3 pagesRECTIFIERSmehakNo ratings yet
- Activity 3Document11 pagesActivity 3Ultima_SarinNo ratings yet
- Radiography Procedure RNDTDocument27 pagesRadiography Procedure RNDTrashmibetuNo ratings yet
- EJ200 Turbofan Engine: The Innovative PowerDocument2 pagesEJ200 Turbofan Engine: The Innovative PowerufcNo ratings yet
- S8VM Power Supplies Will Be Discontinued February 2019: Overview SummaryDocument27 pagesS8VM Power Supplies Will Be Discontinued February 2019: Overview Summaryrizky nurmansyahNo ratings yet
- S11.0 Seismic Restraint SpacingDocument12 pagesS11.0 Seismic Restraint SpacingAndrew WaddingtonNo ratings yet
- Tank Heating Log FormDocument7 pagesTank Heating Log FormGetting 1Million Subs Without Videos CHALLENGENo ratings yet
- Investigation and Analysis of Metallurgical and Mechanical Properties of AA1100 Using FSW by P.vijayasarathi, D.christopher SelvamDocument10 pagesInvestigation and Analysis of Metallurgical and Mechanical Properties of AA1100 Using FSW by P.vijayasarathi, D.christopher Selvamijr_journalNo ratings yet
- Analogue Addressable Repeater - MFAREP Fire Detection SystemDocument20 pagesAnalogue Addressable Repeater - MFAREP Fire Detection SystemShadi AbdelsalamNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report Electronic SensorsDocument19 pagesSeminar Report Electronic SensorsRohan dwivedi100% (1)
- Antenna Theory TutorialDocument20 pagesAntenna Theory TutorialAbhicruiserNo ratings yet
- Adafruit Arduino Lesson 14 Servo Motors - En.idDocument14 pagesAdafruit Arduino Lesson 14 Servo Motors - En.idHabibul ChairNo ratings yet
- Furnace Oil ProjectDocument16 pagesFurnace Oil ProjectRohit PNo ratings yet
- Co2 Components-ServvoDocument1 pageCo2 Components-ServvorizaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 15 It's A Soap Opera!: OutcomesDocument8 pagesExperiment 15 It's A Soap Opera!: OutcomesKrystel Monica ManaloNo ratings yet
- CONDENSED AND DRIED MILK NotesDocument44 pagesCONDENSED AND DRIED MILK NotesALPS AMBAYATHODENo ratings yet
- Chapter8 PDFDocument54 pagesChapter8 PDFJoseph Constantino T. Fagel JrNo ratings yet
- Ebook 4 PrintingDocument91 pagesEbook 4 PrintingManuel AsitimbayNo ratings yet
- LCM FormatDocument2 pagesLCM FormatSIMANTA KUMAR SAHUNo ratings yet
- Article Review CSR 7Document2 pagesArticle Review CSR 7Gwendoline BoucherNo ratings yet
- FM Course OutlineDocument4 pagesFM Course Outlinev rajuNo ratings yet
- Enron Company PDFDocument18 pagesEnron Company PDFJebin JamesNo ratings yet
- ICT Jalna Campus Booklet PDFDocument36 pagesICT Jalna Campus Booklet PDFUmesh khadkeNo ratings yet