Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Prob DB
Uploaded by
SandyArevaloOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Prob DB
Uploaded by
SandyArevaloCopyright:
Available Formats
176
BLOCK DIAGRAM ALGEBRA AND TRANSFER FUNCTIONS OF SYSTEMS
[CHAP. 7
Supplementary Problems
7.29.
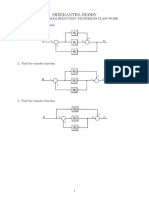
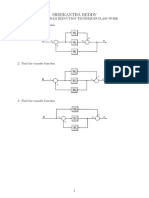
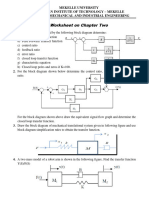
Determine C / R for each system in Fig. 7-55.
Fig. 7-55
7.30.
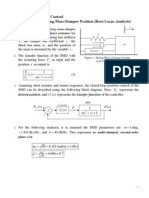
Consider the blood pressure regulator described in Problem 2.14. Assume the vasomotor center (VMC) can
be described by a linear transfer function Gl,(s), and the baroreceptors by the transfer function kls + k ,
(see Problem 6.33). Transform the block diagram into its simplest, unity feedback form.
7.31.
Reduce Fig. 7-56 to canonical form.
Fig. 7-56
CHAP. 71
BLOCK DIAGRAM ALGEBRA AND TRANSFER FUNCTIONS OF SYSTEMS
177
7.32. Determine C for the system represented by Fig. 7-57.
Fig. 7-57
7.33. Give an example of two feedback systems in canonical form having identical control ratios C / R but
different G and H components.
7.34. Determine C / R , for the system given in Fig. 7-58.
Fig. 7-58
7.35. Determine the complete output C, with both inputs R, and R , acting simultaneously, for the system given
in the preceding problem.
7.36. Determine C / R for the system represented by Fig. 7-59.
Fig. 7-59
737. Determine the characteristic equation for each of the systems of Problems ( a ) 7.32, (6) 7.35, ( c ) 7.36.
738. What block diagram transformation rules in the table of Section 7.5 permit the inclusion of a sampler?
178
BLOCK DIAGRAM ALGEBRA AND TRANSFER FUNCTIONS OF SYSTEMS
[CHAP. 7
Answers to Supplementary Problems
7.29.
See Problem 8.15.
7.30.
7.31.
7.38.
The results of Problem 7.21 indicate that any transformation that involves any product of two or more
transforms is not valid if a sampler is included. But all those that simply involve the sum or difference
of signals are valid, that is, Transformations 6, 11, and 12. Each represents a simple rearrangement of
signals as a linear-sum, and addition is a commutative operation, even for sampled signals, that is
Z = X * Y= Y*X.
You might also like
- Control of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesFrom EverandControl of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesNo ratings yet
- Home Work PDFDocument3 pagesHome Work PDFsreekanthaNo ratings yet
- Home WorkDocument3 pagesHome Worksreekantha0% (1)
- Block diagram algebra and transfer functionsDocument7 pagesBlock diagram algebra and transfer functionsSheroz Rajab Ali SoomroNo ratings yet
- Block diagram algebra and transfer functionsDocument7 pagesBlock diagram algebra and transfer functionsDipesh Kumar MishraNo ratings yet
- CHAP. 71 Block Diagram Algebra and Transfer Functions of SystemsDocument6 pagesCHAP. 71 Block Diagram Algebra and Transfer Functions of SystemsIan UdhiliNo ratings yet
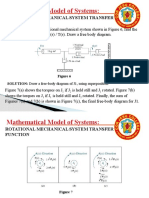
- Mathematical Model of Systems:: Rotational Mechanical System Transfer FunctionDocument4 pagesMathematical Model of Systems:: Rotational Mechanical System Transfer Functionchardo santosNo ratings yet
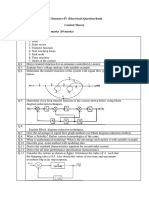
- Control System Unit 1 Question BankDocument2 pagesControl System Unit 1 Question BankAnish John Paul MNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor-Based Robust DC Servo Motor ControlDocument7 pagesMicroprocessor-Based Robust DC Servo Motor ControlVikas PatelNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsDocument4 pagesGujarat Technological University: Instructionsvatsalshah24No ratings yet
- Feedback and Control System Module - 19Document28 pagesFeedback and Control System Module - 19AkiHiro San CarcedoNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics Question BankDocument3 pagesMechatronics Question BankSainand Jadhav100% (1)
- Multiobjective Control Systems Design by Genetic AlgorithmsDocument6 pagesMultiobjective Control Systems Design by Genetic AlgorithmsnainaNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityHerat HirparaNo ratings yet
- Control TheoryDocument4 pagesControl TheorySolid Work and Mechanical software TutorialNo ratings yet
- Fuzzy Control Distillation ColumnDocument5 pagesFuzzy Control Distillation ColumnhardmanpersonNo ratings yet
- Fifth Semester B.E. Degree Examination, July 2007 Me/Ip/Im/Ma/AuDocument2 pagesFifth Semester B.E. Degree Examination, July 2007 Me/Ip/Im/Ma/AuPrashanth M PrashuNo ratings yet
- CHEM ENG 3P4 ASSIGNMENTDocument4 pagesCHEM ENG 3P4 ASSIGNMENTVictoria HillierNo ratings yet
- Modelagem Diagrama de BlocsoDocument12 pagesModelagem Diagrama de BlocsoAlessandro BraatzNo ratings yet
- CS Mod1 QBDocument10 pagesCS Mod1 QBthenithyanagrajNo ratings yet
- Velammal Engineering College, Chennai-600066 Electronics and Communication Engineering Ut I Question Bank Unit I Part ADocument3 pagesVelammal Engineering College, Chennai-600066 Electronics and Communication Engineering Ut I Question Bank Unit I Part Asubramanian subramanianNo ratings yet
- Robust Controller Design For Uncertain Systems: Shreesha.c@manipal - EduDocument4 pagesRobust Controller Design For Uncertain Systems: Shreesha.c@manipal - EduInnovative Research PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Understanding Loop Gain Analysis of DC-DC Switching Converters Using Signal Flow GraphsDocument12 pagesUnderstanding Loop Gain Analysis of DC-DC Switching Converters Using Signal Flow Graphs王睿琛No ratings yet
- Block Diagrams - Lecture NotesDocument8 pagesBlock Diagrams - Lecture NotesMichael HsiaoNo ratings yet
- Print It 2Document5 pagesPrint It 2shihab4806No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Reduction of Multiple SubsystemsDocument37 pagesChapter 5 Reduction of Multiple SubsystemsEugine BalomagaNo ratings yet
- CS QuestionsDocument2 pagesCS QuestionsKarthik MambersNo ratings yet
- Decoupling Control of D and Q CurrentDocument11 pagesDecoupling Control of D and Q CurrentnandarathanaNo ratings yet
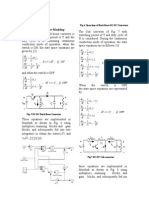
- C. Buck-Boost Converter Modeling D. Cuk Converter Modeling: Di V DT L TDT Qon DV V DT C RDocument6 pagesC. Buck-Boost Converter Modeling D. Cuk Converter Modeling: Di V DT L TDT Qon DV V DT C RTeja VaitlaNo ratings yet
- WS02Document6 pagesWS02fisahabirhane16No ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 Modelling QuestionDocument3 pagesTutorial 1 Modelling QuestionCHEE HOE PONNo ratings yet
- EE582 Control Techniques Laboratory Report Jeswin Mathew 200901475Document11 pagesEE582 Control Techniques Laboratory Report Jeswin Mathew 200901475Jeswin MathewNo ratings yet
- Pid 2Document5 pagesPid 2Sanyaolu AdebodunNo ratings yet
- Non-Linear Controller Applied To Boost DC-DC ConvertersDocument8 pagesNon-Linear Controller Applied To Boost DC-DC ConvertersC_hakan_CNo ratings yet
- Session F4H: Block Diagram in Undergraduate Engineering Courses Other Than Control SystemsDocument5 pagesSession F4H: Block Diagram in Undergraduate Engineering Courses Other Than Control SystemsmailmadoNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Compensator DESIGN Via Root Locus PDFDocument34 pagesControl Systems Compensator DESIGN Via Root Locus PDFm_umair72001100% (2)
- Right Half Plane ZeroDocument2 pagesRight Half Plane ZeroMárcia R G LimaNo ratings yet
- Bode Diagram Transfer Function Controller DesignDocument1 pageBode Diagram Transfer Function Controller DesignrajaraghuramvarmaNo ratings yet
- Reg No:, TO: 16BEC0373 18BEC0007 18BEC2033, 18BML0063, 19BEC0034 TO 19BEC0484Document5 pagesReg No:, TO: 16BEC0373 18BEC0007 18BEC2033, 18BML0063, 19BEC0034 TO 19BEC0484pari mahajanNo ratings yet
- (Ebook) Multivariable Control, An Introduction PDFDocument14 pages(Ebook) Multivariable Control, An Introduction PDFCaterine Feria RamirezNo ratings yet
- Reduction of Multiple SubsystemsDocument52 pagesReduction of Multiple SubsystemsabdulNo ratings yet
- A New Mathematical Model and Control of A Three-Phase AC-DC Voltage Source ConverterDocument8 pagesA New Mathematical Model and Control of A Three-Phase AC-DC Voltage Source ConverterVenktesh MishraNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Control For DC Motor Using MatlabDocument15 pagesModeling and Control For DC Motor Using MatlabelneelNo ratings yet
- Robust Iterative PID Controller Based On Linear Matrix Inequality For A Sample Power SystemDocument9 pagesRobust Iterative PID Controller Based On Linear Matrix Inequality For A Sample Power Systemsjo05No ratings yet
- Control SystemsDocument32 pagesControl Systemsselvi0412100% (1)
- USE MATLAB/SIMULINK/SCILAB/LABVIEW (Use Any One Tool)Document7 pagesUSE MATLAB/SIMULINK/SCILAB/LABVIEW (Use Any One Tool)SanthoshNo ratings yet
- Optimal Controller Design of Three-Phase Controlled Rectifier Using Artificial Intelligence TechniquesDocument9 pagesOptimal Controller Design of Three-Phase Controlled Rectifier Using Artificial Intelligence Techniquesankit_elect27No ratings yet
- MSD2Document47 pagesMSD2moeNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Study of A Shunt Reactor Sub Synchronous Resonance StabilizerDocument14 pagesTheoretical Study of A Shunt Reactor Sub Synchronous Resonance StabilizerFranck Mofati KasangalaNo ratings yet
- Pulse Transfer Function and Block DiagramsDocument41 pagesPulse Transfer Function and Block DiagramsArif HassanNo ratings yet
- Power System Dynamic Performance With STATCOM Controller: Mfareed@kfupm - Edu.sa Ahrahim@kfupm - Edu.saDocument5 pagesPower System Dynamic Performance With STATCOM Controller: Mfareed@kfupm - Edu.sa Ahrahim@kfupm - Edu.sapragatinareshNo ratings yet
- Cse PaperDocument5 pagesCse PaperSachin AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Control System All QuestionsDocument3 pagesControl System All QuestionsRehana Karim TomaNo ratings yet
- MDP410-2020 - Problem Set 01 - Applications PDFDocument2 pagesMDP410-2020 - Problem Set 01 - Applications PDFIman MagdiNo ratings yet
- Ec 502Document1 pageEc 502Shiraz HusainNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityTanvir KaziNo ratings yet
- Study, Analysis and Evaluation of Block Diagram Reduction Name: University of Polytechnic/college ofDocument10 pagesStudy, Analysis and Evaluation of Block Diagram Reduction Name: University of Polytechnic/college ofTana AzeezNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Analysis of The Interaction Between Different FACTS and HVDCDocument5 pagesA Comparative Analysis of The Interaction Between Different FACTS and HVDCfpttmmNo ratings yet
- Transfer FunctionDocument11 pagesTransfer FunctionNagmani KumarNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Roof LoadingDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Roof LoadinghamieraNo ratings yet
- Updating The QR Factorization and The Least Squares Problem (2008)Document73 pagesUpdating The QR Factorization and The Least Squares Problem (2008)Eran MaromNo ratings yet
- Special Issue - 2015 International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT) Position and Speed Control of BLDC MotorDocument3 pagesSpecial Issue - 2015 International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT) Position and Speed Control of BLDC MotorDONE AND DUSTEDNo ratings yet
- Ads 512 Chap 1Document30 pagesAds 512 Chap 1Airin SamuelNo ratings yet
- Catalog Hartland RelayDocument16 pagesCatalog Hartland RelayEslam SalamonyNo ratings yet
- LDS - Materi Online Training Communication, Negotiation ODP (Batch 236) 2021 - 02!10!11 - PESERTADocument117 pagesLDS - Materi Online Training Communication, Negotiation ODP (Batch 236) 2021 - 02!10!11 - PESERTAArie HapsoroNo ratings yet
- Functions and Graphs Technology (Casio)Document2 pagesFunctions and Graphs Technology (Casio)Ava PidgeonNo ratings yet
- Protect Your Home From Thermal ExpansionDocument2 pagesProtect Your Home From Thermal ExpansionDenis HidayatullahNo ratings yet
- Ecommerce-Act 040924Document5 pagesEcommerce-Act 040924Michael BongalontaNo ratings yet
- Gigatron TTL Microcomputer HistoryDocument103 pagesGigatron TTL Microcomputer HistoryOlegOxidNo ratings yet
- TM-1819 AVEVA Everything3D™ (2.1) EI Equipment Modelling Rev 3.0Document80 pagesTM-1819 AVEVA Everything3D™ (2.1) EI Equipment Modelling Rev 3.0kike100% (1)
- TE-6300 Series Temperature Sensors: DescriptionDocument4 pagesTE-6300 Series Temperature Sensors: DescriptionÖzgürNo ratings yet
- 06-08 Civic Grid Charger 1 - 1Document4 pages06-08 Civic Grid Charger 1 - 1MilosNo ratings yet
- Trans 1Document4 pagesTrans 1Saied AbushadiNo ratings yet
- 15 ++103-+115+QH+8 (1) +2022+An++AditiaDocument13 pages15 ++103-+115+QH+8 (1) +2022+An++AditiaSuzan HakyNo ratings yet
- Dell Case Study - G02Document3 pagesDell Case Study - G02Miniteca Mega Rumba0% (1)
- MATHS QUEST Preliminary Mathematics General (4th Edition)Document504 pagesMATHS QUEST Preliminary Mathematics General (4th Edition)JIESHUN (JASON) WANG82% (11)
- Unisonic Technologies Co., LTD: NPN Epitaxial Silicon TransistorDocument5 pagesUnisonic Technologies Co., LTD: NPN Epitaxial Silicon TransistorDuvan AriasNo ratings yet
- Diroots: Created: Gasna GasnaDocument14 pagesDiroots: Created: Gasna GasnaAravinth KumarNo ratings yet
- Amg Remove - Install Camshaft AdjustersDocument5 pagesAmg Remove - Install Camshaft AdjustersRoland HendriksNo ratings yet
- Training Report ON Study of Marketing Strategies at Hyndai Bachelor of Business AdministrationDocument71 pagesTraining Report ON Study of Marketing Strategies at Hyndai Bachelor of Business AdministrationBhola ThNo ratings yet
- USM-Biometric Administration Portal-ENGDocument76 pagesUSM-Biometric Administration Portal-ENGCosmin AnghelNo ratings yet
- Lms Manual GuideDocument17 pagesLms Manual GuidecherrrryNo ratings yet
- How To Use Bigo TV For Live Streaming On Your Mobile DeviceDocument20 pagesHow To Use Bigo TV For Live Streaming On Your Mobile DeviceLive Hosting100% (1)
- CFO - IIM CourseDocument13 pagesCFO - IIM CourseRajesh RamakrishnaNo ratings yet
- Similar Car ScanDocument10 pagesSimilar Car ScanHarsh SladeNo ratings yet
- HHM Unit-1 PDFDocument66 pagesHHM Unit-1 PDFAchyutha AnilNo ratings yet
- Instructions: Hmems80 2020 Semester 1 Assignment 01 (Unique Number: 873964) Due Date: 9 March 2020Document8 pagesInstructions: Hmems80 2020 Semester 1 Assignment 01 (Unique Number: 873964) Due Date: 9 March 2020Matshele SerageNo ratings yet
- Color Space Conversion For The Laser Film Recorder Using 3-D LUTDocument8 pagesColor Space Conversion For The Laser Film Recorder Using 3-D LUT程杰No ratings yet
- Brochure2-Mobil Greases PDFDocument2 pagesBrochure2-Mobil Greases PDFPedro PerezNo ratings yet