Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Configuring SSH
Configuring SSH
Uploaded by
dkhanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Configuring SSH
Configuring SSH
Uploaded by
dkhanCopyright:
Available Formats
Configuring SSH
Objectives
View the default internetwork configuration.
Enable SSH.
Interconnect using SSH.
Background/Scenario
Traditionally, remote administrative access on routers was configured using
Telnet on TCP port 23. However, Telnet was developed in the days when security
was not an issue. For this reason, all Telnet traffic is forwarded in plain text. SSH
has replaced Telnet as the best practice for providing remote router
administration with connections that support strong privacy and session integrity.
SSH uses port TCP 22. It provides functionality that is similar to that of an
outbound Telnet connection, except that the connection is encrypted. With
authentication and encryption, SSH allows for secure communications over an
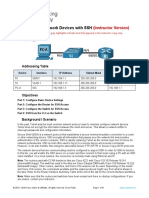
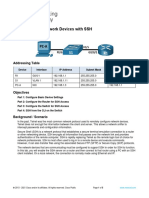
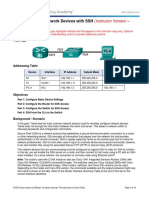
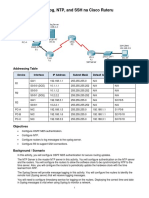
insecure network. In this configuration, four routers are interconnected in a huband-spoke Frame Relay configuration. Router R1 is the hub, and routers R2, R3,
and R4 are the spokes. Dynamic routing has been configured using multiarea
OSPF.
Task 1: View the Default Configuration.
Step 1. Verify the Frame Relay configuration on the routers.
a. On all four routers, enter user EXEC mode with the password cisco.
b. Enter privileged EXEC mode with the password cisco.
c. From privileged EXEC mode on all four routers, issue the show frame-relay
map command to verify Frame Relay connectivity.
Step 2. Verify the routing tables.
From privileged EXEC mode on all four routers, issue the show ip route
command to verify the all network segments are being advertised.
Step 3. Verify connectivity between routers.
a. From R1, ping all LAN interfaces to verify connectivity.
b. Again from router R1, Telnet to R2 using its LAN interface IP address. Exit and
repeat the step for routers R3 and R4.Ping other PCs on the same network.
Task 2: Configure SSH on the Hub Router (R1).
Step 1. Enable and configure SSH on R1.
To enable SSH on the router, the following parameters must be configured:
- Hostname
- Domain name
- Asymmetrical keys
- Local authentication
a. The hostname on R1 is pre-configured. Therefore configure the domain name
cisco.com using the ip domain-name domain-name command.
b. The asymmetrical RSA keys must be generated on R1 using the crypto key
generate rsa command. When prompted for a modulus size, specify a modulus
of 1024 bits.
c. SSH will prompt for a username and password combination when enabled.
Therefore, a local username database entry must be configured using the
username name password password command. Create a local account for the
user admin and password cisco.
d. Configure the SSH version using the ip ssh version command. In this lab, we
will be configuring to use version 2.
e. Next, we need to disable Telnet and enable SSH communication to the VTY
lines. To do so, enter the following commands on R1.
R1(config)# line vty 0 4
R1(config-line)# no transport input all
R1(config-line)# transport input ssh
R1(config-line)# login local
R1(config-line)# end
f. Save the configuration.
Step 2. Check results.
Your completion percentage should be 25%. If not, click Check Results to see
which required components are not yet completed.
Task 3: Configure SSH on the Spoke Routers R2, R3 and R4.
Step 1. Configure SSH on routers R2, R3, and R4.
Repeat the Steps from Task 2 on routers R2, R3 and R4.
Step 2. Check results.
Your completion percentage should be 100%. If not, click Check Results to see
which required components are not yet completed.
Task 4: Verify SSH.
Step 1. Verify the SSH configuration.
After configuring SSH on all routers, verify the SSH configuration on R1.
a. Issue the show ip ssh command to verify which version of SSH is configured,
and what the default settings are.
R1# sho ip ssh
SSH Enabled - version 1.99
Authentication timeout: 120 secs; Authentication retries: 3
b. Next, issue the show ip ssh command to verify if SSH is currently running.
R1#show ssh
%No SSHv2 server connections running.
%No SSHv1 server connections running.
Step 2. connect to R2.ext.
a. Now Telnet to router R2.ext, to issue the show ip ssh command to verify if SSH
is currently running.
R1# telnet 10.20.20.1
Trying 10.20.20.1 ...
[Connection to 10.20.20.1 closed by foreign host]
Recall that Telnet was deactivated using the no transport input all command.
Only SSH can be used to establish a remote connection.
b. Using R1 as the SSH client, SSH to router R2 using the ssh l username ipaddress command.
R1#ssh l admin 10.20.20.1
Password:
c. When prompted for a password, enter cisco. You should now be connected to
router R2.
You might also like
- Network Security All-in-one: ASA Firepower WSA Umbrella VPN ISE Layer 2 SecurityFrom EverandNetwork Security All-in-one: ASA Firepower WSA Umbrella VPN ISE Layer 2 SecurityNo ratings yet
- 16.4.7 Lab - Configure Network Devices With SSH - ILMDocument11 pages16.4.7 Lab - Configure Network Devices With SSH - ILMMariano Pereyra100% (1)
- Cisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3From EverandCisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3No ratings yet
- 4.1.4.6 Lab - Configuring Basic Router Settings With IOS CLIDocument10 pages4.1.4.6 Lab - Configuring Basic Router Settings With IOS CLIAhmadHijaziNo ratings yet
- 11.2.4.6 Lab - Securing Network DevicesDocument8 pages11.2.4.6 Lab - Securing Network DevicesasdfjklNo ratings yet
- Deployment Guide Sc8000Document218 pagesDeployment Guide Sc8000Houssem SandliNo ratings yet
- TP3 Ghazi Ben YahyaDocument12 pagesTP3 Ghazi Ben Yahyakaw birthdayNo ratings yet
- CCNA Security: Chapter Two Securing Network DevicesDocument16 pagesCCNA Security: Chapter Two Securing Network DevicesRatnesh KumarNo ratings yet
- 11.2.4.5 Lab - Accessing Network Devices With SSHDocument11 pages11.2.4.5 Lab - Accessing Network Devices With SSHDragan Filipovic50% (2)
- 作業49Document8 pages作業49許家騏No ratings yet
- Configure Network Devices With SSHDocument5 pagesConfigure Network Devices With SSHMisael Alarcon VillaNo ratings yet
- Sic PRACTICALDocument80 pagesSic PRACTICALbhlmallahNo ratings yet
- SIC Practical1 by STUD - TalksDocument9 pagesSIC Practical1 by STUD - TalksPradeep PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- En Security Chp2 PTActA Syslog-SSH-NTP InstructorDocument5 pagesEn Security Chp2 PTActA Syslog-SSH-NTP InstructoralooshNo ratings yet
- CCNAS - Chp2 - PTActA - Syslog-SSH-NTP - InstructorDocument5 pagesCCNAS - Chp2 - PTActA - Syslog-SSH-NTP - InstructoraditNo ratings yet
- 4.4.9 Lab - Configure Network Devices With SSH - ILMDocument10 pages4.4.9 Lab - Configure Network Devices With SSH - ILMRony Schäfer JaraNo ratings yet
- Security Chp2 PTActA Syslog-SSH-NTP InstructorDocument5 pagesSecurity Chp2 PTActA Syslog-SSH-NTP InstructorNotlin HnrqzNo ratings yet
- Instructor Packet Tracer Manual v1.1Document54 pagesInstructor Packet Tracer Manual v1.1Luis SanchezNo ratings yet
- 1.1.4.6 CiscoDocument11 pages1.1.4.6 CiscoZeratul322100% (2)
- مقدمة أمن2Document19 pagesمقدمة أمن2smsomeksa7No ratings yet
- 11.2.4.6 Lab - Accessing Network Devices With SSH - ILMDocument11 pages11.2.4.6 Lab - Accessing Network Devices With SSH - ILMKevin KimNo ratings yet
- Lab - Configure Network Devices With SSH: TopologyDocument10 pagesLab - Configure Network Devices With SSH: TopologyBárbaraNo ratings yet
- CCNA Security Skills Based Challenge LabDocument9 pagesCCNA Security Skills Based Challenge LabSiaw YsNo ratings yet
- En Security Chp2 PTActA Syslog-SSH-NTP StudentDocument6 pagesEn Security Chp2 PTActA Syslog-SSH-NTP Studentluis alexisNo ratings yet
- Somesh Kale Roll No 630 SICDocument66 pagesSomesh Kale Roll No 630 SICSomesh kaleNo ratings yet
- CCNA Security 1.0: Instructor Packet Tracer ManualDocument53 pagesCCNA Security 1.0: Instructor Packet Tracer ManualJuanJose CMNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 WorksheetDocument11 pagesLab 3 Worksheetpzydf6wjxvNo ratings yet
- 16.4.7 Lab - Configure Network Devices With SSHDocument6 pages16.4.7 Lab - Configure Network Devices With SSHFernando AlburquerqueNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Telnet SSHDocument4 pagesLecture 7 Telnet SSHعلي الجنابيNo ratings yet
- Configure Cisco Routers For Syslog, NTP, and SSH OperationsDocument6 pagesConfigure Cisco Routers For Syslog, NTP, and SSH OperationsMilošKovačevićNo ratings yet
- 11.2.4.6 Lab - Accessing Network Devices With SSHDocument6 pages11.2.4.6 Lab - Accessing Network Devices With SSHParthPatel0% (3)
- Lab 1.6.2Document22 pagesLab 1.6.2Marion SabandalNo ratings yet
- CCNAS v1.1 SBADocument10 pagesCCNAS v1.1 SBACaleb Peters0% (1)
- 11.2.4.8 Lab - Securing Network DevicesDocument8 pages11.2.4.8 Lab - Securing Network DevicesParthPatel60% (5)
- 11.2.4.6 Lab - Securing Network DevicesDocument8 pages11.2.4.6 Lab - Securing Network DevicesRichardWhitleyNo ratings yet
- Configure Cisco Routers For SyslogDocument6 pagesConfigure Cisco Routers For SyslogSameh Eddine HachaichiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - CCNA Sec - NDLDocument95 pagesChapter 2 - CCNA Sec - NDLTung Mai Van100% (1)
- CN Lab PDFDocument39 pagesCN Lab PDFAnup SubhankarNo ratings yet
- 1-1-4-6-Lab-Configuring-Basic-Router-Settings-With-Ios-Cli - PDF EditedDocument10 pages1-1-4-6-Lab-Configuring-Basic-Router-Settings-With-Ios-Cli - PDF EditedYeab SraNo ratings yet
- 16.4.7 Lab - Configure Network Devices With SSHDocument6 pages16.4.7 Lab - Configure Network Devices With SSHCRISTIAN DAVID VIASUS VEGANo ratings yet
- Lab - Configure Basic Router Settings: Part 2: Configure Devices and Verify ConnectivityDocument6 pagesLab - Configure Basic Router Settings: Part 2: Configure Devices and Verify ConnectivityJosé Aarón AponteNo ratings yet
- ISM Journal rUGVEDDocument46 pagesISM Journal rUGVED571TYIT sunilNo ratings yet
- Báo cáo cuối kì môn thực hành an ninh mạngDocument5 pagesBáo cáo cuối kì môn thực hành an ninh mạngDương Thành ĐạtNo ratings yet
- Router Switch CommandscDocument128 pagesRouter Switch CommandscIonel GherasimNo ratings yet
- CCENT Practice Certification Exam 1Document20 pagesCCENT Practice Certification Exam 1INGCESARCol0% (1)
- Day3 Ch2 Manag IOSDocument27 pagesDay3 Ch2 Manag IOSManoj BorahNo ratings yet
- CSC341 - Network Management Lab - 1Document70 pagesCSC341 - Network Management Lab - 1DilawarKhanNo ratings yet
- Lab A, Securing Administrative Access Using AAA and RADIUS: TopologyDocument13 pagesLab A, Securing Administrative Access Using AAA and RADIUS: TopologyGary Giovanni Cabezas GutierrezNo ratings yet
- 02 - CK - Securing Network DevicesDocument64 pages02 - CK - Securing Network DevicesKevin FolliotNo ratings yet
- SSH DHCP CiscoDocument3 pagesSSH DHCP Ciscoblackhorse20032001No ratings yet
- MIT 504 - Lab - 3 Configuring Basic Router Settings With IOS CLI 11Document11 pagesMIT 504 - Lab - 3 Configuring Basic Router Settings With IOS CLI 11umang patnaikNo ratings yet
- Router Switch CommandsDocument121 pagesRouter Switch CommandsIonel GherasimNo ratings yet
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkFrom EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNo ratings yet
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationFrom EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationNo ratings yet
- Wireless and Mobile Hacking and Sniffing TechniquesFrom EverandWireless and Mobile Hacking and Sniffing TechniquesNo ratings yet
- Backend Handbook: for Ruby on Rails AppsFrom EverandBackend Handbook: for Ruby on Rails AppsRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Writ of Kalikasan CaseDocument7 pagesWrit of Kalikasan Casethree_peaceNo ratings yet
- Family Tree 2Document4 pagesFamily Tree 2api-255131144No ratings yet
- 1102 - Chapter 14 Maintaining and Optimizing Operating Systems - Slide HandoutsDocument28 pages1102 - Chapter 14 Maintaining and Optimizing Operating Systems - Slide HandoutsManuel ZambranoNo ratings yet
- Ouat Answer KeyDocument84 pagesOuat Answer Keytushar nathNo ratings yet
- Surah AlakDocument12 pagesSurah AlakImran ShaheenNo ratings yet
- Visual Programming Concepts and DevelopmentDocument18 pagesVisual Programming Concepts and DevelopmentBasildon ShumbaNo ratings yet
- The ChaliceDocument4 pagesThe ChaliceFirst Christian ChurchNo ratings yet
- y Og YIA8 Ew Gcu JMXDocument14 pagesy Og YIA8 Ew Gcu JMXDevendra KunjamNo ratings yet
- CH 01Document21 pagesCH 01Prof. Bhaktabandhu DashNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Data Analysis - Summary of Merriam (2009) BookDocument4 pagesQualitative Data Analysis - Summary of Merriam (2009) BookSafhira AuraliaNo ratings yet
- Lokendra Singh Sekhawat: Internship/training (1 Year-Full Time)Document3 pagesLokendra Singh Sekhawat: Internship/training (1 Year-Full Time)Lokendra Singh ShekhawatNo ratings yet
- Digital MarketingDave Chaffey, Fiona Ellis-Chadwick - Digital Marketing - Strategy, Implementation and Practice-Pearson (2019)Document19 pagesDigital MarketingDave Chaffey, Fiona Ellis-Chadwick - Digital Marketing - Strategy, Implementation and Practice-Pearson (2019)tauqir ghauriNo ratings yet
- Currency Derivatives C (Chapter 5)Document10 pagesCurrency Derivatives C (Chapter 5)Evelina WiszniewskaNo ratings yet
- Endangered Species AnswersDocument6 pagesEndangered Species AnswersHannah Duncan-O'neillNo ratings yet
- Statistical Transfer Learning A Review and Some Extensions To Statistical Process Control - QE - 2018 PDFDocument15 pagesStatistical Transfer Learning A Review and Some Extensions To Statistical Process Control - QE - 2018 PDFCarlos Dario CristianoNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggeris Monday Date: 01.01.2018: Choose An Item. Choose An Item. Choose An Item. Choose An ItemDocument5 pagesBahasa Inggeris Monday Date: 01.01.2018: Choose An Item. Choose An Item. Choose An Item. Choose An ItemmekfatihahNo ratings yet
- Smart Vest and Monitoring System For Airsoft Sport-Games Using Vibration SensorDocument8 pagesSmart Vest and Monitoring System For Airsoft Sport-Games Using Vibration SensorAnanda NeliNo ratings yet
- Boleh Di Download Jika Anda Mau MajuDocument11 pagesBoleh Di Download Jika Anda Mau MajuSalimuddinNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five: The Maintenance of Human ResourceDocument37 pagesChapter Five: The Maintenance of Human ResourceBiruk SisayNo ratings yet
- 12-21-12 EditionDocument32 pages12-21-12 EditionSan Mateo Daily JournalNo ratings yet
- Can't - Can't Have - Could - Don't Need To - Might - Might Not - Must - Must Have - Mustn't - Should - Shouldn'tDocument2 pagesCan't - Can't Have - Could - Don't Need To - Might - Might Not - Must - Must Have - Mustn't - Should - Shouldn'tRobeAvilaNo ratings yet
- AOV SPYC Tours AuditionDocument3 pagesAOV SPYC Tours AuditionJane Limsan PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- ST Augustine of HippoDocument17 pagesST Augustine of HippoJoe SladeNo ratings yet
- Management of Breast EngorgementDocument2 pagesManagement of Breast EngorgementKathleen ColinioNo ratings yet
- Numerisoftreport 89 Subham SarkarDocument57 pagesNumerisoftreport 89 Subham SarkarShovon MajumderNo ratings yet
- One Deped One Pampanga: Porac Model Community High SchoolDocument3 pagesOne Deped One Pampanga: Porac Model Community High SchoolMilcah Roselle CandaNo ratings yet
- The Big Lasagna Recipe - NYT CookingDocument4 pagesThe Big Lasagna Recipe - NYT Cookingsumedha95No ratings yet
- Final Version of DBDDC 2018 2.0docx PDFDocument100 pagesFinal Version of DBDDC 2018 2.0docx PDFbelchiorNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Assignment Brief-New SpecDocument11 pagesUnit 5 Assignment Brief-New SpecArsalan chhipaNo ratings yet