Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Case Study: Singapore As An NIC: Globalisation
Case Study: Singapore As An NIC: Globalisation
Uploaded by
cocopolly0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageSingapore transformed its economy through several stages: from a traditional society dependent on labour-intensive industries, to promoting import substitution, and finally embracing export-oriented, high-technology and capital-intensive industries. It established agencies and improved infrastructure to attract foreign investment and talent. While Singapore leveraged its strengths like education and infrastructure to innovate, it also faces weaknesses due to its small size and dependence on global trade.
Original Description:
Original Title
singapore-case-study1.doc
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSingapore transformed its economy through several stages: from a traditional society dependent on labour-intensive industries, to promoting import substitution, and finally embracing export-oriented, high-technology and capital-intensive industries. It established agencies and improved infrastructure to attract foreign investment and talent. While Singapore leveraged its strengths like education and infrastructure to innovate, it also faces weaknesses due to its small size and dependence on global trade.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageCase Study: Singapore As An NIC: Globalisation
Case Study: Singapore As An NIC: Globalisation
Uploaded by
cocopollySingapore transformed its economy through several stages: from a traditional society dependent on labour-intensive industries, to promoting import substitution, and finally embracing export-oriented, high-technology and capital-intensive industries. It established agencies and improved infrastructure to attract foreign investment and talent. While Singapore leveraged its strengths like education and infrastructure to innovate, it also faces weaknesses due to its small size and dependence on global trade.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Globalisation
Case Study: Singapore as an NIC
Stage 1: traditional society labour-intensive industries
Stage 2: import substitution industries: reduction of expensive
imports by development of home industries, protectionist policies in
place
Protect local economy from foreign competition
Local infant industries need time and shelter to grow
before foreign industries can enter
Stage 3: export-oriented industries: high technology, capitalintensive industries
Stay competitive and learn from others
Attract FDI
Set up JTC (infrastructure) and EDB (advertising, marketing,
administration)
Practice of assembling and manufacturing various goods
from raw material stage
Privatisation: Singapore Telecoms Singtel: telecommunications
industry opened up even further by allowing more competition eg.
Starhub, M1
Entrepreneurship
+
innovation:
globalisation
of
Creative
Technologies: bought over American Music synthesizer company
Kurzweil to boost its hold in computer sound-making market
Strengths
Higher level of IT, higher literacy, good infrastructure
Produce more creative ideas / innovative applications of
technology
Weaknesses
Small size: lacks large market to develop full-scale
economy structure Singapore needs 8m people to
achieve good critical mass foreign talent
Vulnerability to global economic climate: due to
Singapores strong trading emphasis high dependence on
US market
Competition from neighbouring countries
You might also like
- Christopher Clapham-Africa and The International System - The Politics of State Survival (Cambridge Studies in International Relations) (1996)Document355 pagesChristopher Clapham-Africa and The International System - The Politics of State Survival (Cambridge Studies in International Relations) (1996)Rani Putri Nur Amalina100% (1)
- The Global Semiconductor Industry Teaching NoteDocument7 pagesThe Global Semiconductor Industry Teaching NoteAngel Chiang100% (3)
- Technological EnvironmentDocument15 pagesTechnological EnvironmentTejaswi ReddyNo ratings yet
- R J Act 1 Summary NotesDocument4 pagesR J Act 1 Summary NotescocopollyNo ratings yet
- Robert Gilpin - Global Political EconomyDocument5 pagesRobert Gilpin - Global Political EconomyGabriela Ribeiro da CostaNo ratings yet
- TCL Case StudyDocument8 pagesTCL Case StudyParag_Ghatpand_8912No ratings yet
- B - Microchip - 018Document2 pagesB - Microchip - 018GoldNo ratings yet
- Advanced-Electronics StakeholderDocument39 pagesAdvanced-Electronics StakeholderDumindu Anuradha ThilakaratneNo ratings yet
- Aspects of Industrialization:: Vocabulary-Mastering of LanguageDocument4 pagesAspects of Industrialization:: Vocabulary-Mastering of Languagelahbak abderrahmeneNo ratings yet
- Digital Divide - The NoteDocument5 pagesDigital Divide - The NoteKelvin NTAHNo ratings yet
- The Third Industrial RevolutionDocument7 pagesThe Third Industrial RevolutionJ. BautistaNo ratings yet
- Answer:: 1. Since The Initiative of Economic Reform in 1978, China Has Enjoyed High Economic Growth ForDocument4 pagesAnswer:: 1. Since The Initiative of Economic Reform in 1978, China Has Enjoyed High Economic Growth ForSantania syebaNo ratings yet
- IndustrialDocument9 pagesIndustrialJennifer ShabaNo ratings yet
- Dunning Oli EtcDocument8 pagesDunning Oli EtcPranav GadgeNo ratings yet
- BM Practice Questions ChinaDocument3 pagesBM Practice Questions ChinaArsath malik ArsathNo ratings yet
- 7IG - Volume 2 Resource MaterialDocument19 pages7IG - Volume 2 Resource MaterialjeffsaturxohmpawatNo ratings yet
- Chapter9.Strategic Management of The EconomyDocument26 pagesChapter9.Strategic Management of The EconomyMarlon BoucaudNo ratings yet
- Technological Dimension of GlobalizationDocument19 pagesTechnological Dimension of Globalizationfelbert DecanoNo ratings yet
- Emerging Market Characteristics & StrategiesDocument6 pagesEmerging Market Characteristics & StrategiestallalbasahelNo ratings yet
- IntelDocument21 pagesIntelAmit Mulchandani100% (1)
- Apr 4th Econ ClassnotesDocument3 pagesApr 4th Econ ClassnotesJohnnie ZhangNo ratings yet
- IM Lavesh HBMSM240Document8 pagesIM Lavesh HBMSM240lavesh732003No ratings yet
- Technological EnvironmentDocument6 pagesTechnological EnvironmentOrlando Bernard RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Emerging Market Entry Strategies of Multinational Corporations: The Intel Case StudyDocument20 pagesEmerging Market Entry Strategies of Multinational Corporations: The Intel Case StudyFranciane SilveiraNo ratings yet
- Ib Edited Que N AnsDocument32 pagesIb Edited Que N AnsBlackieRjNo ratings yet
- National Policies and International CooperationDocument9 pagesNational Policies and International CooperationfkkfoxNo ratings yet
- The Industrial WorldDocument7 pagesThe Industrial WorldEugene TanNo ratings yet
- Heavy Industries: Large Scale in Operation Deal in Bulky Goods Heavily Dependent On Raw MaterialsDocument23 pagesHeavy Industries: Large Scale in Operation Deal in Bulky Goods Heavily Dependent On Raw MaterialsPako BotsioNo ratings yet
- Case NokiaDocument5 pagesCase NokiaRa'uf MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Disney-Pixar Merger A Case Study AnalysisDocument35 pagesDisney-Pixar Merger A Case Study AnalysisShafaat Azeem0% (1)
- Assignment # 1: Analysis of Pakistani IndustriesDocument3 pagesAssignment # 1: Analysis of Pakistani IndustriesVinod PerkashNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Transnational Companies / Multinational CorporationsDocument9 pagesChapter 1: Transnational Companies / Multinational CorporationsVanreNo ratings yet
- IndustrialisatinDocument10 pagesIndustrialisatinJennifer ShabaNo ratings yet
- Patent Management Group Project NUSDocument67 pagesPatent Management Group Project NUSKyaw SwarNo ratings yet
- Finland and NokiaDocument5 pagesFinland and NokiaEulalie SerhalNo ratings yet
- Logistique Internationale Ou GlobaleDocument3 pagesLogistique Internationale Ou GlobaleAnanya SinghNo ratings yet
- Running Head: INTEL CASE STUDYDocument7 pagesRunning Head: INTEL CASE STUDYWhimsical BrunetteNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 - Industrial SectorDocument38 pagesTopic 5 - Industrial SectorKhairul AfiqNo ratings yet
- Case Study (Motorola)Document3 pagesCase Study (Motorola)Carmela Emma Pascual Garcia100% (1)
- IndustrilisartionDocument8 pagesIndustrilisartiontalithaonkabetse723No ratings yet
- Merits and Demerits of MNCDocument2 pagesMerits and Demerits of MNCShahzad Aziz100% (1)
- Report Ge3Document6 pagesReport Ge3JADE THERESE RAMOSNo ratings yet
- Ib Tutorial AnswerDocument64 pagesIb Tutorial Answerctg.shein.and.youNo ratings yet
- Information and Communications Technology (ICT)Document11 pagesInformation and Communications Technology (ICT)Shainne Anne MarianoNo ratings yet
- Week 4Document6 pagesWeek 4Cipriano GumafelixNo ratings yet
- Global Competitiveness and Technology: National Conference On IP For MSMEDocument29 pagesGlobal Competitiveness and Technology: National Conference On IP For MSMEjeet_singh_deepNo ratings yet
- Multinational Companies & FdiDocument3 pagesMultinational Companies & FdiAdeeba iqbalNo ratings yet
- Intel Corporation Analysis: Strategical Management - Tengiz TaktakishviliDocument12 pagesIntel Corporation Analysis: Strategical Management - Tengiz TaktakishviliSandro ChanturidzeNo ratings yet
- TN Govt's R&D PolicyDocument32 pagesTN Govt's R&D Policysparvindh3001No ratings yet
- Globalisation and GeofragmentationDocument10 pagesGlobalisation and Geofragmentationagarwalharshini17No ratings yet
- Croatian High-Tech Status and ProspectsDocument7 pagesCroatian High-Tech Status and ProspectsAnna BelkschizyNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour Towards ElectronicsDocument46 pagesConsumer Behaviour Towards Electronicskyle_1947456267% (3)
- Growth: To Continue For System-on-ChiDocument1 pageGrowth: To Continue For System-on-ChiMarco MendozaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document4 pagesTutorial 1seee CelinaNo ratings yet
- Pakistan AffairsDocument7 pagesPakistan AffairssaithimranadnanNo ratings yet
- The Information Age and Strategic ParadoxDocument4 pagesThe Information Age and Strategic ParadoxErick GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Task 2 StratgicsDocument11 pagesTask 2 StratgicsHusnyNo ratings yet
- EXPORTS OF MANUFACTURES BY DEVELOPING COUNTRIES - EMERGING PATTERNS OF TRADE AND LOCATION Author(s) - SANJAYA LALL (1998)Document21 pagesEXPORTS OF MANUFACTURES BY DEVELOPING COUNTRIES - EMERGING PATTERNS OF TRADE AND LOCATION Author(s) - SANJAYA LALL (1998)abhinavNo ratings yet
- Kottai and Karthick RajaDocument3 pagesKottai and Karthick Rajanaascom18No ratings yet
- Ai Assignment 2Document3 pagesAi Assignment 2SAKETH ANo ratings yet
- Global Technological Change: From Hard Technology to Soft TechnologyFrom EverandGlobal Technological Change: From Hard Technology to Soft TechnologyNo ratings yet
- First Year English Christmas Examination 1 Hour: InstructionsDocument5 pagesFirst Year English Christmas Examination 1 Hour: InstructionscocopollyNo ratings yet
- The Poetry of Sylvia PlathDocument7 pagesThe Poetry of Sylvia PlathcocopollyNo ratings yet
- Evening Classes Timetable 15th Sep To 20th NovDocument1 pageEvening Classes Timetable 15th Sep To 20th NovcocopollyNo ratings yet
- Statistics For Dummies Rachel EnriquezDocument41 pagesStatistics For Dummies Rachel EnriquezcocopollyNo ratings yet
- King LearDocument14 pagesKing LearcocopollyNo ratings yet
- Analysing Poetry: Focus - How To Analyses Poetry SuccessfullyDocument4 pagesAnalysing Poetry: Focus - How To Analyses Poetry SuccessfullycocopollyNo ratings yet
- Animal QuizDocument5 pagesAnimal QuizcocopollyNo ratings yet
- Youth Chinese Test (YCT) in St Andrew's College 中小学生 汉语考试: Four Levels of YCTDocument3 pagesYouth Chinese Test (YCT) in St Andrew's College 中小学生 汉语考试: Four Levels of YCTcocopollyNo ratings yet
- TY Info On 1st Project 2014Document1 pageTY Info On 1st Project 2014cocopollyNo ratings yet
- Conformity Cripples Creativity (Livia Woolfson)Document3 pagesConformity Cripples Creativity (Livia Woolfson)cocopolly50% (2)
- Hamlet: Quotation Who Said It To Whom Act / Scene What It Tells The AudienceDocument5 pagesHamlet: Quotation Who Said It To Whom Act / Scene What It Tells The AudiencecocopollyNo ratings yet
- Invoice For St. Andrews.Document1 pageInvoice For St. Andrews.cocopollyNo ratings yet
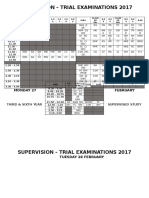
- Supervision ScheduleDocument14 pagesSupervision SchedulecocopollyNo ratings yet
- Boxes and Bullets Persuasive OutlineDocument2 pagesBoxes and Bullets Persuasive OutlinecocopollyNo ratings yet
- God As Omnipotent Loving and JustDocument13 pagesGod As Omnipotent Loving and JustcocopollyNo ratings yet
- Of Mice and Men Chapter TwoDocument2 pagesOf Mice and Men Chapter Twoapi-277918937No ratings yet
- Ghost Writer CastDocument2 pagesGhost Writer CastcocopollyNo ratings yet
- OMAM CHPT 01 StudentDocument2 pagesOMAM CHPT 01 StudentcocopollyNo ratings yet
- Bauman, Zygmunt - The Tourist SyndromeDocument10 pagesBauman, Zygmunt - The Tourist SyndromecrisNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Matrix 2Document3 pagesLiterature Review Matrix 2api-302726915No ratings yet
- Module 6 The Global DividesDocument8 pagesModule 6 The Global DividesCHRISTINE JOY OGOYNo ratings yet
- Human Geography OUTLINEDocument1 pageHuman Geography OUTLINESuzeth NavarroNo ratings yet
- Alimentary AssemblagesDocument13 pagesAlimentary AssemblagesJ.J. KahnNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument6 pagesPDFRuel GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary On Globalization and ConsumerismDocument3 pagesVocabulary On Globalization and Consumerismelleau67% (3)
- Topic 2 Transnational Migration and Overseas Filipino Workers (OFWs)Document3 pagesTopic 2 Transnational Migration and Overseas Filipino Workers (OFWs)Marilyn Dizon100% (7)
- Globalization in The PhilippinesDocument1 pageGlobalization in The PhilippinesKean Laurent CagangNo ratings yet
- What Keynes Warned About GlobalizationDocument6 pagesWhat Keynes Warned About GlobalizationFrank PasqualeNo ratings yet
- Population by Region: 10 Most Populous CountriesDocument3 pagesPopulation by Region: 10 Most Populous CountriesNarendra BabuNo ratings yet
- Jefrrey SachsDocument9 pagesJefrrey SachsEugeneLangNo ratings yet
- ISO Tolerances For HolesDocument3 pagesISO Tolerances For HolesMatthew HaleNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document7 pagesModule 2Joris YapNo ratings yet
- Apples GlobalizationDocument7 pagesApples GlobalizationAbhilash NayakNo ratings yet
- Globalisation, De-territorialisation and the Reconfiguring of БоундариесDocument18 pagesGlobalisation, De-territorialisation and the Reconfiguring of БоундариесSanja StosicNo ratings yet
- 1 Gcworld Midterm Exam Reviewer PDFDocument4 pages1 Gcworld Midterm Exam Reviewer PDFGabreille Rullamas ChavezNo ratings yet
- Presentation On LiberalisationDocument11 pagesPresentation On LiberalisationparasNo ratings yet
- Learning Outcomes: Contemporary World (Ge 3)Document9 pagesLearning Outcomes: Contemporary World (Ge 3)Mary Ann ArceNo ratings yet
- Assembly Automation: Article InformationDocument7 pagesAssembly Automation: Article InformationYao YaoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To GlobalizationDocument32 pagesIntroduction To GlobalizationJayvee Alipio LamsenNo ratings yet
- Becomingistanbul scrd-3Document459 pagesBecomingistanbul scrd-3Koray YilmazNo ratings yet
- Computation With Dumping Duty (R.A 8752)Document11 pagesComputation With Dumping Duty (R.A 8752)Mariel BoncatoNo ratings yet
- Cheek To Cheek - Full ScoreDocument2 pagesCheek To Cheek - Full Scorejoe.sivakNo ratings yet
- Trading CheatsheetDocument5 pagesTrading CheatsheetJansen CadornaNo ratings yet
- M1 Introduction To The Contemporary World and Globalization LectureDocument13 pagesM1 Introduction To The Contemporary World and Globalization LectureJOSHUALUIS GARCIANo ratings yet
- KWL ChartDocument4 pagesKWL ChartAMBROCIO JENALYN A.No ratings yet
- Rodrik The Globalization ParadoxDocument17 pagesRodrik The Globalization ParadoxRusty Bennett100% (2)