Professional Documents
Culture Documents
13 PDFsam GSM System Overview
Uploaded by
Osama ZaidanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
13 PDFsam GSM System Overview
Uploaded by
Osama ZaidanCopyright:
Available Formats
_________________________________________________________________________________
1.5 The Base Station Subsystem (BSS)
Section 1 Introduction to GSM
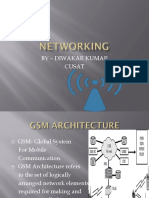
The Base Station Sub-System (BSS)
The BSS comprises:
Base Transceiver Station (B TS)
One or more Base Station Cont rollers (BSC)
BSS
The purpose of the BTS is to:
provide radio access to the mobile stations
manage the radio access aspects of the system
BTS contains:
Radio Transmitter/Receiver (TRX)
Signal processing and control equipment
Antennas and feeder cables
The BSC:
allocates a channel for the duration of a call
maintains the call:
monitoring quality
controlling the power transmitted by the B TS or MS
generating a handover to another cell when required
BTS
BSC
BTS
BTS
BTS
Siting of the BTS is crucial to the provision of
acceptable radio coverage
The effect of gains and losses in the BTS equipment on the signal power sent
to the antenna is an important consideration for link budget calculations.
Planning BTS positions requires a software tool such as Asset. Acquiring sites
and implementing the plan involves a combination of surveying, engineering
and legal work.
Handover in GSM is always hard that is the mobile only ever has a
communication link (traffic channel) open with one base station at one time.
This is true of any system with multiple frequencies, since the mobile must retune at the handover. Single frequency systems (such as CDMA) may use soft
handover.
The quality and power level of the radio link compared with that available
from neighbouring cells are important inputs to the handover decision made
by the BSC.
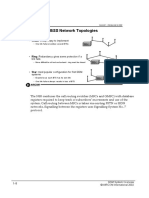
Base stations are linked to the parent BSC in one of several standard network
topologies. The actual physical link may be microwave, optical fibre or cable.
Planning of these links may be done using a tool such as Connect.
GSM System Overview
AIRCOM International 2002
1-7
You might also like
- Mobile Network Optimization: A Guide for 2G and 3G Mobile Network OptimizationFrom EverandMobile Network Optimization: A Guide for 2G and 3G Mobile Network OptimizationRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Functionality MCBSC NokiaDocument6 pagesFunctionality MCBSC NokiaAlieNo ratings yet
- From GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandFrom EverandFrom GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandNo ratings yet
- BSS Base Station Subsystem: Module ObjectivesDocument32 pagesBSS Base Station Subsystem: Module ObjectivesSurya6556No ratings yet
- Bss General AntarikshaDocument30 pagesBss General AntarikshaAntariksha SinghNo ratings yet
- GSM Word FileDocument11 pagesGSM Word FileevilanubhavNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2Document45 pagesChapter - 2Niharica SohalNo ratings yet
- Apis Training GSM System Overview - Base Station SystemDocument6 pagesApis Training GSM System Overview - Base Station SystemKhaja MohiuddinNo ratings yet
- BSC RNC PresentationDocument20 pagesBSC RNC Presentationmartin.taruvinga8335No ratings yet
- The Performance of GSM NetworkDocument2 pagesThe Performance of GSM NetworkDjiems GauthierNo ratings yet
- WMN Chapter 1 Notes by Ur Engineering FriendDocument12 pagesWMN Chapter 1 Notes by Ur Engineering FriendKaran ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Base Station SubsystemDocument72 pagesBase Station SubsystemDivya GoelNo ratings yet
- How To Do RF PlanningDocument95 pagesHow To Do RF PlanningMehdi Abbas100% (2)
- Base Station SubsystemDocument65 pagesBase Station SubsystemRicardo Ngeng PitpituNo ratings yet
- GSM Architecture OverviewDocument442 pagesGSM Architecture OverviewDavidDavidNo ratings yet
- Dronacharya College of Engineering Khentawas (Gurgaon) Affiliated To Maharishi Dayanand University, Rohtak Approved by A.I.C.T.EDocument23 pagesDronacharya College of Engineering Khentawas (Gurgaon) Affiliated To Maharishi Dayanand University, Rohtak Approved by A.I.C.T.EBhuvesh TanejaNo ratings yet
- GSM RF Quick Reference GuideDocument5 pagesGSM RF Quick Reference Guidesantoshkumar2711No ratings yet
- Base Station Subsystem (BSS)Document4 pagesBase Station Subsystem (BSS)mailto_gggggNo ratings yet
- My Seminar 222Document18 pagesMy Seminar 222Rajat NegiNo ratings yet
- By - Diwakar Kumar CusatDocument43 pagesBy - Diwakar Kumar CusatDIWAKAR KUMARNo ratings yet
- MCN Unit 4.1Document18 pagesMCN Unit 4.1venkatNo ratings yet
- BSC - Base Station ControllerDocument21 pagesBSC - Base Station Controllermanthasaikarthik100% (5)
- M0dule-2 WCCDocument56 pagesM0dule-2 WCCAkshathaNo ratings yet
- Base Station SubsystemDocument4 pagesBase Station SubsystemDaniyal AliNo ratings yet
- MC R20 - Unit-2Document43 pagesMC R20 - Unit-2Yadavilli VinayNo ratings yet
- Base Station Subsystem1Document4 pagesBase Station Subsystem1ajune30No ratings yet
- Introduction To Cellular Mobile Systems: Dr. K K SharmaDocument51 pagesIntroduction To Cellular Mobile Systems: Dr. K K SharmaK K SHARMANo ratings yet
- Mobile Wireless CommunicationDocument8 pagesMobile Wireless CommunicationTran Bao DuongNo ratings yet
- GSM Network ArchitectureDocument5 pagesGSM Network Architecturenarayanan07No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Notes CompleteDocument25 pagesUnit 4 Notes Completesolankimohanrao89548No ratings yet
- Base Station Subsystem (BSS) : CH 1: GSM (Global System For Mobile)Document4 pagesBase Station Subsystem (BSS) : CH 1: GSM (Global System For Mobile)Qahwagi MochaNo ratings yet
- An Overview of GSM TechnologyDocument7 pagesAn Overview of GSM TechnologyJaspreet KaurNo ratings yet
- UMTS Release 99Document10 pagesUMTS Release 99Alex MitreaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Radio SystemsDocument21 pagesCellular Radio SystemsYemuraiNo ratings yet
- Wireless Networking: Submitted by Simarpreet Aulakh 513044639 ECE (7 Sem)Document20 pagesWireless Networking: Submitted by Simarpreet Aulakh 513044639 ECE (7 Sem)Sumeet Sharma ANo ratings yet
- Welcome All Trainees: Course No. 270 by Rajesh Suwalka Engineer (WMTDC)Document29 pagesWelcome All Trainees: Course No. 270 by Rajesh Suwalka Engineer (WMTDC)Rajesh Suwalka100% (1)
- BSC ConfigurationDocument13 pagesBSC ConfigurationSantoshKumarNo ratings yet
- Amity School of Engineering: Monika Rajput B.Tech ECE III YearDocument27 pagesAmity School of Engineering: Monika Rajput B.Tech ECE III YearShashank BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- Global System MobileDocument55 pagesGlobal System Mobilekaran ThakurNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument37 pagesProjectSurina KondillyaNo ratings yet
- Mobile Computing Unit 1 PDFDocument22 pagesMobile Computing Unit 1 PDFVani BaskaranNo ratings yet
- GSM ArchitectureDocument442 pagesGSM ArchitecturePritam Kumar ChawlaNo ratings yet
- Basics Communication Theory & Antenna TheoryDocument29 pagesBasics Communication Theory & Antenna TheoryRajesh SuwalkaNo ratings yet
- Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA)Document15 pagesTime Division Multiple Access (TDMA)Swapnarekha NarravulaNo ratings yet
- Mobile and Wireless Communication Complete Lecture Notes #13Document17 pagesMobile and Wireless Communication Complete Lecture Notes #13Student Lecture Notes75% (4)
- What Is Cell Site: The Radio Network Controller (Or RNC) Is A Governing Element in The UMTSDocument10 pagesWhat Is Cell Site: The Radio Network Controller (Or RNC) Is A Governing Element in The UMTSshripalNo ratings yet
- Ziaullah 075 A2Document4 pagesZiaullah 075 A2Umar FarooqNo ratings yet
- BssDocument23 pagesBssXaferNo ratings yet
- Prepared By:: Live On TopDocument23 pagesPrepared By:: Live On TopAhmed GamalNo ratings yet
- GSM (Global System For Mobile Communications)Document44 pagesGSM (Global System For Mobile Communications)Ihab AmerNo ratings yet
- Base Transceiver Station: Figure 1 Subsystems of GSMDocument21 pagesBase Transceiver Station: Figure 1 Subsystems of GSMPravin GaretaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cellular FundamentalsDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Cellular FundamentalsMilinda MendisNo ratings yet
- Handover Analysis: B.L.Jagadesh, I.Kullayamma and Vivekand NareshDocument5 pagesHandover Analysis: B.L.Jagadesh, I.Kullayamma and Vivekand NareshDebasree DuttaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Mobile Communication - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument9 pagesUnit 4 - Mobile Communication - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inRohit kumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Mobile Communication - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument9 pagesUnit 4 - Mobile Communication - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inRohit kumarNo ratings yet
- Advances in Analog and RF IC Design for Wireless Communication SystemsFrom EverandAdvances in Analog and RF IC Design for Wireless Communication SystemsGabriele ManganaroRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Third Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesFrom EverandThird Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Modeling and Dimensioning of Mobile Wireless Networks: From GSM to LTEFrom EverandModeling and Dimensioning of Mobile Wireless Networks: From GSM to LTENo ratings yet
- ZXSDR BS8922 Product DescriptionDocument19 pagesZXSDR BS8922 Product DescriptionOsama ZaidanNo ratings yet
- 15 PDFsam GSM System OverviewDocument1 page15 PDFsam GSM System OverviewOsama ZaidanNo ratings yet
- 20 PDFsam GSM System OverviewDocument1 page20 PDFsam GSM System OverviewOsama ZaidanNo ratings yet
- 18 PDFsam GSM System OverviewDocument1 page18 PDFsam GSM System OverviewOsama ZaidanNo ratings yet
- 17 PDFsam GSM System OverviewDocument1 page17 PDFsam GSM System OverviewOsama ZaidanNo ratings yet
- 19 PDFsam GSM System OverviewDocument1 page19 PDFsam GSM System OverviewOsama ZaidanNo ratings yet
- 16 PDFsam GSM System OverviewDocument1 page16 PDFsam GSM System OverviewOsama ZaidanNo ratings yet
- 9 PDFsam GSM System OverviewDocument1 page9 PDFsam GSM System OverviewOsama ZaidanNo ratings yet
- 14 PDFsam GSM System OverviewDocument1 page14 PDFsam GSM System OverviewOsama ZaidanNo ratings yet
- 12 PDFsam GSM System OverviewDocument1 page12 PDFsam GSM System OverviewOsama ZaidanNo ratings yet
- 11 PDFsam GSM System OverviewDocument1 page11 PDFsam GSM System OverviewOsama ZaidanNo ratings yet
- 10 PDFsam GSM System OverviewDocument1 page10 PDFsam GSM System OverviewOsama ZaidanNo ratings yet
- 8 PDFsam GSM System OverviewDocument1 page8 PDFsam GSM System OverviewOsama ZaidanNo ratings yet
- 6 PDFsam GSM System OverviewDocument1 page6 PDFsam GSM System OverviewOsama ZaidanNo ratings yet
- 7 PDFsam GSM System OverviewDocument1 page7 PDFsam GSM System OverviewOsama ZaidanNo ratings yet
- 3 PDFsam GSM System OverviewDocument1 page3 PDFsam GSM System OverviewOsama ZaidanNo ratings yet
- 5 PDFsam GSM System OverviewDocument1 page5 PDFsam GSM System OverviewOsama ZaidanNo ratings yet
- 1 PDFsam GSM System OverviewDocument1 page1 PDFsam GSM System OverviewOsama ZaidanNo ratings yet
- 4 PDFsam GSM System OverviewDocument1 page4 PDFsam GSM System OverviewOsama ZaidanNo ratings yet