Professional Documents
Culture Documents
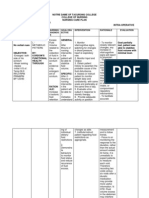
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Evaluation Nsg. Action Rationale
Uploaded by
Rhea Mae Valles - ReyesOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
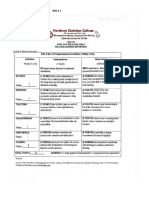
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Evaluation Nsg. Action Rationale
Uploaded by
Rhea Mae Valles - ReyesCopyright:
Available Formats
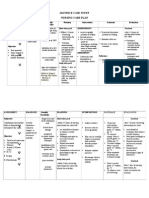
Rhea Mae V.
Valles
BSN-III
Pt. N.A. 1y/o
Assessment
Subjective:
Naninigas ang
kanyang braso at
paa mga ilang
segundo as
verbalized by
patient.
Objectives:
limited
range of
motion
(patient is
on a
decorticate
position)
c pupillary
size of
3mm on
right eye,
2mm on
left eye,
both eyes
with
negative
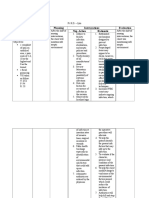
Diagnosis
Planning
Impaired
physical
mobility related
to
neuromuscular
damage
After 12 hours of
nursing interventions,
client will be able to
manifest:
Improve/Stable
level of
consciousness
Improve/Stable
GCS score
No pupillary
changes,
seizures,
widening of
pulse pressure,
irregular
respirations,
hypotension
and bradycardia
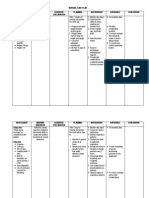
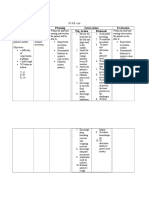
Interventions
Nsg. Action
Rationale
Independent:
Assessment
1. Assess mental
status and
changes in the
level of
consciousness
.
Therapeutic
2. Position client
in lowfowlers
position
(30degrees).
3. Avoid
extreme
rotation of the
neck.
4. Avoid
extreme hip
flexion.
5. Maintain
patent airway.
Dependent
Evaluation
After 12 hours of
nursing
interventions, client
was able to
1. To check for
affected cranial manifest:
Improve/Sta
nerve functions
ble level of
in the brain
consciousne
(for GCS);
ss
check for
Improve/Sta
cerebral hypo
perfusion and
ble GCS
hypoxia.
score
2. Help venous
No pupillary
drainage from
changes,
the brain and
seizures,
promote brain
widening of
expansion.
pulse
3. This will
pressure,
compress the
irregular
jugular veins
respirations,
leading to an
hypotension
increased
and
intracranial
bradycardia
pressure.
4. Increase in
reaction to
light
Muscle
grade of 1/5
for slight
muscle
contraction
on all
extremities,
no joint
motion
With GCS
of 6(best
eye
openingopens to
pain; verbal
response-1
with ET
attached to
VR; motor
response3,flexes
arms and
extension
of legs to
pain)
weak in
appearance
warm to
touch
6. Administer
medications
such as
diuretics (e.g.
Mannitol) and
anticonvulsan
ts(e.g.
Amlodipine,
Verapamil)
Collaborative
7. Review pulse
oximetry.
8. Restore or
maintain fluid
balance.
5.
6.
7.
8.
intraabdominal and
intra-thoracic
pressure
leading to
increased
intracranial
pressure.
Prevents
buildup of
secretions
leading to
increase in
carbon dioxide
and
intracranial
pressure.
Diuretics are
used and
needed to
decrease
cerebral edema
and
anticonvulsant
medications.
Hypoxia is
associated with
reduced
cerebral tissue
perfusion.
It maximizes
V/S taken
as follow:
T: 37.1
P: 120
R: 32
BP: 80/50
cardiac output
and prevents
decreased
cerebral
perfusion
associated with
hypovolemia.
You might also like
- Heart of the Field "Refresher & Nha Certification Quick Notes"From EverandHeart of the Field "Refresher & Nha Certification Quick Notes"No ratings yet
- Step 3 Board-Ready USMLE Junkies 2nd Edition: The Must-Have USMLE Step 3 Review CompanionFrom EverandStep 3 Board-Ready USMLE Junkies 2nd Edition: The Must-Have USMLE Step 3 Review CompanionNo ratings yet
- Nursing Study Guide: Your Nursing Assistant To Do Well In SchoolFrom EverandNursing Study Guide: Your Nursing Assistant To Do Well In SchoolRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- CVA-NCPDocument7 pagesCVA-NCPAiza Oronce0% (1)
- Length Tension Testing Book 2, Upper Quadrant: A Workbook of Manual Therapy TechniquesFrom EverandLength Tension Testing Book 2, Upper Quadrant: A Workbook of Manual Therapy TechniquesRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Assessment Needs Nursing Diagnos IS Goal/Obj Ective Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument10 pagesAssessment Needs Nursing Diagnos IS Goal/Obj Ective Intervention Rationale EvaluationApol Pen67% (3)
- Or NCP (Activity Intolerance)Document1 pageOr NCP (Activity Intolerance)Nikki M. Arapol100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument10 pagesNursing Care PlanmariasomorayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for a Diabetic Patient with Dehydration and FatigueDocument9 pagesNursing Care Plan for a Diabetic Patient with Dehydration and FatigueDanica Salinas100% (1)
- Reaching for Multicolored Object in Supported SittingDocument131 pagesReaching for Multicolored Object in Supported SittingMarilia Farensena100% (1)
- Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesActivity IntoleranceJenny Pearl PasalNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument1 pageIneffective Tissue PerfusionRhae RaynogNo ratings yet
- Activity Intolerance NCPDocument2 pagesActivity Intolerance NCPAlden MendozaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPKrizelle Abadesco Libo-on50% (2)
- NCP MiDocument8 pagesNCP MiPitaca Madiam Annabehl PaulNo ratings yet
- Pih-Ncp - BSN2D ZacalDocument3 pagesPih-Ncp - BSN2D ZacalIllaizah EdictoNo ratings yet
- NCP Cva Impaired Physical MobilityDocument2 pagesNCP Cva Impaired Physical MobilityMaricar Azolae Mascual100% (1)
- Acupuncture and Infrared Imaging: Essays by theoretical physicist & professor of oriental medicine in researchFrom EverandAcupuncture and Infrared Imaging: Essays by theoretical physicist & professor of oriental medicine in researchNo ratings yet
- NCP Myocardial InfarctionDocument1 pageNCP Myocardial InfarctionjamieboyRN88% (8)
- NCP For Impaired Physical MobilityDocument1 pageNCP For Impaired Physical Mobilityitzme_andreaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Raynaud's SyndromeDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Raynaud's SyndromeAmerah Sangcopan Sultan100% (5)
- A Simple Guide to Post-stroke Recovery, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Post-stroke Recovery, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Concept Care Map ExampleDocument5 pagesConcept Care Map ExampleNick HaislipNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Evaluation Nsg. Action RationaleDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Evaluation Nsg. Action RationaleRhea Mae Valles - ReyesNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Evaluation Nsg. Action RationaleDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Evaluation Nsg. Action RationaleRhea Mae Valles - ReyesNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Evaluation Nsg. Action RationaleDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Evaluation Nsg. Action RationaleRhea Mae Valles - ReyesNo ratings yet
- NCP FinalDocument18 pagesNCP FinalJessica Medina100% (1)
- MI Chest Pain AssessmentDocument5 pagesMI Chest Pain AssessmentDharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaNo ratings yet
- 2.mod Geron 2 DocumentationDocument43 pages2.mod Geron 2 Documentationnot your medz duran100% (1)
- Chapter 20 - Examination and Treatment of Vestibular System Disorders PDFDocument17 pagesChapter 20 - Examination and Treatment of Vestibular System Disorders PDFhaechannie leeNo ratings yet
- R: This Provides Baseline Measurement For Future Evaluation and Guides TherapyDocument4 pagesR: This Provides Baseline Measurement For Future Evaluation and Guides TherapyTyron ChuaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanSheng GosepNo ratings yet
- Cervical Spine Range of Motion TestDocument4 pagesCervical Spine Range of Motion TestArooj ZameerNo ratings yet
- Ischemic StrokeDocument25 pagesIschemic Strokebcdpqyck8xNo ratings yet
- CHN AssessmentDocument7 pagesCHN AssessmentKarylle Cheyenne AndresNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument17 pagesNCPShayne Jessemae AlmarioNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument8 pagesNCPJose Benit DelacruzNo ratings yet
- Cubital Tunnel PDFDocument2 pagesCubital Tunnel PDFDilah RahmaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans for Stroke PtDocument13 pagesNursing Care Plans for Stroke PtJuls Flares SycaycoNo ratings yet
- Jaundice Case StudyDocument5 pagesJaundice Case StudyUday KumarNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument10 pagesNCPNefre Dayap DarrocaNo ratings yet
- Administer Medications As IndicatedDocument4 pagesAdminister Medications As IndicatedYza WagayenNo ratings yet
- 2 Actual NCPsDocument4 pages2 Actual NCPsSittie Rohaina SabanNo ratings yet
- NCP FinalDocument7 pagesNCP FinalRuss RussNo ratings yet
- IUFDDocument13 pagesIUFDChristopher Lontoc0% (1)
- Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationJharene BasbañoNo ratings yet
- NCP HeadDocument11 pagesNCP Headann-lisel-manahan-7670100% (2)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanSiena KaleiNo ratings yet
- Client Nursing Care With Musculoskeletal Disorders Mata Kuliah: Bahasa Inggris KeperawatanDocument6 pagesClient Nursing Care With Musculoskeletal Disorders Mata Kuliah: Bahasa Inggris KeperawatanPutri fajrianti SultanNo ratings yet
- Mood Disorderdepression 1Document11 pagesMood Disorderdepression 1Leslie Lagat PaguioNo ratings yet
- Fatigue and Back Pain NCP PresentationDocument18 pagesFatigue and Back Pain NCP PresentationTine Guibao100% (1)
- NCP Epidural HemDocument32 pagesNCP Epidural HemKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- Date/ Time Cues Need Nursing Diagnosis Patient Outcome Planning of Interventions Imple Ment Ation EvaluationDocument4 pagesDate/ Time Cues Need Nursing Diagnosis Patient Outcome Planning of Interventions Imple Ment Ation EvaluationVianah Eve EscobidoNo ratings yet
- NCP CaseDocument35 pagesNCP Caselicservernoida100% (1)
- Scolio, Heart FailureDocument12 pagesScolio, Heart FailureArjay AvesNo ratings yet
- ChicknDocument5 pagesChicknapi-608271845No ratings yet
- Pain Management Nursing InterventionsDocument6 pagesPain Management Nursing InterventionsJeffrey Richmond AguilarNo ratings yet
- Quality and Safety Standards in Nursing CareDocument6 pagesQuality and Safety Standards in Nursing CareDharylle CariñoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for Activity IntoleranceChucky VergaraNo ratings yet
- NCP GrandcaseDocument5 pagesNCP GrandcaseSaima BataloNo ratings yet
- Managing a patient's acute pain after surgeryDocument3 pagesManaging a patient's acute pain after surgeryKarl KiwisNo ratings yet
- Medical Integration Model as it Pertains to Musculoskeletal ConditionsFrom EverandMedical Integration Model as it Pertains to Musculoskeletal ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Patho BPHDocument5 pagesAnaphy Patho BPHRhea Mae Valles - ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ds Pedia WardDocument2 pagesDs Pedia WardRhea Mae Valles - ReyesNo ratings yet
- I Practiced The Following During Childbirth. 4 3 2 1 F WV WM QDDocument2 pagesI Practiced The Following During Childbirth. 4 3 2 1 F WV WM QDRhea Mae Valles - ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ms. Valles Wound Care Center: Submitted By: Rhea Mae V. Valles Bsn-Iii Submitted To: Mr. Ismael LagrasonDocument2 pagesMs. Valles Wound Care Center: Submitted By: Rhea Mae V. Valles Bsn-Iii Submitted To: Mr. Ismael LagrasonRhea Mae Valles - ReyesNo ratings yet
- SWOR AnalysisDocument3 pagesSWOR AnalysisRhea Mae Valles - ReyesNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis For Acute GastroenteritisDocument3 pagesCase Analysis For Acute GastroenteritisRhea Mae Valles - ReyesNo ratings yet
- LepDocument6 pagesLepRhea Mae Valles - ReyesNo ratings yet
- Semi CS BCDocument17 pagesSemi CS BCRhea Mae Valles - ReyesNo ratings yet
- OADocument4 pagesOARhea Mae Valles - ReyesNo ratings yet
- Report Cd1Document6 pagesReport Cd1Rhea Mae Valles - ReyesNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Evaluation Nsg. Action RationaleDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Evaluation Nsg. Action RationaleRhea Mae Valles - ReyesNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid 1Document18 pagesRheumatoid 1Rhea Mae Valles - ReyesNo ratings yet
- Occupational Therapy Helps Daily Living SkillsDocument2 pagesOccupational Therapy Helps Daily Living SkillsRhea Mae Valles - ReyesNo ratings yet
- Most Participative Most BehaveDocument4 pagesMost Participative Most BehaveRhea Mae Valles - ReyesNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluation Nsg. Action RationaleDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluation Nsg. Action RationaleRhea Mae Valles - ReyesNo ratings yet
- NCP Pt. DE ASISDocument3 pagesNCP Pt. DE ASISRhea Mae Valles - ReyesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Rhea Mae V. Valles Bsn-IiiDocument1 pageDrug Study: Rhea Mae V. Valles Bsn-IiiRhea Mae Valles - ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ds Pedia WardDocument2 pagesDs Pedia WardRhea Mae Valles - ReyesNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Evaluation Nsg. Action RationaleDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Evaluation Nsg. Action RationaleRhea Mae Valles - ReyesNo ratings yet
- NCP Pt. DE ASISDocument3 pagesNCP Pt. DE ASISRhea Mae Valles - ReyesNo ratings yet
- NCP Pt. DE ASISDocument3 pagesNCP Pt. DE ASISRhea Mae Valles - ReyesNo ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument3 pagesActivity IntoleranceRhea Mae Valles - ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway ClearanceRhea Mae Valles - ReyesNo ratings yet
- NCP Pt. GomezDocument2 pagesNCP Pt. GomezRhea Mae Valles - ReyesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Rhea Mae V. Valles Bsn-IiiDocument1 pageDrug Study: Rhea Mae V. Valles Bsn-IiiRhea Mae Valles - ReyesNo ratings yet
- NCP Pt. DE ASISDocument3 pagesNCP Pt. DE ASISRhea Mae Valles - ReyesNo ratings yet
- NCP Pt. DE ASISDocument3 pagesNCP Pt. DE ASISRhea Mae Valles - ReyesNo ratings yet