Professional Documents
Culture Documents
T1 TorsionThinSections PDF
T1 TorsionThinSections PDF
Uploaded by
Rutuj ShahOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
T1 TorsionThinSections PDF
T1 TorsionThinSections PDF
Uploaded by
Rutuj ShahCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial # 1: Torsion of thin-walled sections
Figure 1
Figure 2
Figure 3
1. The two tubular sections shown in Figure 1 have the same wall thickness t and same circumference.
Cross-section of Sections 1 and 2 is circular and square respectively and the mean radius of Section 1 is a.
Neglecting stress concentration, find the ratio of the shear stress for
a) Equal twisting moments in the two cases and
b) Equal angles of twist in the two cases.
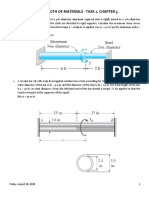
2. A thin-walled box section of dimension 2a x a x t is to be compared with a solid section of diameter a
(Figure 2). Find the thickness t so that the two sections have
a) the same maximum stress for the same torque,
b) the same stiffness.
3. A thin-walled box shown in Figure 3 is subjected to a torque T. Determine the shear stresses in the
walls and the angle of twist per unit length of the box.
Figure 4
Figure 5
4. Calculate the magnitude of the maximum torsional shear stress if the cross-section shown in Figure 4 is
subjected to a torque T = 900 N-m.
5. The aluminum (G = 27.1 GPa) hollow thin-wall torsion member in Figure 5 has the dimensions shown.
Its length is 3.00 m. If the member is subjected to a torque T= 11.0 kN-m, determine the maximum shear
stress and angle of twist.
You might also like
- HW1 TorsionThinSectionsDocument1 pageHW1 TorsionThinSectionsAjay KotwalNo ratings yet
- r09222502 Mechanics of SolidsDocument9 pagesr09222502 Mechanics of SolidsNida Bagoyboy NatichoNo ratings yet
- Shear Force and Shear StressDocument3 pagesShear Force and Shear StressAGEGTAMNo ratings yet
- 30 Questions SOMDocument5 pages30 Questions SOMQs 19No ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids PDFDocument8 pagesMechanics of Solids PDFprashanthreddy26No ratings yet
- Som Part B CDocument16 pagesSom Part B CSrini VasanNo ratings yet
- G For The Material Is 82 GN/m2. If The I-Section Is Replaced by A T-Section Made of TheDocument6 pagesG For The Material Is 82 GN/m2. If The I-Section Is Replaced by A T-Section Made of Theክበር ተመስጌንNo ratings yet
- Torsion Mod1Document49 pagesTorsion Mod1Beveh G SupSupNo ratings yet
- 9A01401 Strength of Materials - IIDocument4 pages9A01401 Strength of Materials - IIsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- TorsionDocument49 pagesTorsionBandula PrasadNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials-Ii: Instruction To CandidatesDocument2 pagesStrength of Materials-Ii: Instruction To CandidatesRAJEEV SHABOTRANo ratings yet
- Bending, Torsion, and StressDocument18 pagesBending, Torsion, and StressnasirfahimNo ratings yet
- TUT 1 Bending StressDocument8 pagesTUT 1 Bending StressVictoriaNo ratings yet
- Strength of Material One MarkDocument8 pagesStrength of Material One MarkdsathiyaNo ratings yet
- 7 - Torsion of Thin-Walled BarsDocument7 pages7 - Torsion of Thin-Walled Barsmustafa1011No ratings yet
- MET201 Tutorial 2Document1 pageMET201 Tutorial 2Dheeraj PNo ratings yet
- Assignment 07 AE670Document3 pagesAssignment 07 AE670Audrey BrooksNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of SolidsDocument8 pagesMechanics of Solidsprashanthreddy26No ratings yet
- Quiz2 2022 SolutionDocument4 pagesQuiz2 2022 SolutionSanu SouravNo ratings yet
- B. Tech. 1 Year (Civil) Solid Mechanics (CEN-102) Tutorial Sheet 4: Torsion, Shear Force and Bending MomentDocument4 pagesB. Tech. 1 Year (Civil) Solid Mechanics (CEN-102) Tutorial Sheet 4: Torsion, Shear Force and Bending MomentKumar ShivamNo ratings yet
- Ex1 Unsymmetrical BendingDocument3 pagesEx1 Unsymmetrical Bendinganon_530669663No ratings yet
- Geas FormulaDocument29 pagesGeas Formularoy016No ratings yet
- 9A01301 Mechanics of SolidsDocument4 pages9A01301 Mechanics of SolidssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- SOM Question BankDocument8 pagesSOM Question BankprakashmenmoliNo ratings yet
- Shear Centre 2 Thin WalledDocument3 pagesShear Centre 2 Thin WalledAdil GhazanfarNo ratings yet
- MOS Unit 1-Model QuestionsDocument11 pagesMOS Unit 1-Model QuestionsBhuvan RockNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids: GEC-R14 II B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2016Document2 pagesMechanics of Solids: GEC-R14 II B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2016srihari357No ratings yet
- MOS Assignment II Autumn 2022-23Document6 pagesMOS Assignment II Autumn 2022-23PankajNo ratings yet
- Mechanical ScienceDocument12 pagesMechanical ScienceFernando EyzaguirreNo ratings yet
- Jj310-Strength of Material: TorsionDocument42 pagesJj310-Strength of Material: TorsionHafiezul HassanNo ratings yet
- Mos Comprehnsice MCQDocument18 pagesMos Comprehnsice MCQshahzilezNo ratings yet
- TEST No. 1 - Strength of Materials: ReadDocument4 pagesTEST No. 1 - Strength of Materials: ReadJames CENo ratings yet
- 10bt30301-Strength of MaterialsDocument1 page10bt30301-Strength of Materialsvinay MurakambattuNo ratings yet
- Question B.Tech (CE) PDFDocument148 pagesQuestion B.Tech (CE) PDFLawrence NgariNo ratings yet
- Torsion of Thin Walled TubesDocument7 pagesTorsion of Thin Walled TubesJRovick M.No ratings yet
- 9A01401 Strength of Materials - IIDocument4 pages9A01401 Strength of Materials - IIsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Sample Questions: Manufacturing Process IDocument3 pagesSample Questions: Manufacturing Process IAnonymous 2xjDjAcZNo ratings yet
- SOM3601 Assignment 2Document3 pagesSOM3601 Assignment 2Elendu Emmanuel ChigozieNo ratings yet
- Stresses in Rigid PavementsDocument84 pagesStresses in Rigid PavementsCharl de Reuck100% (1)
- Code: 9A01302 B.Tech II Year I Semester (R09) Supplementary Examinations June 2015Document1 pageCode: 9A01302 B.Tech II Year I Semester (R09) Supplementary Examinations June 2015YohannesNo ratings yet
- Mos QBDocument15 pagesMos QBKarnalPreethNo ratings yet
- R5210103 Strength of Materials - IDocument1 pageR5210103 Strength of Materials - IsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A01302 Strength of Materials - IDocument8 pages9A01302 Strength of Materials - IsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- SM2-3 Chap3 Design Welded Joints Tutorial1Document7 pagesSM2-3 Chap3 Design Welded Joints Tutorial1AhmedNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials-II 2-2 Set-2 (A)Document13 pagesStrength of Materials-II 2-2 Set-2 (A)Sri DNo ratings yet
- 04a Torsion of ThinWalled StructuresDocument35 pages04a Torsion of ThinWalled StructuresYan NingNo ratings yet
- Assignment MEC236Document2 pagesAssignment MEC236fastminds- yha sab kuch milta haiNo ratings yet
- Solder CreepDocument5 pagesSolder CreepBerk işlerNo ratings yet
- Chpt4Torsion in RCMembers (F) CDocument13 pagesChpt4Torsion in RCMembers (F) CIsmail A Ismail100% (1)
- CE6306 SOM Important QuestionsDocument4 pagesCE6306 SOM Important QuestionsUTHIRANo ratings yet
- Tutorial I April 4, 2018Document2 pagesTutorial I April 4, 2018litebele litebeleNo ratings yet
- Torsion of Box SectionDocument8 pagesTorsion of Box SectionBhupendra69No ratings yet
- Torsion of Noncircular Prismatic Bars - Extract From Craig Mechanics of MaterialsDocument5 pagesTorsion of Noncircular Prismatic Bars - Extract From Craig Mechanics of MaterialsAlmudena9No ratings yet
- 081 CH 12Document4 pages081 CH 12ElaineAsiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Timber DesignDocument16 pagesAssignment 2 Timber Designkyle catarunganNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts, Rectangular and T Beams PDFDocument49 pagesBasic Concepts, Rectangular and T Beams PDFAhmed Hussein KamelNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5 Torsion in Reinforced Concrete MembersDocument8 pagesChapter - 5 Torsion in Reinforced Concrete MembersHelen NegashNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - Task 2. Chapter 3Document2 pagesStrength of Materials - Task 2. Chapter 3NEIVER ALEVIS CASTRO JULIONo ratings yet