Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Halao Alkane and Halo Arenes Test 1
Uploaded by
aleena'Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Halao Alkane and Halo Arenes Test 1
Uploaded by
aleena'Copyright:
Available Formats
HALAO ALKANE AND HALO ARENES TEST -1
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
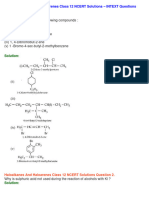
A hydrocarbon C5H10 does not react with chlorine in dark but gives a single monochloro
compound C5H9Cl in bright sunlight. Identify the hydrocarbon.
write chemical equation for Finkelstein Reaction
Write the structures of the following organic halogen compounds1-Bromo-4-sec-butyl-2-methylbenzene
Name the following compounds according to IUPAC system (i)CH3C(p-ClC6H4)2CH(Br)CH3
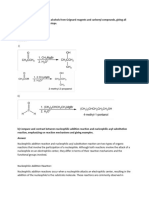
Explain the mechanism of alkaline hydrolysis of tert-butylchloride
In the following pairs of halogen compounds, which compound undergoes faster SN1 reaction?
(i)
(ii)
and
Explain why :-Haloalkanes react with KCN to form alkyl cyanides as main product while AgCN forms
isocyanides as the chief product.
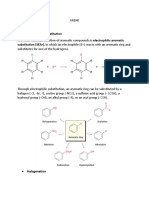
Although chlorine is an electron withdrawing group, yet it is ortho-,
paradirecting
in
electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions. Why?
Arrange each set of compounds in order of increasing order of
(i) Bromomethane, Bromoform, Chloromethane, Dibromomethane. [boiling points]
(ii) 1-Bromobutane, 1-Bromo-2,2-dimethylpropane, 1-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 1-Bromo-3methylbutane[ reactivity towards SN2]
10.
11. Draw the structures of major monohalo products in each of the following reactions:
12.
13.
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
Explain why :(i)
p-Dichlorobenzene has higher m.p. and lower solubility than those of o- and m-isomers.
(ii)
alkyl halides, though polar, are immiscible with water?
(iii)
The treatment of alkyl chlorides with aqueous KOH leads to the formation ofalcohols but in the
presence of alcoholic KOH, alkenes are major products.
Identify A, B, C, D, E, R and R1 in the following
14. Write the products of the following reactions:
1
1
1
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
3
3
You might also like
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12 NCERT SolutionsDocument32 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12 NCERT Solutionschithiraikumar83No ratings yet
- Haloalkane and Haloarenes by Aditya Sir ChemDocument19 pagesHaloalkane and Haloarenes by Aditya Sir Chempranav.padhle6No ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument3 pagesHaloalkanes and HaloarenesRAUNAK DEYNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument2 pagesHaloalkanes and HaloarenesCharviNo ratings yet
- Revision Sheet HaloalkaneDocument3 pagesRevision Sheet HaloalkaneSahil PandeyNo ratings yet
- The Reaction Gives Pure Alkyl HalidesDocument8 pagesThe Reaction Gives Pure Alkyl HalidesMohammed IliasNo ratings yet
- Aliphatics Home PackageDocument6 pagesAliphatics Home PackageelishamahubiNo ratings yet
- Alcohols Q.A.Document41 pagesAlcohols Q.A.Abhinav BishtNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes Q BankDocument7 pagesHaloalkanes Q BankVishnuNo ratings yet
- Grade Xii (Chemistry) : Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids (Term - 2) : Most Expecting QuestionsDocument5 pagesGrade Xii (Chemistry) : Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids (Term - 2) : Most Expecting QuestionsSupreeta KhatiwadaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Alcohols Phenole and EthersDocument20 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Alcohols Phenole and EthersNitin ChahalNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Alcohols Phenole and EthersDocument20 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Alcohols Phenole and EthersPundir DeeptiNo ratings yet
- AldehydesDocument5 pagesAldehydeslove.mansijhaNo ratings yet
- Reasoning Questions in Organic ChemistryDocument6 pagesReasoning Questions in Organic ChemistryPavankumar SNo ratings yet
- Organic TestDocument4 pagesOrganic Testpritam neogiNo ratings yet
- Assignment - HydrocarbonsDocument7 pagesAssignment - HydrocarbonsYash KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter-12 - Aldehydes-Ketones-and-Carboxylic-Acids Important QuestionDocument13 pagesChapter-12 - Aldehydes-Ketones-and-Carboxylic-Acids Important QuestionPonuNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Keypoints Revision Questions Chapter 10 PDFDocument13 pages12 Chemistry Keypoints Revision Questions Chapter 10 PDFSahil Kalra100% (1)
- Class: Xii Max. Marks: 50 Subject: Chemistry. TIME: 2 HoursDocument2 pagesClass: Xii Max. Marks: 50 Subject: Chemistry. TIME: 2 HoursPrerak Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Chemistry 12Document5 pagesWorksheet Chemistry 12mohit kumarNo ratings yet
- HaloalkanesDocument2 pagesHaloalkanesSameer DahiyaNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes SOLUTIONSDocument3 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes SOLUTIONSDr. Rupy dhirNo ratings yet
- Reasoning Questions in Organic Chemistry Text ExerciseDocument14 pagesReasoning Questions in Organic Chemistry Text ExerciseEr Purushottam PalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes PDFDocument40 pagesChemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes PDFGanesh KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Letter 203/2/2018: General Chemistry 1BDocument17 pagesTutorial Letter 203/2/2018: General Chemistry 1BLeigh MakanNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Phenols EthersDocument31 pagesAlcohol Phenols Etherssyedasifbasha1990No ratings yet
- Organic COMPETENCY BASED QUESTIONSDocument1 pageOrganic COMPETENCY BASED QUESTIONSbs766418No ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkenes and HaloarenesDocument31 pagesNCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkenes and HaloarenesVidyakulNo ratings yet
- Alkyl Halides: S5 Chemistry 29/NOV/2021Document31 pagesAlkyl Halides: S5 Chemistry 29/NOV/2021Nelima Stella mercyNo ratings yet
- CH7 Alcoholsphenols and Ethers HHW WorksheetDocument4 pagesCH7 Alcoholsphenols and Ethers HHW WorksheetAaditya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument14 pagesHaloalkanes and HaloarenesHarshitha GowdaNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons Dps AssignmentDocument6 pagesHydrocarbons Dps AssignmentharshillbhartiNo ratings yet
- PhenolDocument32 pagesPhenolchithiraikumar83No ratings yet
- Nabila Qna XM 4 5Document4 pagesNabila Qna XM 4 5skmahfuzahmed.bd3No ratings yet
- Nabila Qna XMDocument4 pagesNabila Qna XMskmahfuzahmed.bd3No ratings yet
- Solutions CH 1 NcertDocument40 pagesSolutions CH 1 NcertRadhika BasistaNo ratings yet
- JF PVQQ FRFFNC Eu HCMGAMDocument67 pagesJF PVQQ FRFFNC Eu HCMGAMelonmuskonmoonNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid and Their DerivativesDocument13 pagesCarboxylic Acid and Their DerivativesaqidahNo ratings yet
- Examples Example.10.1 Intext 10.3 Intext 10.4: Ashish TyagiDocument1 pageExamples Example.10.1 Intext 10.3 Intext 10.4: Ashish TyagiChandra VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes-Imp QNSDocument3 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes-Imp QNSjamesNo ratings yet
- F6 Note Alcohol2Document17 pagesF6 Note Alcohol2Ang chong bengNo ratings yet
- Pdf-Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument159 pagesPdf-Haloalkanes and HaloarenesOmkar Singh Shekhawat100% (2)
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes QDocument35 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes QAbhinav BishtNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Test 1 MemorandumDocument7 pagesOrganic Chemistry Test 1 MemorandumSandile SynthaxError Mabika0% (1)
- ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Class NotesDocument19 pagesORGANIC CHEMISTRY Class NotesWolam guyNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - Mock ExamDocument3 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Mock ExamAashif MohammedNo ratings yet
- Hand-Out: Chemistry Chapter 4: Haloalkanes & HaloarenesDocument11 pagesHand-Out: Chemistry Chapter 4: Haloalkanes & HaloarenesLuisgarciaBerlangaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Alcohols Phenols and EthersDocument19 pagesChapter 11 Alcohols Phenols and EthersNaina SinghNo ratings yet
- Reasoning Questions in Organic ChemistryDocument10 pagesReasoning Questions in Organic ChemistryAasthaNo ratings yet
- ) Reactions Those Involving Carbon - Carbon Bond FormationsDocument88 pages) Reactions Those Involving Carbon - Carbon Bond Formationsuvir iitmNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers - Board QuestionsDocument7 pagesAlcohols, Phenols, Ethers - Board QuestionsIron ManNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers Test - 1Document1 pageAlcohols, Phenols & Ethers Test - 1aleena'No ratings yet
- Very Short Answer Type Questions (1 Mark)Document10 pagesVery Short Answer Type Questions (1 Mark)Ꮢupesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDocument99 pagesAlcohols, Phenols and EthersSanya VermaNo ratings yet
- Alcohols PDFDocument33 pagesAlcohols PDFDINESH DHANUSH KODINo ratings yet
- Alcohol, Phenols and EtherDocument4 pagesAlcohol, Phenols and EtherShayaan & friend's vlogNo ratings yet
- ARENEDocument16 pagesARENEkaslana kianaNo ratings yet
- Either X-Ray Diffraction or (Infrared Spectroscopy)Document16 pagesEither X-Ray Diffraction or (Infrared Spectroscopy)Amna HaarisNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Transition Metal Catalyzed Furans Synthesis: Transition Metal Catalyzed Heterocycle Synthesis SeriesFrom EverandTransition Metal Catalyzed Furans Synthesis: Transition Metal Catalyzed Heterocycle Synthesis SeriesNo ratings yet
- VB Biology Eng 12Document27 pagesVB Biology Eng 12aleena'No ratings yet
- Exam Analysis PhysicsDocument4 pagesExam Analysis Physicsaleena'No ratings yet
- Emi and AcDocument11 pagesEmi and AcAmy GreenNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper-04 Class - XII Physics (Theory) Time Allowed: 3 Hours M. M: 70 General InstructionsDocument3 pagesSample Paper-04 Class - XII Physics (Theory) Time Allowed: 3 Hours M. M: 70 General Instructionsaleena'0% (1)
- Wave Optics Animation - PpsDocument20 pagesWave Optics Animation - Ppsaleena'No ratings yet
- Question Bank in Biology Class XIIDocument64 pagesQuestion Bank in Biology Class XIIaleena'No ratings yet
- Class 12 - Bio PDFDocument20 pagesClass 12 - Bio PDFaleena'No ratings yet
- Investigation of The Effect of Temperature On Enzyme ActivitiesDocument4 pagesInvestigation of The Effect of Temperature On Enzyme Activitiesaleena'No ratings yet
- Sample 3561Document16 pagesSample 3561aleena'No ratings yet
- VB Biology Eng 12 KvsDocument22 pagesVB Biology Eng 12 Kvsaleena'No ratings yet
- 11 - Chemistry For Half YyearlyDocument82 pages11 - Chemistry For Half Yyearlyaleena'No ratings yet
- 05 D & F-Block Elements (12th) (E) - WADocument11 pages05 D & F-Block Elements (12th) (E) - WAaleena'No ratings yet
- Amines MCQDocument3 pagesAmines MCQaleena'No ratings yet
- Assignment On Periodic TableDocument2 pagesAssignment On Periodic Tablealeena'No ratings yet
- Assignment On Periodic TableDocument2 pagesAssignment On Periodic Tablealeena'No ratings yet
- 24 Biology PDFDocument11 pages24 Biology PDFaleena'100% (1)
- COLLOIDSconcise Notes OptDocument6 pagesCOLLOIDSconcise Notes Optaleena'No ratings yet