Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Title: To Study The Fundamentals & Block Diagram of Drives Theory
Title: To Study The Fundamentals & Block Diagram of Drives Theory
Uploaded by
yash sharma0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 page1) The document presents a block diagram of an electric drive system consisting of a power source, power modulator, motor, sensing unit, and control unit.
2) The power source provides either DC or AC supply to the system. The power modulator converts the power from the source into a form suitable for the motor and selects the motor's mode of operation.
3) Sensors monitor drive parameters like speed and current, feeding this data to the control unit. The control unit then operates the power modulator and provides protection for the motor and modulator components.
Original Description:
electric drive
Original Title
To Study the Fundamentals
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) The document presents a block diagram of an electric drive system consisting of a power source, power modulator, motor, sensing unit, and control unit.
2) The power source provides either DC or AC supply to the system. The power modulator converts the power from the source into a form suitable for the motor and selects the motor's mode of operation.
3) Sensors monitor drive parameters like speed and current, feeding this data to the control unit. The control unit then operates the power modulator and provides protection for the motor and modulator components.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageTitle: To Study The Fundamentals & Block Diagram of Drives Theory
Title: To Study The Fundamentals & Block Diagram of Drives Theory
Uploaded by
yash sharma1) The document presents a block diagram of an electric drive system consisting of a power source, power modulator, motor, sensing unit, and control unit.
2) The power source provides either DC or AC supply to the system. The power modulator converts the power from the source into a form suitable for the motor and selects the motor's mode of operation.
3) Sensors monitor drive parameters like speed and current, feeding this data to the control unit. The control unit then operates the power modulator and provides protection for the motor and modulator components.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Title: To Study the Fundamentals & Block diagram of drives
Theory:
Fig.1
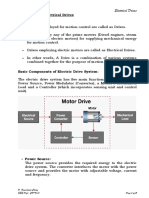
Block diagram of an electric drive as given in fig.1
1. Source: It is either d.c. or a.c. supply.
2. Power modulator: It performs the following function :
It converts electrical energy received from the source in the form suitable to
the motor i.e. if the source is d.c. and an induction motor is to be employed
then it converts d.c. into a variable frequency a.c.
It selects the mode of operation of motor i.e. motoring or braking.
3. Load: is usually a machinery designed to perform a given operation i.e. fans, machine
tools, domestic appliances, trains, pumps etc.
4. Motors: motors commonly used in electrical drives are DC motors-shunt, series,
compound and permanent magnet. Induction motor-squirrel cage and wound rotor;
synchronous motor-wound field and permanent magnet; Brushless dc motors; stepper
motors; and switched reluctance motors.
5. Sensing unit: It is employed for sensing the drive parameters such as speed, motor
current etc. which may be required for protection purpose or for closed loop
operations. These signals are fed to control unit.
6. Control unit: It control the power modulator besides generating commands for the
protection of motor and power modulator. It usually operates at much lower voltage
and power levels.
You might also like
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Electrical Drives and Control - Unit-I (MECHANICAL ENGINEERING)Document83 pagesElectrical Drives and Control - Unit-I (MECHANICAL ENGINEERING)Thivya PrasadNo ratings yet
- 1.development of Self Charging Dynamo and Solar Powered Based TricycleDocument100 pages1.development of Self Charging Dynamo and Solar Powered Based TricycleSRL MECHNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Electrical DrivesDocument16 pagesUnit 4 Electrical DrivesVaishnavi BharatiNo ratings yet
- DC Motors and TypesDocument13 pagesDC Motors and TypesLjubisa RaimovicNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 - Module 8: Electric Motor and GeneratorDocument12 pagesQuarter 2 - Module 8: Electric Motor and GeneratorMarilyn Castro LaquindanumNo ratings yet
- Types and Applications of The DC MotorsDocument11 pagesTypes and Applications of The DC MotorsaliNo ratings yet
- DC DrivesDocument10 pagesDC DrivesEuoshy HussainNo ratings yet
- To Study Induction Motor Speed Control by Variable Frequency AC Drive.Document8 pagesTo Study Induction Motor Speed Control by Variable Frequency AC Drive.Rushiraj DesaiNo ratings yet
- Development of A Microcontoller-Based Motor Speed Control System Using Intel 8051Document6 pagesDevelopment of A Microcontoller-Based Motor Speed Control System Using Intel 8051Nguyễn HòaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Part - One - LecturesDocument74 pages1 - Part - One - Lecturesrida.hamza.muhammadNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Electric Vehicle 2.2Document3 pagesHybrid Electric Vehicle 2.2AmanNo ratings yet
- What Is Electric Motor D1Document9 pagesWhat Is Electric Motor D1Shiv TonyNo ratings yet
- ED - Notes Inroduction To Electric Drives-0Document8 pagesED - Notes Inroduction To Electric Drives-0Manideep ManiNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machine 7-26-2016Document94 pagesElectrical Machine 7-26-2016Engr. Raheel khanNo ratings yet
- Module 1 FinalDocument32 pagesModule 1 Finalmeenujataj469481No ratings yet
- Characteristics of Electric Drives: Subject Name: Electric Drives Class: 4 Year/ VII SemesterDocument35 pagesCharacteristics of Electric Drives: Subject Name: Electric Drives Class: 4 Year/ VII SemesterBabbu DograNo ratings yet
- Electrical DrivesDocument194 pagesElectrical DrivesKITSAO SAMUELNo ratings yet
- What Is Electric MotorDocument9 pagesWhat Is Electric MotorElectrifying GuyNo ratings yet
- Ayush Kashyav Professional PracticeDocument21 pagesAyush Kashyav Professional PracticeDEZ Automation And ControlNo ratings yet
- Electrical Terminologies.Document20 pagesElectrical Terminologies.brazilacademicNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electrical DrivesDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Electrical DrivesGaurav SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Electric DriveDocument7 pagesElectric DriveAVIDIP DEYNo ratings yet
- REVIEWERDocument7 pagesREVIEWERDhafnylynn MacasaetNo ratings yet
- Projectreportmain PDFDocument36 pagesProjectreportmain PDFAnshul TailorNo ratings yet
- 19P205 Electrical MachinesDocument34 pages19P205 Electrical Machinessumanthlogn007No ratings yet
- 4 Types of DC Motors&GeneratorsDocument8 pages4 Types of DC Motors&GeneratorsAbdulhakim TREKINo ratings yet
- Industrial Drives and Control - ReviewerDocument10 pagesIndustrial Drives and Control - Reviewer21-09696No ratings yet
- ست خطوات العاكس لقيادة المحرك التعريفي ثلاث مراحلDocument113 pagesست خطوات العاكس لقيادة المحرك التعريفي ثلاث مراحلMOUHSSINE BEN HAMMOUNo ratings yet
- Final PDF EditedDocument6 pagesFinal PDF EditedFirdous NaazNo ratings yet
- Dumaguin Facma42l-Elep08 Module4Document7 pagesDumaguin Facma42l-Elep08 Module4Mike DumaguinNo ratings yet
- IELMO401 Operate Electrical MotorsDocument75 pagesIELMO401 Operate Electrical MotorsdoveemmyNo ratings yet
- Marpower Week 5 To 8Document8 pagesMarpower Week 5 To 8Haeisy SimsuangcoNo ratings yet
- Plant Utilities & Maintenance: .: Karte 01.aDocument33 pagesPlant Utilities & Maintenance: .: Karte 01.aHidayat StafaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Interview Guide BookDocument8 pagesElectrical Engineering Interview Guide BookshubhampattiNo ratings yet
- Adhiparasakthi College of Engineering: Ee2352 - Solid State DrivesDocument23 pagesAdhiparasakthi College of Engineering: Ee2352 - Solid State DrivesSidali ChaibNo ratings yet
- Lecture-9: Load Equalization and Two Mark QuestionsDocument6 pagesLecture-9: Load Equalization and Two Mark QuestionsTimoNo ratings yet
- DC GeneratorDocument2 pagesDC GeneratorRowan AlawiNo ratings yet
- Term Paper: Subject: Ele 102Document20 pagesTerm Paper: Subject: Ele 102Rajesh VermaNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: 1.1 What Are Dewatering Pumps?Document22 pagesChapter One: 1.1 What Are Dewatering Pumps?Odejobi Oluseyi JonathanNo ratings yet
- DRIVES NotesDocument44 pagesDRIVES NotesChase GarciaNo ratings yet
- Solid State Drives Ee2352 SSD NotesDocument19 pagesSolid State Drives Ee2352 SSD NotesGooge ReviewerNo ratings yet
- Motor Output Speed vs. Input Voltage: Experıment 6 Characterıstıc of A Permanent Magnet DC MotorDocument8 pagesMotor Output Speed vs. Input Voltage: Experıment 6 Characterıstıc of A Permanent Magnet DC MotorŞemsettin karakuşNo ratings yet
- Applications DC MotorDocument16 pagesApplications DC MotorSujeev GyawaliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 DC Machine Part 1Document34 pagesChapter 10 DC Machine Part 1Shobanraj LetchumananNo ratings yet
- Edc NotesDocument101 pagesEdc Notesneelam sanjeev kumarNo ratings yet
- EEOM AssignmentDocument4 pagesEEOM Assignmentjoseph5689No ratings yet
- Drives: Electric MotorDocument12 pagesDrives: Electric MotorShubham KumarNo ratings yet
- DC Generators Jkuat 2024Document10 pagesDC Generators Jkuat 2024sikolia.wanjalaNo ratings yet
- Three-Phase Squirrel-Cage Induction Motor Drive Analysis Using LabVIEWDocument26 pagesThree-Phase Squirrel-Cage Induction Motor Drive Analysis Using LabVIEWCarlos Roberto Amaya Rodriguez100% (1)
- ECEL LAB#3 AngeladaDocument19 pagesECEL LAB#3 AngeladaAlehamarie AngeladaNo ratings yet
- DC Motor - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument2 pagesDC Motor - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediadonodoni0008No ratings yet
- DCMotor Ahmed AlnaibDocument18 pagesDCMotor Ahmed Alnaibclaudia mutaneNo ratings yet
- Installation and Maintenance of Industrial Induction MotorsDocument59 pagesInstallation and Maintenance of Industrial Induction MotorsMichael HailuNo ratings yet
- Electric Motor Voltage: Chapter 1: Fundamentals of Electric DrivesDocument17 pagesElectric Motor Voltage: Chapter 1: Fundamentals of Electric DrivesRAJOLI GIRISAI MADHAVNo ratings yet
- Electtrical Motors: Figures 4.1Document11 pagesElecttrical Motors: Figures 4.1Cholan PillaiNo ratings yet
- M1 BasicsDocument15 pagesM1 BasicsSenpai GamingNo ratings yet
- Institute Uie Department Academic Unit-1: Discover - . EmpowerDocument23 pagesInstitute Uie Department Academic Unit-1: Discover - . EmpowerZeeshan ModiNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics: Lecture Notes of Power Electronics CourseFrom EverandPower Electronics: Lecture Notes of Power Electronics CourseNo ratings yet