Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TCP - IP Model - Intro Notes
Uploaded by
Anonymous OsssbjOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TCP - IP Model - Intro Notes
Uploaded by
Anonymous OsssbjCopyright:
Available Formats
TYBCA SEM 5 2016
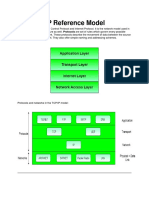
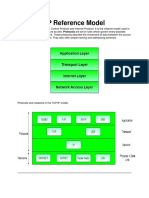
What is TCP/IP reference model?
We have already discussed that we need a common set of rules to
communicate between different computers in the heterogeneous
computer network. One such common set rule is specified in TCP/IP
reference model. This is equivalent to the already discussed ISO-OSI
reference model. But it has 4 layers instead of 7 layers.
TCP/IP reference model named after two of its primary protocols. That
is Transmission Control Protocol which resides in Transport Layer and
the other one is Internet Protocol which resides in Internet Layer
What is a Protocol?
Protocol is a set of rules. Thus Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
means it is a set rules followed to perform the functionalities of
Transport Layer. Similalry Internet Protocol means it is a set of rules
followed to perform the functions of Interent layer in the TCP/IP
reference model
HETA J DESAI SDJ INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE,VESU NT
TYBCA SEM 5 2016
1) Host to Netwrok Layer: The job of this layer is to transmit the
packets given by the Internet layer from the Host to the network to
which the Host connected.
2) Internet Layer: The job of this layer is to create the packet which is
known as Datagram and route it to the proper destination. It adds a lot
of control information so as to make the packet reach the correct
destination. The protocol present in this layer is known as Internet
Protocol (IP). IP is a connectionless protocol. Different pakcets created
in this layer may not follow the same path to reach the destination. For
example you want to send some packets to a Server in New York then
some packets may be sent through a specific route and some packets
may be sent through some other route and may not be the same route.
Why is it doing this? This is because, if a specific route through which it
sent the packet becomes busy then it will send the packet through
some other route. Becuase of this it may so happen that the packet
may not reach the destination in sequence and it will be the job of
upper layer to arrange the packets in proper sequence and recreate the
message.
3) Transport layer: The task of this layer is to establish the connection
between the peer entities in the source and destination host. Two
protocols reside in this layer one is Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
which is reliable, connection oriented protocol and the other one is the
User Datagram Protocol (UDP) which is unreliable, connectionless
protocol. Other function of TCP is to flow control between the slower
and faster entities. TCP is also responsible for the errorless transmission
of packets from source to destination. At the source TCP divides the
stream of bits it receives from the upper layer and creates packets and
gives it to the Internet Layer. At the destination it assembles the
packets receieved in proper sequence even if the packets are received
out of sequence, check for errors and if any, it is notified to the
HETA J DESAI SDJ INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE,VESU NT
TYBCA SEM 5 2016
Transport layer at the source machine and the Transport Layer at the
source machine resends the requested packet.
4) Application Layer: Different types of application and the protocols
reside in this layer and they handle different types of communication
Protocols and networks in the TCP/IP family
HETA J DESAI SDJ INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE,VESU NT
You might also like
- Jason Zandri : TCP/IP Protocol Within Windows XP ProfessionalDocument29 pagesJason Zandri : TCP/IP Protocol Within Windows XP ProfessionalruvinduNo ratings yet
- OSI and TCP/IP Model ComparisonDocument42 pagesOSI and TCP/IP Model ComparisonPvkkiy EceNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument24 pagesComputer NetworksJeena Mol AbrahamNo ratings yet
- TCP/IP Model ExplainedDocument14 pagesTCP/IP Model ExplainedLovepreet SinghNo ratings yet
- 1.assignment On 15 Well-Known Protocols, Their Port Number and FunctionsDocument6 pages1.assignment On 15 Well-Known Protocols, Their Port Number and FunctionsLimitless StatusNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks TCP IpDocument15 pagesComputer Networks TCP IpSudarshan KrishnaNo ratings yet
- TCP IpDocument6 pagesTCP Ipkannanperu123No ratings yet
- Acn May 2018Document45 pagesAcn May 2018shraddha_mundadadaNo ratings yet
- Lec 6Document7 pagesLec 6mariwan zaminNo ratings yet
- Overview of TCP/IP Reference ModelDocument3 pagesOverview of TCP/IP Reference ModelReign Earl B. Gup-ayNo ratings yet
- 10ec71 NotesDocument129 pages10ec71 NotesMSAMHOURINo ratings yet
- TCP IP Explained 17.01.2024Document5 pagesTCP IP Explained 17.01.2024aloishp36No ratings yet
- TCPIP ModelDocument9 pagesTCPIP Modelroysayanccp05No ratings yet
- TCP/IP vs OSI - A Comparison of the Two Networking ModelsDocument5 pagesTCP/IP vs OSI - A Comparison of the Two Networking ModelsRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Overview of the TCP/IP reference modelDocument4 pagesOverview of the TCP/IP reference modelJawad SandhuNo ratings yet
- 9IP Model-1Document4 pages9IP Model-1Jawad SandhuNo ratings yet
- The TCP/IP Reference ModelDocument4 pagesThe TCP/IP Reference ModelJawad SandhuNo ratings yet
- TCP IP ModelDocument31 pagesTCP IP ModelJaveed AhamedNo ratings yet
- Physical Layer Data Link Layer: Logical Link Control (LLC) Media Access Control (MAC)Document44 pagesPhysical Layer Data Link Layer: Logical Link Control (LLC) Media Access Control (MAC)GauravNo ratings yet
- CMPN 370 - Handout 3.5 Protocol Suites - TCP/IP: Application LayerDocument5 pagesCMPN 370 - Handout 3.5 Protocol Suites - TCP/IP: Application LayerShania LallNo ratings yet
- Assignment On NetworksDocument7 pagesAssignment On NetworksLimitless StatusNo ratings yet
- NetworkingDocument3 pagesNetworkingKshitij PanditNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking 3Document28 pagesComputer Networking 3ahmed abuidrisNo ratings yet
- TCP Ip ModelDocument5 pagesTCP Ip ModelJJ JainNo ratings yet
- TCP - IP PROTOCOL AND LayersDocument3 pagesTCP - IP PROTOCOL AND Layerssimon sylvesterNo ratings yet
- The OSI and TCPDocument8 pagesThe OSI and TCPSreejith VaneryNo ratings yet
- Fig.1.14 Logical Connections Between Layers of The TCP/IP Protocol SuiteDocument34 pagesFig.1.14 Logical Connections Between Layers of The TCP/IP Protocol SuiteNadeem PashaNo ratings yet
- 10ec71 - CCN - Notes PDFDocument127 pages10ec71 - CCN - Notes PDFRashmi Samant100% (2)
- Key Architectural PrinciplesDocument9 pagesKey Architectural Principlesablog165No ratings yet
- TCP/IP Reference Model ExplainedDocument3 pagesTCP/IP Reference Model ExplainedsangeetadineshNo ratings yet
- The OSI Network Model StandardDocument10 pagesThe OSI Network Model Standardcheal_che2No ratings yet
- A Technical Guide To IPSec Virtual Private NetworksDocument348 pagesA Technical Guide To IPSec Virtual Private NetworksRet SecNo ratings yet
- TCP IP Model Explained notesDocument12 pagesTCP IP Model Explained notesFake AccountNo ratings yet
- Network Layer Samia'Document10 pagesNetwork Layer Samia'Dark GardianNo ratings yet
- Computer Science (9618) 17.02 PROTOCOLS: Prepared by Rakesh Kumar Chaudhari Rato Bangala SchoolDocument32 pagesComputer Science (9618) 17.02 PROTOCOLS: Prepared by Rakesh Kumar Chaudhari Rato Bangala SchoolUttam PathakNo ratings yet
- IncredibleDocument2 pagesIncredibleDemixNo ratings yet
- Tcp/Ip: Protocol, TCP/IP Is A Set of Rules (Protocols) Governing Communications Among All Computers On TheDocument5 pagesTcp/Ip: Protocol, TCP/IP Is A Set of Rules (Protocols) Governing Communications Among All Computers On TheAmardeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment-II: Gagandeep KaurDocument12 pagesAssignment-II: Gagandeep KaurYolomanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document10 pagesAssignment 4anil rajputNo ratings yet
- The Best Guide To Understand What Is TCP (03.01.2024)Document8 pagesThe Best Guide To Understand What Is TCP (03.01.2024)aloishp36No ratings yet
- TCP/IP Protocol Stack ExplainedDocument24 pagesTCP/IP Protocol Stack ExplainedToni-ann WillisNo ratings yet
- Submitted To: Submitted By: Mrs. Ruchi Nanda Diksha Mangal Kajal JainDocument13 pagesSubmitted To: Submitted By: Mrs. Ruchi Nanda Diksha Mangal Kajal Jainpooja guptaNo ratings yet
- D. The Tcp/Ip Reference Model: ProtocolDocument7 pagesD. The Tcp/Ip Reference Model: ProtocolEcho greenNo ratings yet
- A Brief Summary On TCP/IPDocument30 pagesA Brief Summary On TCP/IPShubham VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- TCP/IP Protocol Suite & IP Addressing ExplainedDocument7 pagesTCP/IP Protocol Suite & IP Addressing ExplainedGrecu GianiNo ratings yet
- CN 1Document7 pagesCN 1T024KOUSTAV CHATTERJEENo ratings yet
- Demystifying The Full Stack TCPIP Protocol On Computer NetworksDocument11 pagesDemystifying The Full Stack TCPIP Protocol On Computer NetworksArun SomashekarNo ratings yet
- The Reference Model Part 2Document6 pagesThe Reference Model Part 2roysayanccp05No ratings yet
- Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)Document10 pagesTransmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)Sanjoy Basak100% (1)
- Unit 2 - Advance Computer Networks - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument21 pagesUnit 2 - Advance Computer Networks - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inprince keshriNo ratings yet
- 3.9 Draw TCP IP Reference Model and State The Functions of Each LayerDocument3 pages3.9 Draw TCP IP Reference Model and State The Functions of Each Layernarendra kumar bNo ratings yet
- PDF DocumentDocument5 pagesPDF DocumentBritney PitttersonNo ratings yet
- DCN TCP AssignmentDocument11 pagesDCN TCP Assignmenttalwandi bhindranNo ratings yet
- CH 05Document10 pagesCH 05Hari PrasadNo ratings yet
- Network Layers: The OSI Network Model StandardDocument4 pagesNetwork Layers: The OSI Network Model StandardPrasanna Venkatesan100% (1)
- Introduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyFrom EverandIntroduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyNo ratings yet
- TCP/IP: Network+ Protocols And Campus LAN Switching FundamentalsFrom EverandTCP/IP: Network+ Protocols And Campus LAN Switching FundamentalsNo ratings yet
- IPv4 Subnetting for Beginners: Your Complete Guide to Master IP Subnetting in 4 Simple Steps: Computer Networking, #1From EverandIPv4 Subnetting for Beginners: Your Complete Guide to Master IP Subnetting in 4 Simple Steps: Computer Networking, #1Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- The Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionFrom EverandThe Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)