Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tyndal
Uploaded by
mkmr4840 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pagecgffgjijiuu9
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentcgffgjijiuu9
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageTyndal
Uploaded by
mkmr484cgffgjijiuu9
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
The Tyndall effect, also known as Tyndall scattering, is light scattering by particles in a colloid
or else particles in a very fine suspension. It is named after the 19th-century physicist
John Tyndall.
It is caused by reflection of the incident radiation from the surfaces of the particles, reflection
from the interior walls of the particles, and refraction and diffraction of the radiation as it passes
through the particles. Other eponyms include Tyndall beam (the light scattered by colloidal
particles).
You might also like
- Institute of Nano Science and Technology: Form For Purchase of Goods Under GFR 145Document1 pageInstitute of Nano Science and Technology: Form For Purchase of Goods Under GFR 145mkmr484No ratings yet
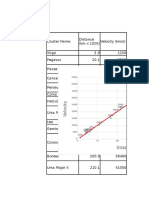
- Velocity Vs DistanceDocument2 pagesVelocity Vs Distancemkmr484No ratings yet
- Angular MomentumDocument3 pagesAngular Momentummkmr484No ratings yet
- Lab Beers LawDocument5 pagesLab Beers LawNurul AzizahNo ratings yet
- Max Max Max Max Max MaxDocument1 pageMax Max Max Max Max Maxmkmr484No ratings yet
- Fee AjitDocument1 pageFee Ajitmkmr484No ratings yet
- Himedia Products Catalogue 2012-13: Rapid Rapid Rapid Rapid Rapid Rapid RapidDocument1 pageHimedia Products Catalogue 2012-13: Rapid Rapid Rapid Rapid Rapid Rapid Rapidmkmr484No ratings yet
- DBTIndi May2017 2Document1 pageDBTIndi May2017 2mkmr484No ratings yet
- Registration Form CRIKC NanoDocument1 pageRegistration Form CRIKC Nanomkmr484No ratings yet
- Derivation of Physical Parameters From Raman Spectra of Hard Carbon FilmsDocument4 pagesDerivation of Physical Parameters From Raman Spectra of Hard Carbon Filmsmkmr484No ratings yet
- IISER Mohali PhD student course registration formDocument1 pageIISER Mohali PhD student course registration formmkmr484No ratings yet
- Product Information: LA653 Dialysis Tubing Size 1 Dia 8/32, 6.3 MMDocument1 pageProduct Information: LA653 Dialysis Tubing Size 1 Dia 8/32, 6.3 MMmkmr484No ratings yet
- PH 2Document2 pagesPH 2mkmr484No ratings yet
- Full TextDocument28 pagesFull Textmkmr484No ratings yet
- AjitDocument3 pagesAjitmkmr484No ratings yet
- DBTProformaDocument3 pagesDBTProformamkmr484No ratings yet
- Derivation of Physical Parameters From Raman Spectra of Hard Carbon FilmsDocument4 pagesDerivation of Physical Parameters From Raman Spectra of Hard Carbon Filmsmkmr484No ratings yet
- DBTProformaDocument3 pagesDBTProformamkmr484No ratings yet
- DBTProformaDocument3 pagesDBTProformamkmr484No ratings yet
- DBTProformaDocument3 pagesDBTProformamkmr484No ratings yet
- DBTProformaDocument3 pagesDBTProformamkmr484No ratings yet
- Time Table For Even-Sem INST Courses Jan-Apr 2017Document2 pagesTime Table For Even-Sem INST Courses Jan-Apr 2017mkmr484No ratings yet
- Time Table For Even-Sem INST Courses Jan-Apr 2017Document2 pagesTime Table For Even-Sem INST Courses Jan-Apr 2017mkmr484No ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)