Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cranial Nerves
Uploaded by
Kelly YeowOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cranial Nerves
Uploaded by
Kelly YeowCopyright:
Available Formats
Origins
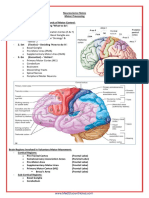
There are twelve cranial nerves in total. The olfactory nerve (CN I) and optic nerve (CN II) originate
from the cerebrum.
Cranial nerves III XII arise from the brain stem (Figure 1). They can arise from a specific part of
the brain stem (midbrain, pons or medulla), or from a junction between two parts:
Midbrain the trochlear nerve (IV) comes from the posterior side of the midbrain. It has the
longest intracranial length of all the cranial nerves.
Midbrain-pontine junction oculomotor (III).
Pons trigeminal (V).
Pontine-medulla junction abducens, facial, vestibulocochlear (VI-VIII).
Medulla Oblongata posterior to the olive: glossopharyngeal, vagus, accessory (IX-XI).
Anterior to the olive: hypoglossal (XII).
The cranial nerves are numbered by their location on the brain stem (superior to inferior, then medial
to lateral) and the order of their exit from the cranium (anterior to posterior) (Figures 1 & 2).
Sensory (afferent) Modalities:
General somatic sensory (GSS) general sensation from skin.
General visceral sensory (GVS) general sensation from viscera.
Special somatic sensory (SSS) senses derived from ectoderm (sight, sound, balance).
Special visceral sensory (SVS) senses derived from endoderm (taste).
Motor (efferent) Modalities:
General somatic motor (GSM) skeletal muscles.
General visceral motor (GVM) smooth muscles of gut and autonomic motor.
Special visceral motor (SVM) muscles derived from pharyngeal arche
Number Name Exit Modality Function
1 (CNI) Olfactory Cribriform Sensory Smell
plate (SVS)
2 (CNII) Optic Optic canal Sensory Vision
(SSS)
3 (CNIII) Oculomotor Superior Motor GSM: 4 extrinsic eye muscles
orbital fissure (GSM & and levator palpebrae
GVM) superioris.
GVM: pupillary sphincter
4 (CNIV) Trochlear Superior Motor Superior oblique
orbital fissure (GSM)
5 (CNV) Trigeminal:
Ophthalmic Superior GSS Scalp, forehead and nose.
orbital fissure
Maxillary F. rotundum GSS Cheeks, lower eye lid, nasal
mucosa, upper lip, upper teeth
and palate.
Mandibular F. ovale GSS GSS: anterior 2/3 tongue, skin
SVM over mandible and lower teeth.
SVM: muscles of mastication.
6 (CNVI) Abducens Superior Motor Lateral rectus
orbital fissure (GSM)
7 Facial Internal Both: GSS: sensation to part of ext.
(CNVII) acoustic GSS ear.
meatus > SVS SVS: taste from ant. 2/3 tongue,
stylomastoid GSM hard and soft palate.
f. GVM
GSM: muscles of facial
expression.
GVM: lacrimal, submandibular,
sublingual glands and mucous
glands of mouth and nose.
8 Vestibulocochlear Internal Sensory Hearing and balance
(CNVIII) acoustic (SSS)
meatus
9 (CNIX) Glossopharyngeal Jugular f. Both: GSS: post. 1/3 tongue, ext. ear,
GSS and middle ear cavity.
GVS GVS: carotid body and sinus.
SVS
GVM SVS: taste from post. 1/3
SVM tongue.
GVM: parotic gland. SVM:
stylopharyngeus
10(CNX) Vagus Jugular f. Both: GSS: ext. ear, larynx and
GSS pharynx.
GVS GVS: larynx, pharynx and,
SVS thoracic & abdominal viscera.
GVM
SVM SVS: taste from epiglottis region
of tongue
GVM: smooth muscles of
pharynx, larynx and most of the
GIT.
SVM: most muscles of pharynx
and larynx.
11 Spinal accessory Jugular f. Motor GSM: trapezius and
(CNXI) (GSM & sternocleidomastoid.
SVM) SVM: a few fibres run with CNX
to viscera.
12 Hypoglossal Hypoglossal Motor Intrinsic and extrinsic tongue
(CNXII) canal (GSM) muscles (except the
palatoglossus).
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Cranial Nerves 7-12Document62 pagesCranial Nerves 7-12jangyNo ratings yet
- Nervous System NotesDocument6 pagesNervous System NotesHannah Grace CorveraNo ratings yet
- Nbme FlashcardsDocument150 pagesNbme Flashcardsyasir saeed88% (8)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Neurological EmergenciesDocument492 pagesNeurological EmergenciesKalvin Adala100% (1)
- Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesNervous SystemGee PascalNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion Reaction 3032018Document33 pagesBlood Transfusion Reaction 3032018Kelly YeowNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion Reaction 3032018Document33 pagesBlood Transfusion Reaction 3032018Kelly YeowNo ratings yet
- The Role of Early Experience in Infant DevelopmentDocument307 pagesThe Role of Early Experience in Infant DevelopmentDaru Kristiyono100% (2)
- Module 3 PDFDocument20 pagesModule 3 PDFSuiluj Omatsodlab100% (1)
- Surveying2 170728043839Document82 pagesSurveying2 170728043839Kelly Yeow50% (2)
- The Cerebellum-8 PDFDocument83 pagesThe Cerebellum-8 PDFlovelots1234No ratings yet
- Approach To ComaDocument33 pagesApproach To ComaDương Đình ThuậnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Cognitive Psychology NotesDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Cognitive Psychology NotesShekinah Pearl Niog100% (1)
- Major Histocompatibility Complex 12032018Document39 pagesMajor Histocompatibility Complex 12032018Kelly YeowNo ratings yet
- Lymphadenopathy LymphomaDocument72 pagesLymphadenopathy LymphomaKelly YeowNo ratings yet
- Dentin Pulp ComplexDocument41 pagesDentin Pulp ComplexKelly YeowNo ratings yet
- Tongue LesionDocument17 pagesTongue LesionKelly YeowNo ratings yet
- Tissue ResponseDocument89 pagesTissue ResponseKelly YeowNo ratings yet
- Mal OcclusionDocument24 pagesMal OcclusionKelly YeowNo ratings yet
- Cementum and Alv Bone 2Document55 pagesCementum and Alv Bone 2Kelly YeowNo ratings yet
- Stress HealthDocument18 pagesStress HealthKelly YeowNo ratings yet
- History Taking: Patient's Full Name: Age: Gender: Occupation: Marital StatusDocument6 pagesHistory Taking: Patient's Full Name: Age: Gender: Occupation: Marital StatusKelly YeowNo ratings yet
- Motoric SystemDocument32 pagesMotoric SystemAnisa Zulfiya RahmahNo ratings yet
- Brainstem Rule of 4Document11 pagesBrainstem Rule of 4Anonymous 0gUash0BxNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerve 8 (Vestibulo-Cochlear)Document14 pagesCranial Nerve 8 (Vestibulo-Cochlear)osakaNo ratings yet
- A&P - 7. Motor Proessing (13p)Document13 pagesA&P - 7. Motor Proessing (13p)Gabriel StratulatNo ratings yet
- Mayo Clinic Neurology Board Review Mayo Clinic Scientific Press Kelly D Flemming Download PDF ChapterDocument51 pagesMayo Clinic Neurology Board Review Mayo Clinic Scientific Press Kelly D Flemming Download PDF Chapterdavid.mason150100% (12)
- Report Text The Brainy BodyDocument3 pagesReport Text The Brainy BodyHana alkhairaNo ratings yet
- Brainstem - Pons MidbrainDocument24 pagesBrainstem - Pons MidbrainjabirNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Practical OSPEDocument33 pagesAnatomy Practical OSPEAbdi Ñãśìr Møhàmèď ŚàĺàhNo ratings yet
- Medical NeurobiologyDocument682 pagesMedical NeurobiologyMaría CristinaNo ratings yet
- REVIEWER - Biological PsychologyDocument59 pagesREVIEWER - Biological PsychologyMendoza Bernalyn DCNo ratings yet
- Pons and Midbrain Neuroanatomy: Abbas A. A. Shawka Medical Student 2nd GradeDocument47 pagesPons and Midbrain Neuroanatomy: Abbas A. A. Shawka Medical Student 2nd GradePlutokidNo ratings yet
- Intro Animal Physiology Ch-2.1Document97 pagesIntro Animal Physiology Ch-2.1Jojo MendozaNo ratings yet
- Clinical NeurocardiologyDocument317 pagesClinical NeurocardiologyadnanNo ratings yet
- Isotropic Fractionator Suzana Herculano-Houzel - NeurociênciaDocument4 pagesIsotropic Fractionator Suzana Herculano-Houzel - NeurociênciaMaxNel100% (1)
- The Midbrain 2Document43 pagesThe Midbrain 2Vensun ReddyNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Science ReviewerDocument25 pagesGrade 10 Science ReviewertinaNo ratings yet
- Weakness and Hypotonia: Prepared by DR Hodan Jama MDDocument38 pagesWeakness and Hypotonia: Prepared by DR Hodan Jama MDabdisalaan hassanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesLesson 3 Nervous SystemMARY JANE ANGELICA SEVANo ratings yet
- CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Word.Document8 pagesCENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Word.Noor Fadillah AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 BrainDocument7 pagesChapter 19 BrainUloko ChristopherNo ratings yet