Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anti Bit Ocs
Uploaded by
Alexa TimOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anti Bit Ocs
Uploaded by
Alexa TimCopyright:
Available Formats
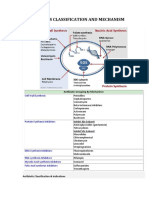
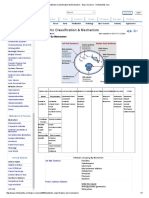
Overview by Mechanism
Antibiotic Grouping by Mechanism
Cell wall synthesis inhibitors Penicillins
Cephalosporins
Vancomycin
Beta-lactamase inhibitors
Carbepenems
Aztreonam
Polymycin
Bacitracin
Protein synthesis inhibitors Inhibit 30S subunit
Aminoglycosides (gentamycin)
Tetracyclines
Inhibit 50S subunit
Macrolides
Chloramphenicol
Clindamycin
Linezolid
Streptogramins
DNA synthesis inhibitors Fluoroquinolones
Metronidazole
RNA synthesis inhibitors Rifampin
Mycolic acid synthesis inhibitors Isoniazid
Folic acid synthesis inhibitors Sulfonamides
Trimethoprim
Classification & Indications
Cell Wall Synthesis Inhibitors
Penicillins
(Bactericidal: inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis via competitive inhibition of the transpeptidase
enzyme)
Class Name of Drug(s) Indications
Penicillin Penicillin G S. pnuemoniae
Aqueous (crystalline) S. pyogenes (group A
penicillin G strep)
Procaine penicillin G N. meningitidis
Benzathine penicillin G T. pallidum
Penicillin V L. monocytogenes
A. israelii
P. multocida
Aminopenicillins Ampicillin gram-negative
Amoxicillin coverage
Enterococci (group D
strep)
All others listed above
Penicillinase-resistant penicillins Methicillin Penicillinase-
Nafcillin producing S. aureus
Oxacillin All others listed above
Cloxacillin
Dicloxacillin
Antipseudomonal penicillins Carbenicillin P. aeruginosa
Ticarcillin Anaerobic bacteria
Piperacillin All others listed
above
Cephalosporins
(Bactericidal: inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis via competitive inhibition of the transpeptidase
enzyme)
1st generation Cefazolin Gram-positives
Cephalexin Some gram-negatives
Skin infection
prophylaxis
2nd generation Cefoxitin Gram-positives
Cefaclor Improved gram-
Cefuroxime negative coverage
Anaerobes
3rd generation Ceftriaxone Serious gram-
Cefotaxime negative infections
Ceftazidime Meningitis
Pseudomonas
Same coverage as
cephalosporins +
expanded
Cefepime Pseudomonas
4th generation
coverage + expanded
gram-positive
coverage
Expanded gram-
positive and gram-
Ceftaroline negative coverage,
5th generation
non-suitable coverage
of Pseudomonas
Other Cell Wall Inhibitors
Vancomycin (bactericidal: Vancomycin MRSA
inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis by Patients with PCN
disrupting peptioglycan cross linking) or ceph allergies
S aureus
S epidermidis
C. difficile
Beta-lactamase inhibitors Clavulanic acid Gram-positive
(beta-lactamse inhibitors that prevent the Sulbactam S. aureus
degradation of beta-lactam antibiotics) Tazobactam S. epidermis
Gram-negative
E. coli
Klebsiella
Carbapenems Imipenem (+ cilastatin) Broadest activity of
(Inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis) Meropenem any antibiotic (does
Doripenem NOT cover MRSA,
Ertapenem Mycoplasma, and
some Pseudomonas)
Aztreonam Aztreonam Gram-negative rods
(inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis) Aerobes
Difficult-to-treat
hospital-acquired
infections
Polymyxins Polymyxin B Topical gram-negative
Polymyxin E infections
Bacitracin Bacitracin Topical gram-positive
infections
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors
Anti-30S Ribosomal Subunit
Aminoglycosides Gentamicin Severe gram-negative
(bactericidal) Neomycin infections
Amikacin Aerobes only
Tobramycin
Streptomycin
Tetracyclines (bacteriostatic) Tetracycline Chlamydia
Doxycycline Rickettsia
Minocycline Bacteria without
Demeclocycline peptidoglycan cell
walls
Spirochetes
V. cholerae
H. pylori
Anti-50S Ribosomal Subunit
Macrolides Erythromycin Outpatient URI, LRI
Azithromycin Atypical pneumonia
Clarithromycin STDs
Gram-positive cocci
Chloramphenicol Chloramphenicol H. influenzae
(bacteriostatic) Bacterial meningitis
Brain abscess
Bacteroides fragilis
Clindamycin Clindamycin Anaerobes above the
(bacteriostatic) diaphragm
Female GU
TSS
Linezolid (variable) Linezolid Resistant gram-positives
(MRSA, VRE)
Streptogramins Quinupristin VRE
Dalfopristin GAS and S. aureus
skin infections
Note: bacteriocidal
when used together
DNA Synthesis Inhibitors
Fluoroquinolones
(Bactericidal: inhibit DNA gyrase enzyme, inhibiting DNA synthesis)
1st generation Nalidixic acid Gram-negative UTIs
2nd generation Ciprofloxacin Gram-negative UTIs
Norfloxacin Gram-negative GI
Enoxacin tract
Ofloxacin Pseudomonas
Levofloxacin
3rd generation Gatifloxacin As above + gram-
positives
4th generation Moxifloxacin As above + gram-
Gemifloxacin positives + anaerobes
Other DNA Inhibitors
Metronidazole (bacteridical: Metronidazole (Flagyl) Bacteria AND
metabolic byproducts disrupt DNA) protozoa
Anaerobes below the
diaphragm
C. difficile
H. pylori
RNA Synthesis Inhibitors
Rifampin Rifampin TB
(bactericidal: inhibits RNA transcription) Leprosy
H.
influenzae prophylaxis
Antistaphylococcal
Mycolic Acids Synthesis Inhibitors
Isoniazid Isoniazid TB
Latent TB
Folic Acid Synthesis Inhibitors
Sulfonamides Sulfamethoxazole Respiratory (S.
(SMX) pneumoniae, H.
Sulfisoxazole influenzae)
Sulfadiazine GI (enterics)
UTIs
PCP and T. gondii
Trimethoprim Trimethoprim See Sulfonamides
Pyrimethamine Pyrimethamine Malaria
T. gondii
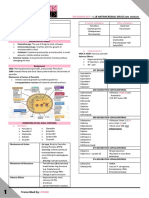
Miscellaneous
Drugs Mechanism of Action Indications and Side Effects
Uncertain mechanism: Part of RIPE therapy
potentially accumulates for TB
in cells dsirupting Can cause
Pyrazinamide
membrane potential and hyperuricemia and
fatty acid synthesis hepatoxicity
Part of RIPE therapy
for TB and used
Inhibits
for M. avium-
arabinosyltransferase
intracellulare
Ethambutol (inhibiting production of
Can cause optic
mycobacterium cell wall)
neuropathy (red-green
color blindness)
Multi-resistant gram-
positives such as
Lipopeptide that disrupts MRSA and VRE
Daptomycin cell membrane Can cause myopathy
(elevated CK and
rhabdomyolysis
You might also like
- Antibiotic Classification & Indications OverviewDocument16 pagesAntibiotic Classification & Indications Overviewdaven100% (1)
- Klasifikasi Dan Mekanisme ABDocument8 pagesKlasifikasi Dan Mekanisme ABDeboyjackNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Classification & Mechanism - Basic Science - OrthobulletsDocument9 pagesAntibiotic Classification & Mechanism - Basic Science - OrthobulletsHossam Elden Helmy HaridyNo ratings yet
- List of Antibiotics: Bactericidal vs BacteriostaticDocument4 pagesList of Antibiotics: Bactericidal vs BacteriostaticMuthu Kumar100% (2)
- AntibioticsDocument4 pagesAntibioticsTan Geok Eng100% (1)
- Cell Wall InhibitorsDocument2 pagesCell Wall InhibitorsSeptember ButterflyNo ratings yet
- Reviewer PcolDocument3 pagesReviewer PcolMycaela Archivido De AlvaNo ratings yet
- AntibacterialsDocument2 pagesAntibacterialsakeelNo ratings yet
- DAFTAR ANTIBIOTIK DAN KERJANYADocument13 pagesDAFTAR ANTIBIOTIK DAN KERJANYAYudistra R ShafarlyNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics Handout ReferenceDocument3 pagesAntibiotics Handout Referencebl9nkverseNo ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases IDocument7 pagesInfectious Diseases ITiff VoNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics ListDocument14 pagesAntibiotics ListBrenda LiawNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Classification Mechanism - Sheet1Document2 pagesAntibiotic Classification Mechanism - Sheet1api-329501044No ratings yet
- Antimikroba Anti Jamur Antiparasit Antibiotik Antiviral Antimico-Bacterium Antimikosis Antihelmintik Antiamuba AntimalariaDocument22 pagesAntimikroba Anti Jamur Antiparasit Antibiotik Antiviral Antimico-Bacterium Antimikosis Antihelmintik Antiamuba AntimalariaHaris GaulNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument8 pagesAntibioticsmohamed mowafeyNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics Quick ReviewDocument5 pagesAntibiotics Quick Reviewpranjl100% (5)
- 2.2.1 - Cell Wall Inhibitors-Introduction - Oct2012-Oct 2019Document30 pages2.2.1 - Cell Wall Inhibitors-Introduction - Oct2012-Oct 2019Frank Dany M'endormir MebeliNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics by Class: Escherichia ColiDocument8 pagesAntibiotics by Class: Escherichia ColiCremona ElenaNo ratings yet
- Drug-Study CefepimeDocument2 pagesDrug-Study Cefepimeprince gonzalesNo ratings yet
- Mecanismo de Accao AntibioticoDocument1 pageMecanismo de Accao Antibioticocassimo2009No ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument5 pagesAntibioticsgitama9904No ratings yet
- Cell Wall Synthesis InhibitorsDocument6 pagesCell Wall Synthesis Inhibitorshoa1212No ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Drugs Summary TableDocument7 pagesAntimicrobial Drugs Summary TableFiona JulietaNo ratings yet
- Resistance To: Antibacterial AgentsDocument15 pagesResistance To: Antibacterial AgentsZeth MoturiNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument4 pagesAntibioticsJan Leanne OrbigosoNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobal Drugs #Dental 1Document30 pagesAntimicrobal Drugs #Dental 1ggNo ratings yet
- Target AB Ke BakteriDocument1 pageTarget AB Ke Bakterimazz.rianNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument2 pagesAntibioticsdewitt.bernardNo ratings yet
- Main Antibiotics Discussed in Pharmacology DocumentDocument117 pagesMain Antibiotics Discussed in Pharmacology DocumentLusi MunawarohNo ratings yet
- Penicinillase - Sensible: Inhibit Clasification AntibioticsDocument1 pagePenicinillase - Sensible: Inhibit Clasification AntibioticsАндрій ДанильцівNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Drugs: Powerpoint Presentations Prepared by Bradley W. Christian, Mclennan Community CollegeDocument35 pagesAntimicrobial Drugs: Powerpoint Presentations Prepared by Bradley W. Christian, Mclennan Community CollegeTiffany Jane Huertas100% (1)
- Antibiotics, The Basics: Classification of Veterinary AntibioticsDocument2 pagesAntibiotics, The Basics: Classification of Veterinary Antibioticsgalihja100% (1)
- Prinsip Biologis dan Klinis Penggunaan AntibiotikDocument66 pagesPrinsip Biologis dan Klinis Penggunaan AntibiotikAnindia LarasatiNo ratings yet
- Anti-Infective Pharmacology ReviewerDocument5 pagesAnti-Infective Pharmacology ReviewerArianne Pearl PrimeroNo ratings yet
- Pharm Drug ListDocument17 pagesPharm Drug Listanon_523534678No ratings yet
- Antibiotic KatsungDocument13 pagesAntibiotic KatsungJeffrey SutedjaNo ratings yet
- Ppra Ab Terapi PDFDocument83 pagesPpra Ab Terapi PDFDIONYSIUS BENINo ratings yet
- Presentation On Penicillin AntibioticsDocument7 pagesPresentation On Penicillin Antibioticsj9pnsj55j5No ratings yet
- Antibiotics - Compleate ClassificationDocument2 pagesAntibiotics - Compleate ClassificationNeal Gupta83% (12)
- Penisilin: Sensitif Terhadap PenicilinaseDocument2 pagesPenisilin: Sensitif Terhadap PenicilinaseSanti ParambangNo ratings yet
- Chart Antibacterial Drugs PDFDocument1 pageChart Antibacterial Drugs PDFMunaf AlsumaryNo ratings yet
- INFORMATION ON Group of ANTIBIOTICSDocument8 pagesINFORMATION ON Group of ANTIBIOTICStarun paulNo ratings yet
- MicrobialsDocument5 pagesMicrobialsMARIEMIL FOLLOSONo ratings yet
- Antibiotics: (Example) Mechanism of Action Cellular Tissue Organ System Indication/s Side Effects ResistanceDocument58 pagesAntibiotics: (Example) Mechanism of Action Cellular Tissue Organ System Indication/s Side Effects ResistanceAdrian SiuNo ratings yet
- Katzung Pharmacology Semester 5 TablesDocument29 pagesKatzung Pharmacology Semester 5 TablesfatimaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyKristelle Joy MontesNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic in Daily Practice IARW 2017Document50 pagesAntibiotic in Daily Practice IARW 2017Benny Chris TantoNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics Chart Antibiotics ChartDocument9 pagesAntibiotics Chart Antibiotics ChartAnaliza Kitongan Lantayan100% (1)
- Antibiotic Classification and MechanismsDocument43 pagesAntibiotic Classification and Mechanismsyoza_kidNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument9 pagesAntibioticsJanie-Vi GorospeNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument2 pagesAntibioticsFamela Anne GOmez MadambaNo ratings yet
- MICROBIO 1.2 Antimicrobial DrugsDocument3 pagesMICROBIO 1.2 Antimicrobial DrugsPatricia Elena ManaliliNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial GroupsDocument13 pagesAntimicrobial GroupsLeichel AlbertoNo ratings yet
- Pharma Notes 3Document10 pagesPharma Notes 3Mayya FirdousNo ratings yet
- Notes Diagnostic MicrobiologyDocument7 pagesNotes Diagnostic MicrobiologyTae KimNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument5 pagesAntibioticsLaureece Salm ApduhanNo ratings yet
- Cell Wall Inhibitors (2t)Document3 pagesCell Wall Inhibitors (2t)Vivian VillaNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic classification by mechanism and indicationsDocument7 pagesAntibiotic classification by mechanism and indicationsVicky Xie100% (1)
- Antibiotics in Periodontal DiseaseDocument57 pagesAntibiotics in Periodontal DiseaseReshmaaRajendranNo ratings yet
- Adult Infectious Disease Bulletpoints HandbookFrom EverandAdult Infectious Disease Bulletpoints HandbookRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- Yale Histo ChecklistDocument1 pageYale Histo ChecklistAlexa TimNo ratings yet
- DIT Solid Pharm ChecklistDocument2 pagesDIT Solid Pharm ChecklistAlexa TimNo ratings yet
- Usmle Step 2 CK Exp-PashaDocument6 pagesUsmle Step 2 CK Exp-PashaAlexa TimNo ratings yet
- SIFARSHAT - Secrets To 260s.abdullah Umer Rehan 263 Step1Document8 pagesSIFARSHAT - Secrets To 260s.abdullah Umer Rehan 263 Step1Alexa TimNo ratings yet
- My Step 1 Experience 268 - Sara A KDocument3 pagesMy Step 1 Experience 268 - Sara A KAlexa TimNo ratings yet
- Anti Bit OcsDocument6 pagesAnti Bit OcsAlexa TimNo ratings yet
- 02 PharmacokineticsDocument8 pages02 PharmacokineticsanilmddmNo ratings yet
- GoljanDocument2 pagesGoljanAlexa TimNo ratings yet
- Concepts and stuff that must know for QuestionsDocument1 pageConcepts and stuff that must know for QuestionsAlexa TimNo ratings yet
- Immune Dysfunction and Risk of Infection in CKD - 2019Document8 pagesImmune Dysfunction and Risk of Infection in CKD - 2019Lú VillalobosNo ratings yet
- The building blocks of proteins and their importance for healthDocument1 pageThe building blocks of proteins and their importance for healthMaribel Reyes BathanNo ratings yet
- Focus Life Sciences Grade 10 Exam Practice BookDocument32 pagesFocus Life Sciences Grade 10 Exam Practice BookStars232375% (12)
- The Treatment and Management of Selfharm in Emergency Departments Slide Set Powerpoint 189897661Document41 pagesThe Treatment and Management of Selfharm in Emergency Departments Slide Set Powerpoint 189897661Zorbey TurkalpNo ratings yet
- Pharmacognostic Studies On Stem Bark of Oroxylum IndicumDocument7 pagesPharmacognostic Studies On Stem Bark of Oroxylum IndicumInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Arthropod Mass Rearing and Quality Control: Iobc OilbDocument67 pagesArthropod Mass Rearing and Quality Control: Iobc OilbFranJim FjdNo ratings yet
- Aplasia and Hypoplasia of The Radius Studies On 64 Cases and On Epiphyseal Transplantation in Rabbits With The Imitated DefectDocument154 pagesAplasia and Hypoplasia of The Radius Studies On 64 Cases and On Epiphyseal Transplantation in Rabbits With The Imitated DefectJunji Miller FukuyamaNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About AneurysmsDocument4 pagesEverything You Need to Know About AneurysmsElmer DizonNo ratings yet
- The Business of Biotechnology PDFDocument15 pagesThe Business of Biotechnology PDFYedhaGuerreroNo ratings yet
- 4 Complete Punnett Square LessonDocument39 pages4 Complete Punnett Square Lessonapi-312176473No ratings yet
- Mastectomy (Case Analysis)Document7 pagesMastectomy (Case Analysis)Lester_Ocuaman_2248No ratings yet
- Zhu2012 - Eye AnatomyDocument9 pagesZhu2012 - Eye Anatomytobing704No ratings yet
- The Aspect of Gene TherapyDocument15 pagesThe Aspect of Gene TherapyAbegail Dimaano100% (1)
- As Biology Unit 2 Key Terms and DefinitionsDocument6 pagesAs Biology Unit 2 Key Terms and DefinitionsVIctoriakayNo ratings yet
- Giardia Intestinalis (Giardiasis) : Matthew Washam and Robert W. Frenck, JRDocument7 pagesGiardia Intestinalis (Giardiasis) : Matthew Washam and Robert W. Frenck, JRErick GtrNo ratings yet
- GM Organisms Benefits RisksDocument13 pagesGM Organisms Benefits Risksalem0100% (1)
- Multidisciplinary Management of Hepatocellular CarcinomaDocument45 pagesMultidisciplinary Management of Hepatocellular CarcinomaSalmanArifNo ratings yet
- Comparative - Study - of - The - Major - Component Indigofera PDFDocument9 pagesComparative - Study - of - The - Major - Component Indigofera PDFNur AishaNo ratings yet
- 4 6001055797780414555 PDFDocument245 pages4 6001055797780414555 PDFAtomNo ratings yet
- Mono - Betaine Betaine Hydrochloride - EnglishDocument9 pagesMono - Betaine Betaine Hydrochloride - EnglishTom DelongeNo ratings yet
- ArticlesDocument955 pagesArticlesMuhammad ChohanNo ratings yet
- Phrasebank ManchesterDocument25 pagesPhrasebank ManchesterJhai-ki-ChanNo ratings yet
- Hardy-WeinbergEquilibriumSept2012 002 PDFDocument6 pagesHardy-WeinbergEquilibriumSept2012 002 PDFGuntur FaturachmanNo ratings yet
- FAO Guidance of Embryo TransferDocument153 pagesFAO Guidance of Embryo TransferscribdsunflowerNo ratings yet
- Scenar DosesDocument4 pagesScenar DosesElizabeth Fernandez100% (2)
- Test Bank For Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology 6th Edition by MahonDocument8 pagesTest Bank For Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology 6th Edition by MahonShirley Young97% (29)
- Immune Response in The Skin of AgingDocument7 pagesImmune Response in The Skin of AgingInmunoBlogNo ratings yet
- M. Preterm and Postterm - NewDocument93 pagesM. Preterm and Postterm - NewRinaNo ratings yet
- МартDocument55 pagesМартLuisAngelPonceTorresNo ratings yet
- CancerEpi PDFDocument441 pagesCancerEpi PDFMark EbrahimNo ratings yet