Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NGN
Uploaded by
m rauf tabassumOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NGN
Uploaded by
m rauf tabassumCopyright:
Available Formats
NGN
a next generation network is a packet-based network that can be used for both
telephony and data and that supports mobilility. Initially, the term Next
Generation Network was used to refer to the transformation of the core network to
IP. Sometimes a NGN is referred to as an all-IP network.
The ITU defined an NGN as:
A Next Generation Network (NGN) is a packet-based network able to provide services
including Telecommunication Services and able to make use of multiple broadband,
QoS-enabled transport technologies and in which service-related functions are
independent from underlying transport-related technologies. It offers unrestricted
access by users to different service providers. It supports generalized mobility
which will allow consistent and ubiquitous provision of services to users.
The NGN is characterized by the following fundamental aspects:
Packet-based transfer
Separation of control functions among bearer capabilities, call/session, and
application/ service
Decoupling of service provision from network, and provision of open interfaces
Support for a wide range of services, applications and mechanisms based on service
building blocks (including real time/ streaming/ non-real time services and multi-
media)
Broadband capabilities with end-to-end QoS and transparency
Interworking with legacy networks via open interfaces
Generalized mobility
Unrestricted access by users to different service providers
A variety of identification schemes which can be resolved to IP addresses for the
purposes of routing in IP networks
Unified service characteristics for the same service as perceived by the user
Converged services between Fixed/Mobile
Independence of service-related functions from underlying transport technologies
Compliant with all Regulatory requirements, for example concerning emergency
communications and security/privacy, etc.
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
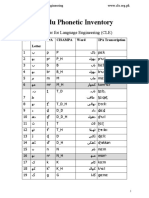
- Urdu Phonetic Inventory ChartDocument4 pagesUrdu Phonetic Inventory Chartm rauf tabassumNo ratings yet
- Building Brand Image Through Event Sponsorship: The Role of Image TransferDocument12 pagesBuilding Brand Image Through Event Sponsorship: The Role of Image Transferm rauf tabassumNo ratings yet
- DS LabDocument94 pagesDS LabanandreddyrNo ratings yet
- Matlab ManualDocument7 pagesMatlab ManualMoosa NaseerNo ratings yet
- Data Structure Lab ManualDocument48 pagesData Structure Lab ManualKavitha RaniNo ratings yet
- Urdu Phonetic InventoryDocument4 pagesUrdu Phonetic Inventorym rauf tabassum100% (2)
- AridDocument1 pageAridm rauf tabassumNo ratings yet
- Advance Operating System: Submitted byDocument7 pagesAdvance Operating System: Submitted bym rauf tabassumNo ratings yet
- FYP Report FormatDocument34 pagesFYP Report Formatm rauf tabassumNo ratings yet
- VLANDocument1 pageVLANm rauf tabassumNo ratings yet
- What Is DSLAM?Document6 pagesWhat Is DSLAM?m rauf tabassumNo ratings yet
- Expression Class (System - Linq.expression)Document24 pagesExpression Class (System - Linq.expression)m rauf tabassumNo ratings yet
- The OSI Reference Model ExplainedDocument10 pagesThe OSI Reference Model Explainedm rauf tabassumNo ratings yet
- What Is DSL?: Figure 1: Common Type of XDSLDocument8 pagesWhat Is DSL?: Figure 1: Common Type of XDSLm rauf tabassumNo ratings yet
- Temp CPPDocument1 pageTemp CPPm rauf tabassumNo ratings yet
- Frame (Networking) - WikipediaDocument2 pagesFrame (Networking) - Wikipediam rauf tabassumNo ratings yet
- What is a VLAN? Virtual LAN explainedDocument1 pageWhat is a VLAN? Virtual LAN explainedm rauf tabassumNo ratings yet
- Concurrency ControlDocument24 pagesConcurrency Controlm rauf tabassumNo ratings yet
- The OSI Reference Model ExplainedDocument10 pagesThe OSI Reference Model Explainedm rauf tabassumNo ratings yet