Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ch4 Problems
Uploaded by
Sary Kilany0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pagesOriginal Title
ch4_problems.doc
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pagesch4 Problems
Uploaded by
Sary KilanyCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
4.7 In order to compute composition, in atom percent, of a 92.5 wts Ag-7.5 wie Cu alloy, we employ
Equation 4.6 as,
¢
Chg "= atte x 100
Cradew “Couns
z (092.5463.58 g/mol) isto
CLINGS g/mol) + 750787 el mel)
= 87.9 a1%
Cond
— eae ss
Cagteu*Keudag
(7.500787 g/mol) .
(©2.5(63.55 g/mol) + (7.510787 / mo)
100
= 12.1 a%
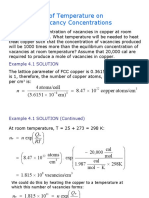
4.1 In order to compute the fraction of atom sites that are vacant in copper at 1357 K, we must employ
Equation 4.1. As stated in the problem, Q, = 0.90 eV/atom. ‘Thus,
0.90 eV /atomn
€V/atom-K) (1357 &)
=4.86x 10"
42 Determination of the number of vacancies per cubie meter in gold at 900°C (1173 K) requires the
utilization of Equations 4.1 and 4.2 as follows.
W, ~ Nexp
= 6028 + WA soms imo (1868 sven!)
1969 #/ mol Ges 0
0.98 eV atom
eV /atom—K) (1173 K)
2 x 10! cm = 3,52 10% ar
44 In this problem we are asked to cite which of the elements listed form with Ni the thee possible solid
solution types. For complete substitutional solubility the following criteria must be met: 1) the difference in atomic
radii between Ni and the other element (AR%) must be less than £15%, 2) the crystal stictares mast be the same,
3) the electronegativities must be similar, and 4) the valences should be the same, or nearly the same. Below are
tabulated, for the various elements, these criteria.
Crystal ABlectro=
Element ARY% Structue negativity Valence
Ni Fcc &
c 8
H 83
oO 52
Ag +16 FOC +01 ia
Al +15 FOC 03 #
Co +06 HCP 0 »
cr +02 Bec 02 Be
Fe 4 BCC 0 »
Pt +l FOC +04 »
Za 4 HCP 02 »
(a) Pris the only element that meets all of the criteria and thus forms a substitutional solid solution having
complete solubility, At elevated temperatures Co and Fe experience allotropic transformations to the ECC crystal
structure and thus display complete solid solubility at these temperatures.
(b) Ag. Al. Co, Cr, Fe, and Za form substitutional solid solutions of incomplete solubility. All these metals
have either BCC or HCP crystal structures, andlor the difference between their atomic radii and that for Ni are
‘greater than +15%, and/or have a valence different than 2+.
(© C, H, and O form interstitial solid solutions, These elements have atomic radi that are significantly
smaller than the atomic radius of Ni.
You might also like
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Ch2 BondingDocument31 pagesCh2 BondingSary KilanyNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Ch2 BondingDocument31 pagesCh2 BondingSary KilanyNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- XRD Peakpositions PDFDocument17 pagesXRD Peakpositions PDFSary KilanyNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- ch19 Thermal PropertiesDocument15 pagesch19 Thermal PropertiesSary KilanyNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- ch12 Ppts Callister7eDocument36 pagesch12 Ppts Callister7eSary KilanyNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Ch19 ProblemsDocument3 pagesCh19 ProblemsSary KilanyNo ratings yet
- Phys 371: Materials Physics Introduction To Materials Science)Document27 pagesPhys 371: Materials Physics Introduction To Materials Science)Sary KilanyNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- ch6 Mechanical Pro of MetalsDocument27 pagesch6 Mechanical Pro of MetalsSary KilanyNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- ch3 p1Document42 pagesch3 p1Sary KilanyNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- ch04 ImperfectionsDocument33 pagesch04 ImperfectionsSary KilanyNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- ch3 p2Document27 pagesch3 p2Sary KilanyNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- ch6 ExamplesDocument9 pagesch6 ExamplesSary KilanyNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- CH5 - Diffusion: Selected Problems Callister 7 EditDocument3 pagesCH5 - Diffusion: Selected Problems Callister 7 EditSary KilanyNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- ch4 ExamplesDocument11 pagesch4 ExamplesSary KilanyNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- ch3 Peak IndexingDocument12 pagesch3 Peak IndexingSary KilanyNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- ch3 ProblemsDocument3 pagesch3 ProblemsSary KilanyNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Ch2 ProblemsDocument5 pagesCh2 ProblemsSary KilanyNo ratings yet
- ch3 p3Document18 pagesch3 p3Sary KilanyNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)