Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gupta
Uploaded by
Namdev SuryawanshiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gupta
Uploaded by
Namdev SuryawanshiCopyright:
Available Formats
Gupta http://www.theindianpractitioner.com/index.php/tip/rt/prin...
Correlation between the Sputum Bacteriology and Lung Function in
Patients with Stable Bronchiectasis
K. B. Gupta, S. Vishvkarma, A. S. Sandhya, S. Magu, U. Choudhary, M. Gupta
Abstract
Rationale: To study the correlation between the sputum bacteriology and lung function in patients with stable
bronchiectasis.
Materials and Methods: 80 patients suffering from stable bronchiectasis belonging to both the sexes and age
above 14 years were included in study. All patients were assessed clinically with detailed history and thorough
clinical examination. Patients were subjected to assessment of microbiological flora in their sputum. Lung
functions were measured with spirometry and parameters recorded were PEFR in l/min, FEV1 in litres, FVC in
litres, and FEV1/FVC. Sputum samples of +1 and +2 grade were inoculated on blood agar, MacConkey's agar
and chocolate agar at 37C for 48 hours.
Results: P aeruginosa was seen as the most common colonizing bacteria and these patients had de-creased %
predicted FEV1, FVC, FEV1/FVC and PEFR with mean values of 43.6114.6, 51.8716.8, 79.8314.6,
42.1714.6 respectively as compared to patients of non P aeruginosa group. The % predicted FEV1, FVC,
FEV1/FVC and PEFR in non P aeruginosa group were 47.6721.8, 59.3222.8, 81.8917.7, 49.5821.7
respectively. Though the values of FEV1, FVC, FEV1/FVC and PEFR in P aeruginosa group were decreased they
were not statistically significant.
Conclusion: P aeruginosa was the main colonizing bacteria especially in patients having air fluid levels on
radiology which can also be a predictor of bacterial colonization. Lung functions were de-creased in patients
having P Aeruginosa in their sputum as compared to non P Aeruginosa group but they were statistically not
significant.
1 of 1 7/23/17, 8:16 PM
You might also like
- Assay of Protein and Polypeptide Hormones: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied Biology Modern Trends in Physiological SciencesFrom EverandAssay of Protein and Polypeptide Hormones: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied Biology Modern Trends in Physiological SciencesNo ratings yet
- Dingemans 2018Document9 pagesDingemans 2018angelica barrazaNo ratings yet
- Lung Transplantation: Evolving Knowledge and New HorizonsFrom EverandLung Transplantation: Evolving Knowledge and New HorizonsGanesh RaghuNo ratings yet
- Patients With Non-Cystic Fibrosis Bronchiectasis: A Retrospective StudyDocument8 pagesPatients With Non-Cystic Fibrosis Bronchiectasis: A Retrospective StudyKarito FloresNo ratings yet
- Aspergilus 2015 CFDocument8 pagesAspergilus 2015 CFLudmila BalanetchiNo ratings yet
- 792 FullDocument9 pages792 Fullwinter wineNo ratings yet
- Laryngeal Measurements and Diagnostic Tools For Diag-Nosis of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument4 pagesLaryngeal Measurements and Diagnostic Tools For Diag-Nosis of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseBudi RiyantoNo ratings yet
- AMJ-Volume 50-Issue 2 - Page 1489-1496Document8 pagesAMJ-Volume 50-Issue 2 - Page 1489-1496Pandu Putra Wijaya RestaNo ratings yet
- Reflux and LaryngitisDocument7 pagesReflux and LaryngitisyannecaNo ratings yet
- Snijders 2007Document6 pagesSnijders 2007carlaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Kekerapan Esofagitis-Dr - AgusDocument15 pagesJurnal Kekerapan Esofagitis-Dr - AgusJamaluddin Ahmad100% (1)
- Bronkiolitis AkutDocument10 pagesBronkiolitis AkutNamira Firdha KNo ratings yet
- Value of Pneumococcal PCR in Respiratory Samples For Exclusion of PneumococcalDocument5 pagesValue of Pneumococcal PCR in Respiratory Samples For Exclusion of PneumococcalWilliam BarreraNo ratings yet
- 2211-Article Text-8778-10260-10-20230620Document8 pages2211-Article Text-8778-10260-10-20230620IdmNo ratings yet
- 178 PDFDocument6 pages178 PDFmanalNo ratings yet
- s41598 018 26327 2 PDFDocument13 pagess41598 018 26327 2 PDFRegina Dwindarti DarostyNo ratings yet
- 1685 6467 1 PBDocument6 pages1685 6467 1 PBnurmaya sariNo ratings yet
- Is Pepsin Detected in The Saliva of Patients Who Experience Pharyngeal Reflux?Document5 pagesIs Pepsin Detected in The Saliva of Patients Who Experience Pharyngeal Reflux?anon_740277752No ratings yet
- The Positive Result of Cytology Brushing at Flexible Fiberoptic Bronchoscopy Compared With Transthoracic Needle Aspiration in Central Lung TumorDocument10 pagesThe Positive Result of Cytology Brushing at Flexible Fiberoptic Bronchoscopy Compared With Transthoracic Needle Aspiration in Central Lung TumorBayuptrNo ratings yet
- Cap AsmaDocument10 pagesCap AsmaAuliaNo ratings yet
- Eosinophilic Bronchitis Is An Important Cause of Chronic CoughDocument5 pagesEosinophilic Bronchitis Is An Important Cause of Chronic CoughNurfitrianti ArfahNo ratings yet
- Aetiology in Adult Patients With Bronchiectasis: A. Shoemark, L. Ozerovitch, R. WilsonDocument8 pagesAetiology in Adult Patients With Bronchiectasis: A. Shoemark, L. Ozerovitch, R. WilsonIrina VolosciucNo ratings yet
- Bacterial and Viral Infection in Patients Hospitalized For Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Implication For Antimicrobial-1Document10 pagesBacterial and Viral Infection in Patients Hospitalized For Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Implication For Antimicrobial-1Ayu SusiyanthiNo ratings yet
- BB LampDocument5 pagesBB LampMay NguyenNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory Phenotypes in Patients With Severe Asthma Are Associated With Distinct Airway MicrobiologyDocument25 pagesInflammatory Phenotypes in Patients With Severe Asthma Are Associated With Distinct Airway MicrobiologykiaNo ratings yet
- Impact of Immunoglobulin E and Airway Obstruction On BronchiectasisDocument7 pagesImpact of Immunoglobulin E and Airway Obstruction On BronchiectasisRichie Irvanto CiandraNo ratings yet
- Li 33 135Document5 pagesLi 33 135Citra CesiliaNo ratings yet
- Ficha 5Document12 pagesFicha 5mariaNo ratings yet
- Utilizing Pulmonary Function Parameters To Predict Dysphagia in Individuals With Cervical Spinal Cord InjuriesDocument9 pagesUtilizing Pulmonary Function Parameters To Predict Dysphagia in Individuals With Cervical Spinal Cord InjuriesElsie Dyana Pretty StephanieNo ratings yet
- Non-Invasive Assessment Determine The Swallowing and RespirationDocument6 pagesNon-Invasive Assessment Determine The Swallowing and RespirationDaniela OrtizNo ratings yet
- Validation of Nasal Tracheal Aspiration in Children With Lung DiseaseDocument12 pagesValidation of Nasal Tracheal Aspiration in Children With Lung DiseaseMega ArfiyantiNo ratings yet
- Cytological Analysis of Bronchial Washings in RSUD Pasar MingguDocument8 pagesCytological Analysis of Bronchial Washings in RSUD Pasar MingguReza DigambiroNo ratings yet
- PIIS0091674921017978Document10 pagesPIIS0091674921017978Diane Lois ManicdaoNo ratings yet
- Chaud Huri 2015Document6 pagesChaud Huri 2015Fakhriyah Dwi Amirah KhalidNo ratings yet
- 3013 11254 1 PB PDFDocument6 pages3013 11254 1 PB PDFRenanda PrihastinaNo ratings yet
- Proteína C Reactiva en Suero Como Complemento de La Identificación de Derrames Paraneumónicos ComplicadosDocument5 pagesProteína C Reactiva en Suero Como Complemento de La Identificación de Derrames Paraneumónicos ComplicadosLulú García VargasNo ratings yet
- 55.wilson1989pharyngoesophageal DysmotilityDocument5 pages55.wilson1989pharyngoesophageal DysmotilityWahyu JuliandaNo ratings yet
- MainDocument10 pagesMainmuthiaNo ratings yet
- A Study of Efficiency of Breathing Exercises To Improve Pulmonary FX in SCi PtsDocument6 pagesA Study of Efficiency of Breathing Exercises To Improve Pulmonary FX in SCi PtsMarion AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Laboratory Testing Methods For The Diagnosis of Tuberculous Pleurisy in ChinaDocument5 pagesComparison of Laboratory Testing Methods For The Diagnosis of Tuberculous Pleurisy in ChinaclaryntafreyaaNo ratings yet
- Bronchoscopic Procedures During COVID-19 PandemicDocument8 pagesBronchoscopic Procedures During COVID-19 PandemicwantoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory MethodDocument6 pagesLaboratory MethodSyifa SariNo ratings yet
- Bronchoscopy in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients - Findings, Microbiological Profile, and CoinfectionDocument5 pagesBronchoscopy in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients - Findings, Microbiological Profile, and CoinfectionJeisson Osorio TrujilloNo ratings yet
- Characterization of Pediatric Patients Diagnosed With Post-Infectious Bronchiolitis Obliterans 2600 Meters Above Sea LevelDocument8 pagesCharacterization of Pediatric Patients Diagnosed With Post-Infectious Bronchiolitis Obliterans 2600 Meters Above Sea LevelazevedoNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis With Chronic Pulmonary AspergilosisDocument4 pagesPulmonary Tuberculosis With Chronic Pulmonary AspergilosisfirdaNo ratings yet
- 10 1080@02770903 2020 1805750Document19 pages10 1080@02770903 2020 1805750locolocomedicinaNo ratings yet
- How Does Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Affect The Progression of Bronchiectasis - 1Document6 pagesHow Does Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Affect The Progression of Bronchiectasis - 1Brenda EstradaNo ratings yet
- Buku Modul Kuliah KewarganegaraanDocument4 pagesBuku Modul Kuliah KewarganegaraanYunita KimNo ratings yet
- BMJ c4978 FullDocument6 pagesBMJ c4978 Fulljesusm_115No ratings yet
- Airway Sensory Nerves in Asthma-Targets For TherapyDocument18 pagesAirway Sensory Nerves in Asthma-Targets For TherapySaraNo ratings yet
- The Positive Result of Cytology Brushing at Flexible Fiberoptic Bronchoscopy Compared With Transthoracic Needle Aspiration in Central Lung TumorDocument10 pagesThe Positive Result of Cytology Brushing at Flexible Fiberoptic Bronchoscopy Compared With Transthoracic Needle Aspiration in Central Lung TumorKezzia Putri WazaneNo ratings yet
- Airway-Centered Fibroelastosis 2016Document8 pagesAirway-Centered Fibroelastosis 2016Edoardo CavigliNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis With Chronic Pulmonary Aspergilosis: Patient Had No Fever, Neither Chest Pain, Nor Night SweatsDocument4 pagesPulmonary Tuberculosis With Chronic Pulmonary Aspergilosis: Patient Had No Fever, Neither Chest Pain, Nor Night SweatsfirdaNo ratings yet
- AnthracosisDocument8 pagesAnthracosisNaveed AhamedNo ratings yet
- Eosinophilic Inflammation in Cough Variant Asthma: A. Niimi, R. Amitani, K. Suzuki, E. Tanaka, T. Murayama, F. KuzeDocument6 pagesEosinophilic Inflammation in Cough Variant Asthma: A. Niimi, R. Amitani, K. Suzuki, E. Tanaka, T. Murayama, F. KuzeYediftrisnawan 1995No ratings yet
- Summary of DNB ThesisDocument3 pagesSummary of DNB Thesismugesh mc mugesh mcNo ratings yet
- Reflux Laryngitis: An Update, 2009-2012: Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and Ylancaster, CaliforniaDocument9 pagesReflux Laryngitis: An Update, 2009-2012: Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and Ylancaster, CaliforniaJaime Crisosto AlarcónNo ratings yet
- Pepsi NaDocument11 pagesPepsi NaOscar OsorioNo ratings yet
- A Randomized Trial of Convalescent Plasma in Covid-19 Severe PneumoniaDocument11 pagesA Randomized Trial of Convalescent Plasma in Covid-19 Severe PneumoniaChintia GautamaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Accuracy of Xpert MTB/RIF On Bronchoscopy Specimens in Patients With Suspected Pulmonary TuberculosisDocument6 pagesDiagnostic Accuracy of Xpert MTB/RIF On Bronchoscopy Specimens in Patients With Suspected Pulmonary TuberculosisMARTIN FRANKLIN HUAYANCA HUANCAHUARENo ratings yet
- CSSDDocument6 pagesCSSDNamdev SuryawanshiNo ratings yet
- Cbse - Neet Test 2017 ResultsDocument1 pageCbse - Neet Test 2017 ResultsNamdev SuryawanshiNo ratings yet
- CSSD Policy1Document58 pagesCSSD Policy1Namdev Suryawanshi100% (1)
- Cleaning Hand Washing With Chlorine PowderDocument1 pageCleaning Hand Washing With Chlorine PowderNamdev SuryawanshiNo ratings yet
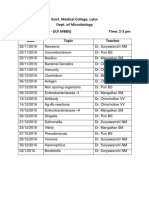
- Govt. Medical College, Latur Dept. of Microbiology Lecture Time Table - (II/I MBBS) Time: 2-3 PMDocument1 pageGovt. Medical College, Latur Dept. of Microbiology Lecture Time Table - (II/I MBBS) Time: 2-3 PMNamdev SuryawanshiNo ratings yet
- Govt. Medical College, Latur Dept. of Microbiology Lecture Time Table - (II/I MBBS) Time: 2-3 PMDocument1 pageGovt. Medical College, Latur Dept. of Microbiology Lecture Time Table - (II/I MBBS) Time: 2-3 PMNamdev SuryawanshiNo ratings yet
- Operation Theatre Sterilization and DisinfectionDocument9 pagesOperation Theatre Sterilization and DisinfectionNamdev Suryawanshi100% (2)
- Research MethodologyDocument1 pageResearch MethodologyNamdev SuryawanshiNo ratings yet
- Miscellaneous VirusesDocument36 pagesMiscellaneous VirusesNamdev Suryawanshi50% (2)
- Review of Literature Asnacjfs, Vukfefbjkvsgdvxvxv Kksa, Dadac Nadjdd NadbaDocument1 pageReview of Literature Asnacjfs, Vukfefbjkvsgdvxvxv Kksa, Dadac Nadjdd NadbaNamdev SuryawanshiNo ratings yet
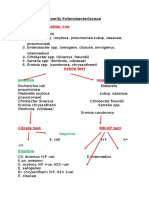
- Family EnterobacteriaceaeDocument2 pagesFamily EnterobacteriaceaeNamdev SuryawanshiNo ratings yet
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (28)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDFrom EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (404)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (81)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningFrom EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)From EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)No ratings yet
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (44)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlFrom EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (58)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- Dark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingFrom EverandDark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1138)
- Troubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassFrom EverandTroubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (27)