Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transport of Substances Through Cell Membranes
Uploaded by
Concepcion R. Aquino0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesThis document summarizes different methods of transporting substances through cell membranes, including diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis, and active transport. It discusses the roles of membrane proteins like channels and pumps in these transport processes. It also explains membrane potentials and action potentials, focusing on how ion gradients established by the sodium-potassium pump generate the resting membrane potential and how voltage-gated ion channels produce and propagate nerve action potentials.
Original Description:
phys
Original Title
Lecture 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes different methods of transporting substances through cell membranes, including diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis, and active transport. It discusses the roles of membrane proteins like channels and pumps in these transport processes. It also explains membrane potentials and action potentials, focusing on how ion gradients established by the sodium-potassium pump generate the resting membrane potential and how voltage-gated ion channels produce and propagate nerve action potentials.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesTransport of Substances Through Cell Membranes
Uploaded by
Concepcion R. AquinoThis document summarizes different methods of transporting substances through cell membranes, including diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis, and active transport. It discusses the roles of membrane proteins like channels and pumps in these transport processes. It also explains membrane potentials and action potentials, focusing on how ion gradients established by the sodium-potassium pump generate the resting membrane potential and how voltage-gated ion channels produce and propagate nerve action potentials.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Lecture 2
TRANSPORT OF SUBSTANCES THROUGH CELL MEMBRANES
THE LIPID BARRIER OF THE CELL MEMBRANE & CELL MEMBRANE TRASNPORT PROTEINS
- review of the lipid barrier of the cell membrane
- transport proteins
- diffusion versus active transport
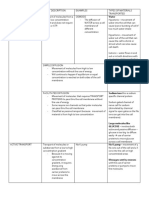
DIFFUSION
DIFFUSION THROUGH THE CELL MEMBRANE
Diffusion of lipid-soluble substances through lipid bilayer
Diffusion of water & other lipid-insoluble molecules through protein channels
DIFFUSION THROUGH PROTEIN PORES & CHANNELS
Selective permeability of protein channels
Gating of protein channels
FACILITATED DIFFUSION
Factors that affect net rate of diffusion
OSMOSIS
ACTIVE TRANSPORT OF SUBSTANCES THROUGH MEMBRANES
PRIMARY ACTIVE TRANSPORT
SECONDARY ACTIVE TRANSPORT
Co-transport of glucose and amino acid
Sodium counter transport of calcium & hydrogen ions
ACTIVE TRANSPORT THROUGH CELLULAR SHEETS
MEMBRANE POTENTIALS & ACTION POTENTIALS
BASIC PHYSICS OF MEMBRANE POTENTIAL
Diffusion potential caused by an ion concentration difference on the 2 sides of the membrane
Relation of the diffusion potential to the concentration difference the Nernst potential
RESTING MEMBRANE POTENTIAL
Active transport of sodium and potassium ions through the membrane Na-K Pump
Leakage of potassium through the nerve membrane
ORIGIN OF THE NORMAL RMP
Contribution of the potassium diffusion potential
Contribution of sodium diffusion through the nerve membrane
Contribution of the Na-pump
NERVE ACTION POTENTIAL
Resting stage
Depolarization stage
Volatage-gated sodium channel activation and inactivation of the channel
Repolarization Stage
Volatage-gated potassium channel & its activation
Role of calcium ions
PROPAGATION OF ACTION POTENTIAL
Direction of propagation
All-or-Nothing Principle
RE-ESTABLISHING SODIUM & POTASSIUM IONIC GRADIENTS AFTER ACTION POTENTIALS ARE
COMPLETED
PLATEAU IN SOME ACTION POTENTIAL
You might also like
- Channels, Carriers, and Pumps: An Introduction to Membrane TransportFrom EverandChannels, Carriers, and Pumps: An Introduction to Membrane TransportNo ratings yet
- Physiology Chap4 (Transport of Substances Through Cell Membrane)Document5 pagesPhysiology Chap4 (Transport of Substances Through Cell Membrane)Man Dejelo100% (1)
- Chapter 3 Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneDocument24 pagesChapter 3 Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneKeith ConneryNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 - The Cellular Level of OrganizationDocument82 pagesCHAPTER 3 - The Cellular Level of OrganizationMarin Jr., Reynaldo J.No ratings yet
- MembraneDocument34 pagesMembraneAhmad2301306No ratings yet
- Cellular TransportDocument30 pagesCellular TransportShreya ChakrobortyNo ratings yet
- Topical Review: Membrane BiologyDocument20 pagesTopical Review: Membrane BiologyHei MistoireNo ratings yet
- Chapter 004Document52 pagesChapter 004Esteban Tabares GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Bio 11 Lecture Notes Lecture 5: Cell Membrane Structure and TransportDocument3 pagesBio 11 Lecture Notes Lecture 5: Cell Membrane Structure and TransportNiña Claire BahinNo ratings yet
- 02 Cell1Document42 pages02 Cell1Keith CheangNo ratings yet
- Water and Electrolytes Final NASPGHANDocument42 pagesWater and Electrolytes Final NASPGHANsankarNo ratings yet
- Movement of Substances Across The Plasma Membrane: Compiled & Prepared by Dsalleh (2021)Document25 pagesMovement of Substances Across The Plasma Membrane: Compiled & Prepared by Dsalleh (2021)Dewi SallehNo ratings yet
- Paper No and Title 15: Bioinorganic Chemistry Module No and Title 8: Ion Transport Through Cell Membrane and Na /K Pump Module Tag CHE - P15 - M8Document9 pagesPaper No and Title 15: Bioinorganic Chemistry Module No and Title 8: Ion Transport Through Cell Membrane and Na /K Pump Module Tag CHE - P15 - M8kottooranjohnbNo ratings yet
- Bio 122 Lec 1.2Document4 pagesBio 122 Lec 1.2Jara RogacionNo ratings yet
- Transport Membrane (Lengkap)Document53 pagesTransport Membrane (Lengkap)Isma Suss LolaloadingNo ratings yet
- Ch. 8-Transport Across Membranes - Overcoming The Permeability BarrierDocument20 pagesCh. 8-Transport Across Membranes - Overcoming The Permeability Barriernkorkmaz1357No ratings yet
- 11-1. Structure/Function of The Plasma Membrane: Topic 11-1 1Document22 pages11-1. Structure/Function of The Plasma Membrane: Topic 11-1 1sssfirengNo ratings yet
- Movement of Substance Across The MembraneDocument47 pagesMovement of Substance Across The MembranenoralizaaliNo ratings yet
- Movement of Substances Across The Plasma Membrane: Active TransportDocument41 pagesMovement of Substances Across The Plasma Membrane: Active Transportaida maroNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: 7-Membranes & TransportDocument53 pagesBiochemistry: 7-Membranes & Transportkhalito1991No ratings yet
- Cell Membrane TransportDocument48 pagesCell Membrane TransportFatima Ahmed CheemaNo ratings yet
- 2 TransportDocument36 pages2 Transportapi-19916399No ratings yet
- 6 Cell Membrane-Sv22Document41 pages6 Cell Membrane-Sv22ThiệnÂnDươngNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - 1 - ForeignerDocument35 pagesChapter 2 - 1 - Foreignerapi-19916399No ratings yet
- AS Biology, Cell Membranes and Transport 1Document48 pagesAS Biology, Cell Membranes and Transport 1Numan TariqNo ratings yet
- Wa0009.Document20 pagesWa0009.Anchal YadavNo ratings yet
- 3 Cell Physiology Transport Across The Membranes F21 MOODLEDocument28 pages3 Cell Physiology Transport Across The Membranes F21 MOODLEraman grewalNo ratings yet
- The Movement of Substances Across The Plasma Membrane.: EnterDocument13 pagesThe Movement of Substances Across The Plasma Membrane.: EnterUdeyaTarshiniy Cïñü UdeyaSurianNo ratings yet
- Transport of Substance (Autosaved)Document32 pagesTransport of Substance (Autosaved)Mary AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Facilitated DiffusionDocument15 pagesFacilitated DiffusionShaaru TharshiniNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane TransportDocument47 pagesCell Membrane TransportBeyhNo ratings yet
- Transport Mechanism SendDocument14 pagesTransport Mechanism Sendchloe rederrickNo ratings yet
- Cell-Transport (From Prof)Document39 pagesCell-Transport (From Prof)Rhea Anne DemoticaNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane TransportDocument49 pagesCell Membrane TransportgamalsolimanNo ratings yet
- Membrane Transport: Medical English 2 Dora ŠeketaDocument12 pagesMembrane Transport: Medical English 2 Dora ŠeketaDora ŠeketaNo ratings yet
- Physiology TransDocument8 pagesPhysiology TranschayChay gapolNo ratings yet
- 05 Membrane Transport VDocument27 pages05 Membrane Transport Vmaksud alaNo ratings yet
- Nota Biologi Tingkatan 4 BAB 3Document12 pagesNota Biologi Tingkatan 4 BAB 3Firas Muhammad50% (4)
- 1.4 Membrane TransportDocument8 pages1.4 Membrane TransportmariamNo ratings yet
- Cell Physiology 1.Document3 pagesCell Physiology 1.Raj SinghNo ratings yet
- Transmembrane Transport of Small Ions and MoleculesDocument42 pagesTransmembrane Transport of Small Ions and MoleculesGolden ChildNo ratings yet
- Practical Work 3Document7 pagesPractical Work 3Achraf RabadiNo ratings yet
- Plasma-Membrane-Structure-And-Function EP DKP 23102020Document40 pagesPlasma-Membrane-Structure-And-Function EP DKP 23102020umar hafizNo ratings yet
- 1 Ion Channel - Pertemuan 8-MhsDocument35 pages1 Ion Channel - Pertemuan 8-MhsDwi Amalia husnaNo ratings yet
- 2014 Molecular Kinetic of DrugsDocument49 pages2014 Molecular Kinetic of DrugsDarry AprilioNo ratings yet
- Government College University Faisalabad Department of Bio-Information and BiotechnologyDocument5 pagesGovernment College University Faisalabad Department of Bio-Information and BiotechnologyShahzad Ahmad NomanNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Cells TYPE OF TRANSPORTDocument1 page2.2 Cells TYPE OF TRANSPORTjmd5qbmt4kNo ratings yet
- 4 - Membrane PhysiologyDocument31 pages4 - Membrane PhysiologysadaffardoosNo ratings yet
- Membrane Potential and Action PotentialDocument30 pagesMembrane Potential and Action Potentialironik kimiaNo ratings yet
- Neural Conduction and Synaptic TransmissionDocument87 pagesNeural Conduction and Synaptic TransmissionRose BernardoNo ratings yet
- SHS.108.Lect-10 Tubular ReabsorptionDocument61 pagesSHS.108.Lect-10 Tubular ReabsorptionAzlan YasirNo ratings yet
- S.N. Character Active Transport Passive TransportDocument2 pagesS.N. Character Active Transport Passive TransportFred SantosNo ratings yet
- TransportDocument45 pagesTransportMuhammad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Biofisika Neuron 2013Document49 pagesBiofisika Neuron 2013Bima Ewando KabanNo ratings yet
- Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneDocument40 pagesMovement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneNorizan DarawiNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane and Cell TransportDocument35 pagesCell Membrane and Cell Transportaayesha.fatima.rajaNo ratings yet
- Membrane Transport: Dr. Kevin AhernDocument32 pagesMembrane Transport: Dr. Kevin AhernYumeChanNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane and TransportDocument31 pagesCell Membrane and Transportmary balansagNo ratings yet
- 1st Year 2nd Week PHYS Lecture 6 2019 2020Document14 pages1st Year 2nd Week PHYS Lecture 6 2019 2020Ahmed TarekNo ratings yet
- Morbidity April 2022: Aileen Concepcion M. AgustinDocument24 pagesMorbidity April 2022: Aileen Concepcion M. AgustinConcepcion R. AquinoNo ratings yet
- Date and Time: June 23, 2018, 3PM Chief Complaint: Difficulty of Breathing History of Present IllnessDocument3 pagesDate and Time: June 23, 2018, 3PM Chief Complaint: Difficulty of Breathing History of Present IllnessConcepcion R. AquinoNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Kidney Disease: Joel M. Topf, MDDocument20 pagesPolycystic Kidney Disease: Joel M. Topf, MDConcepcion R. AquinoNo ratings yet
- Major Depression and Bipolar Disorder: By: Aileen Concepcion M. AgustinDocument52 pagesMajor Depression and Bipolar Disorder: By: Aileen Concepcion M. AgustinConcepcion R. AquinoNo ratings yet
- Alternative MedicineDocument3 pagesAlternative MedicineConcepcion R. AquinoNo ratings yet
- Which He Initially Termed "Polyglandular Syndrome": Overnight 1mg Dexamethasone Suppression TestDocument2 pagesWhich He Initially Termed "Polyglandular Syndrome": Overnight 1mg Dexamethasone Suppression TestConcepcion R. AquinoNo ratings yet
- ObjectDocument1 pageObjectConcepcion R. AquinoNo ratings yet
- "An Ailment Not To Be Treated" - Earliest ReferenceDocument3 pages"An Ailment Not To Be Treated" - Earliest ReferenceConcepcion R. AquinoNo ratings yet
- Admitting Diagnosis: Chronic Kidney Disease Stage V Secondary To Polycystic Kidney Disease, Ascites Secondary ToDocument7 pagesAdmitting Diagnosis: Chronic Kidney Disease Stage V Secondary To Polycystic Kidney Disease, Ascites Secondary ToConcepcion R. AquinoNo ratings yet
- First Judicial RegionDocument6 pagesFirst Judicial RegionConcepcion R. AquinoNo ratings yet
- Finals Finals Finals Finals Finals Finals Finals Finals Finals Finals Finals Finals FinalsDocument1 pageFinals Finals Finals Finals Finals Finals Finals Finals Finals Finals Finals Finals FinalsConcepcion R. AquinoNo ratings yet
- Rehabilitation of Spinal Cord InjuryDocument23 pagesRehabilitation of Spinal Cord InjuryConcepcion R. AquinoNo ratings yet
- CultureDocument11 pagesCultureConcepcion R. AquinoNo ratings yet
- Increased Cartilage, Recoil, and Outer Ridge Curving InwardDocument2 pagesIncreased Cartilage, Recoil, and Outer Ridge Curving InwardConcepcion R. AquinoNo ratings yet
- AcneDocument9 pagesAcneConcepcion R. AquinoNo ratings yet
- GraphDocument1 pageGraphConcepcion R. AquinoNo ratings yet
- Bes After Nung EpidemiologyDocument4 pagesBes After Nung EpidemiologyConcepcion R. AquinoNo ratings yet
- Gallbladder: Picture Series by MaiDocument22 pagesGallbladder: Picture Series by MaiConcepcion R. AquinoNo ratings yet
- Case #9 Mariter Mendoza vs. Adriano Casumpang Et. Al G.R. No. 197987 March 19, 2012Document2 pagesCase #9 Mariter Mendoza vs. Adriano Casumpang Et. Al G.R. No. 197987 March 19, 2012Concepcion R. AquinoNo ratings yet
- EsophagusDocument21 pagesEsophagusConcepcion R. AquinoNo ratings yet
- The Nose and Paranasal SinusesDocument31 pagesThe Nose and Paranasal SinusesConcepcion R. AquinoNo ratings yet
- New Doc 2018-03-22 08.34.44 - 20180322083931Document7 pagesNew Doc 2018-03-22 08.34.44 - 20180322083931Concepcion R. AquinoNo ratings yet
- InfectionsDocument21 pagesInfectionsConcepcion R. AquinoNo ratings yet
- Legal MedDocument10 pagesLegal MedConcepcion R. AquinoNo ratings yet
- Open Questioning: Ob GynDocument1 pageOpen Questioning: Ob GynConcepcion R. AquinoNo ratings yet
- HeadacheDocument15 pagesHeadacheConcepcion R. AquinoNo ratings yet