Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Monitor Serum Uric Acid and Creatinine Levels, and BUN. Administer Platelets As Indicated
Uploaded by
jay5ar5jamorabon5torOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Monitor Serum Uric Acid and Creatinine Levels, and BUN. Administer Platelets As Indicated
Uploaded by
jay5ar5jamorabon5torCopyright:
Available Formats
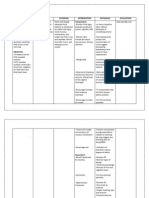
Assessment:
Objective: Sudden weight loss
Decreased urine output
(+) dry skin
(+) dry mucous membranes
Muscle weakness
Diagnosis: Deficit fluid volume r/t fluid loss to subcutatneous tissue
Planning: After 8 hours of duty, no signs of dehydration will be noted
Intervention:
Weight px regularly
`
Monitor intake and output. Note urine color, and measure specific gravity as indicated
Monitor Blood pressure and Pulse Rate
Check on dietary intake of proteins and calories
Place px on strict regimen of bedrest; encourage lateral position
Increase fluid intake as needed
Encourage to avoid food that cause dehydration such as coffee and tea
Monitor serum uric acid and creatinine levels, and BUN.
Administer platelets as indicated
Rationale:
Changes in weight provide information in fluid imbalance and the adequacy of fluid volume
replacement
1.040 indicates severe hypovolemia and kidney involvement. Note: Administration of MgSO4
may cause transient increase increase in output
These changes of v/s are associated with fluid volume loss and/or hypovelemia
Proper nutrition decreases incidence of prenatal hypovolemia and hypoperfusion. Intake of 80
100 g of protein may be required daily to replace losses.
This enhances placental and renal perfusion, reduces adrenal activity, and may lower BP
Fluid replacement treats hypovolemia, yet must be given cautiously to prevent overload
To prevent further dehydration
Elevated levels, especially of uric acid, indicate impaired kidney function, worsening of
maternal condition, and poor fetal outcome
Patients with HELLP syndrome awaiting delivery of the fetus may benefit from transfusion of
platelets when count is below 20,000
You might also like
- Equine Fluid TherapyFrom EverandEquine Fluid TherapyC. Langdon FieldingNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Induced Hypertension Nursing Diagnosis NANDADocument9 pagesPregnancy Induced Hypertension Nursing Diagnosis NANDASanal S SalimNo ratings yet
- NCP Liver CirrosisDocument2 pagesNCP Liver CirrosisRosebud RoseNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis: May Be Related To: Fluid Volume Deficit (Isotonic)Document26 pagesNursing Diagnosis: May Be Related To: Fluid Volume Deficit (Isotonic)Ric Nacional75% (4)
- Manage Ascites with Diet, MedicationDocument12 pagesManage Ascites with Diet, MedicationShilpaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument3 pagesChronic Renal FailureNurol-Ainah Hafizah U. PimpingNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal FailureDocument35 pagesAcute Renal FailureKaelyn Bello Giray100% (1)
- Assessment Nsg. Diagnosis Sci. Explanation Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesAssessment Nsg. Diagnosis Sci. Explanation Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationRoMarie AbainzaNo ratings yet
- Assessing Ascites in a Patient with Liver DiseaseDocument1 pageAssessing Ascites in a Patient with Liver Diseasehaniehaehae100% (1)
- Lanjutan NCP DMDocument14 pagesLanjutan NCP DMVera Andri YaniNo ratings yet
- Presentation on Cirrhosis of LiverDocument34 pagesPresentation on Cirrhosis of LiverAnshu kumariNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Chief Complaint: IndependentDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Chief Complaint: IndependentTed Cipriano VistaNo ratings yet
- DKADocument5 pagesDKAMariel BernabeNo ratings yet
- NCP for AGE Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesNCP for AGE Deficient Fluid VolumekarenbelnasNo ratings yet
- Guidance For Intravenous Fluid and Electrolyte Prescription in AdultsDocument8 pagesGuidance For Intravenous Fluid and Electrolyte Prescription in AdultsfrakturhepatikaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Type-2Document1 pageDiabetes Mellitus Type-2Sara SabraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument9 pagesNursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationJezza Sanchez-Rellita VillariasNo ratings yet
- LactuloseDocument1 pageLactuloseMsOrangeNo ratings yet
- DIURETICS Flow ChartDocument3 pagesDIURETICS Flow Chartdonnam86No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Renal FailureDocument18 pagesNursing Care Plan Renal FailureKundan KumarNo ratings yet
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument14 pagesDiabetic KetoacidosisGlen MedrosoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Patient With Renal FailureDocument18 pagesNursing Care Plan For Patient With Renal FailureRanusha AnushaNo ratings yet
- Deficient Fluid Volume Related To Polyuria and Dehydration AEB Dry Mucus MembraneDocument1 pageDeficient Fluid Volume Related To Polyuria and Dehydration AEB Dry Mucus MembraneNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Hypokalemia: Presented By: Group 4 Dolfo, Dominise, Ejercito, FloraldeDocument20 pagesHypokalemia: Presented By: Group 4 Dolfo, Dominise, Ejercito, FloraldeKyle De Sagun OtedaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Imbalance (NCP)Document9 pagesFluid Imbalance (NCP)Putry RainismNo ratings yet
- Fluid Electrolytes and Acid-Base BalanceDocument12 pagesFluid Electrolytes and Acid-Base BalanceHajra Al-Khuwaitem100% (1)
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument3 pagesChronic Renal FailureirismgallNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans for Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plans for Deficient Fluid VolumeLalaine RomeroNo ratings yet
- CirrhoisDocument6 pagesCirrhoisAslimah RakimNo ratings yet
- DKADocument4 pagesDKAJacques BoucalNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte TherapyDocument16 pagesFluid and Electrolyte Therapydamion clarkeNo ratings yet
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument4 pagesNursing DiagnosisMavy AndresNo ratings yet
- NCP 3 DEFICIT IN FLUID VOLUMEDocument2 pagesNCP 3 DEFICIT IN FLUID VOLUMEGenEsis CarandangNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument15 pagesAcute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanRanusha AnushaNo ratings yet
- Liver Cirrhosis Case PresDocument77 pagesLiver Cirrhosis Case Presmarlx580% (5)
- NCP DM 1Document6 pagesNCP DM 1Shin AblangNo ratings yet
- Nursing Patho CardsDocument195 pagesNursing Patho Cardsgiogmail100% (1)
- Electrolytes & FluidimbalancesDocument80 pagesElectrolytes & FluidimbalancesDennis Nyambane MomanyiNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal FailureDocument2 pagesAcute Renal FailureRaymund Christopher Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume DeficitDocument12 pagesFluid Volume DeficitKersee GailNo ratings yet
- Group 1 HypokalemiaDocument6 pagesGroup 1 HypokalemiaAdegboye AdedayoNo ratings yet
- Sodium, and 350-500 Meq/L of Chloride. The Combined Effects of Serum Hyperosmolarity, Dehydration, and Acidosis Result in Increased Osmolarity in Brain Cells That ClinicallyDocument5 pagesSodium, and 350-500 Meq/L of Chloride. The Combined Effects of Serum Hyperosmolarity, Dehydration, and Acidosis Result in Increased Osmolarity in Brain Cells That ClinicallyMorgan Mitchell100% (10)
- Fluid Volume Assessment for Amoebiasis PatientDocument3 pagesFluid Volume Assessment for Amoebiasis PatientRellie CastroNo ratings yet
- Diabetes InsipidusDocument20 pagesDiabetes InsipidusleenaNo ratings yet
- Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument11 pagesFluids and Electrolytescarlo evardo100% (2)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanWhela SabueroNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis Case StudyDocument6 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis Case StudyJohn AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis Case StudyDocument6 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis Case StudyHomework Ping100% (2)
- Liver Cirrhosis Patient Case StudyDocument6 pagesLiver Cirrhosis Patient Case StudyAngelica Barcelona Yumang67% (3)
- Alteration in Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument118 pagesAlteration in Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceRenuga SureshNo ratings yet
- Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument1 pageDeficient Fluid VolumeSheila ErpeloNo ratings yet
- Medical Diagnosis: Kidney Failure and Fluid Volume ExcessDocument74 pagesMedical Diagnosis: Kidney Failure and Fluid Volume ExcessSheela Khrystyn LeeNo ratings yet
- Fluid and ElectrolytesDocument179 pagesFluid and ElectrolytesTrixie Al Marie75% (4)
- Ascites, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandAscites, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- The Renal Diet Kitchen: 60+ Quick and Delicious Renal Diet Recipes to Improve Kidney FunctionFrom EverandThe Renal Diet Kitchen: 60+ Quick and Delicious Renal Diet Recipes to Improve Kidney FunctionNo ratings yet
- Soluzioni al Diabete e all'Ipoglicemia - Come prevenire e disfarsene naturalmente e senza medicineFrom EverandSoluzioni al Diabete e all'Ipoglicemia - Come prevenire e disfarsene naturalmente e senza medicineNo ratings yet
- Notes For BioChemistryDocument1 pageNotes For BioChemistryjay5ar5jamorabon5torNo ratings yet
- Saint Paul Nursing Practicum at PRCDocument3 pagesSaint Paul Nursing Practicum at PRCjay5ar5jamorabon5torNo ratings yet
- BP Monitoring CardDocument1 pageBP Monitoring Cardjay5ar5jamorabon5torNo ratings yet
- Nursing Practice Test/Exam About Communicable Diseases (NLE 1-20)Document4 pagesNursing Practice Test/Exam About Communicable Diseases (NLE 1-20)jay5ar5jamorabon5torNo ratings yet
- St. Paul University Philippines: Professional Regulation Commission Work PlanDocument3 pagesSt. Paul University Philippines: Professional Regulation Commission Work Planjay5ar5jamorabon5torNo ratings yet
- St. Paul University Philippines: School of Nursing and Allied Health SciencesDocument2 pagesSt. Paul University Philippines: School of Nursing and Allied Health Sciencesjay5ar5jamorabon5torNo ratings yet
- Nmat Usa November 22 2014 Supplementary HandoutDocument2 pagesNmat Usa November 22 2014 Supplementary Handoutjay5ar5jamorabon5torNo ratings yet
- HISTORICAL EVOLUTION OF IV STANDARDSDocument45 pagesHISTORICAL EVOLUTION OF IV STANDARDSjodipotpot77% (13)
- St. Paul University Philippines: TaskingDocument2 pagesSt. Paul University Philippines: Taskingjay5ar5jamorabon5torNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing II: Labor and Delivery StagesDocument130 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing II: Labor and Delivery Stagesjay5ar5jamorabon5torNo ratings yet
- Family Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesFamily Nursing Care Planjay5ar5jamorabon5torNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument4 pagesDocumentjay5ar5jamorabon5torNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument8 pagesChemistryjay5ar5jamorabon5torNo ratings yet
- NMAT National Medical Admission Test HandoutDocument2 pagesNMAT National Medical Admission Test Handoutjay5ar5jamorabon5torNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nursing Growth and DevelopmentDocument56 pagesPediatric Nursing Growth and Developmentjay5ar5jamorabon5torNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing II: Labor and Delivery StagesDocument130 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing II: Labor and Delivery Stagesjay5ar5jamorabon5torNo ratings yet
- NMAT supplementary handout provides medical school codesDocument2 pagesNMAT supplementary handout provides medical school codesjay5ar5jamorabon5torNo ratings yet
- St. Paul University Philippines: Work Plan (Cluster 3)Document2 pagesSt. Paul University Philippines: Work Plan (Cluster 3)jay5ar5jamorabon5torNo ratings yet
- Ap C3 July 22 29Document5 pagesAp C3 July 22 29jay5ar5jamorabon5torNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nursing PDFDocument69 pagesPediatric Nursing PDFGeevee Naganag VentulaNo ratings yet
- Physical Asessment DengueDocument11 pagesPhysical Asessment Denguejay5ar5jamorabon5torNo ratings yet
- Biology Msa ReviewerDocument9 pagesBiology Msa Reviewerjay5ar5jamorabon5torNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument1 pageNCPjay5ar5jamorabon5torNo ratings yet
- Emotional and Physiologic Elements of Death and DyingDocument17 pagesEmotional and Physiologic Elements of Death and DyinghengkihanggaraNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint 2016 TutorialDocument20 pagesPowerpoint 2016 TutorialTriAstutiNo ratings yet
- Aggressive PrintDocument11 pagesAggressive Printjay5ar5jamorabon5torNo ratings yet
- Emotional and Physiologic Elements of Death and DyingDocument17 pagesEmotional and Physiologic Elements of Death and DyinghengkihanggaraNo ratings yet
- Effects On Lab Test ResultsDocument18 pagesEffects On Lab Test Resultsjay5ar5jamorabon5torNo ratings yet
- Disaster and Emergency NXDocument11 pagesDisaster and Emergency NXjay5ar5jamorabon5torNo ratings yet