Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Revision Question Answer
Uploaded by
安 娜 胡0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pagespm bio revision answer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentspm bio revision answer
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageRevision Question Answer
Uploaded by
安 娜 胡spm bio revision answer
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
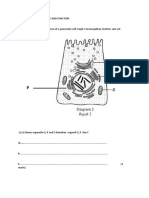
Question 1
(a) Able to state the substrate and explain why.
Answers:
Substrate : Q
Reason : Q has the shape that can fit the active site of the enzyme.
(b) Able to name substrate.
Answers: Sucrose
(c) Able to explain why enzyme is needed in small quantity to act on substrate.
Answers:
P1 : Enzymes do not change/destroy at the end of the reaction
P2 : The same enzyme molecule can react on a large number of substrate molecules.
(Any 1)
(d) Able to explain why most laundry detergents contain enzyme amylase
Sample answers:
P1 : Amylase dissolves variety of stains/dirts
P2 : Breaks down starches/carbohydrate stains on clothes.
P3 : by hydrolysis
P4 : The clothes can be washed easily/faster
P5 : (It is) effective in a small amount.
(Any 3)
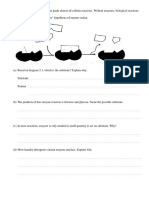
(e)(i) Able to explain the graph part PQ.
Sample answers:
P1 : When the substrate concentration increases, the rate of (enzymatic) reaction increases.
P2 : The rate of reaction depends on the substrate concentration // Substrate concentration is the limiting factor.
P3 : More collision between the enzymes (molecules) and the substrates
P4 : More enzyme-substrate complexes form
(Any 2)
(ii) Able to suggest how to increase the rate of reaction in part RS.
Sample answers:
P1 : There is an excess of substrate molecules. // Substrate molecules compete with one another for the active sites on
enzymes.
P2 : There is not enough/limited enzymes molecules to react // Enzyme concentration has become the limiting factor.
P3 : To increase the rate of reaction, increase the enzyme concentration.
P4 : More active sites / enzymes available for the reaction.
P5 : Or increase the temperature (to optimum level)
P6 : More collision between the enzymes (molecules) and the substrates // More enzyme-substrate complexes form
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Resu Me TampletDocument3 pagesResu Me Tamplet安 娜 胡No ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Palm OilDocument1 pagePalm Oil安 娜 胡No ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- G 6 PDDocument2 pagesG 6 PD安 娜 胡No ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- 90 Day Review Template 13Document2 pages90 Day Review Template 13安 娜 胡No ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- 90 Day Review Template 07Document2 pages90 Day Review Template 07安 娜 胡No ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Question 1Document2 pagesQuestion 1安 娜 胡No ratings yet
- Cheetah Annual Report 2017Document98 pagesCheetah Annual Report 2017安 娜 胡No ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- 11768Document10 pages11768安 娜 胡No ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- VolkswagenDocument3 pagesVolkswagen安 娜 胡No ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Marketing Strategy of Toyota Motor CorpoDocument37 pagesMarketing Strategy of Toyota Motor CorpoJean Tine MoralesNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Customer Orientation Such As Service Quality, Customer Satisfaction, Etc. I Would Then Identify The Strength From My Analysis.)Document3 pagesCustomer Orientation Such As Service Quality, Customer Satisfaction, Etc. I Would Then Identify The Strength From My Analysis.)安 娜 胡No ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Customer Orientation Such As Service Quality, Customer Satisfaction, Etc. I Would Then Identify The Strength From My Analysis.)Document3 pagesCustomer Orientation Such As Service Quality, Customer Satisfaction, Etc. I Would Then Identify The Strength From My Analysis.)安 娜 胡No ratings yet
- Assessment of The Key Political Risks of China's Overseas Direct InvestmentDocument8 pagesAssessment of The Key Political Risks of China's Overseas Direct Investment安 娜 胡No ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Joints PPT NsDocument89 pagesJoints PPT Ns安 娜 胡No ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Epithelia DR - RaviDocument60 pagesEpithelia DR - Ravi安 娜 胡No ratings yet
- Blood VesselDocument22 pagesBlood Vessel安 娜 胡No ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Bones of Limbs - Pharmacy - 12-9Document41 pagesBones of Limbs - Pharmacy - 12-9安 娜 胡No ratings yet
- 27-Male Rep. Organs 14.11.11Document45 pages27-Male Rep. Organs 14.11.11安 娜 胡No ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Bones of Limbs - Pharmacy - 12-9Document41 pagesBones of Limbs - Pharmacy - 12-9安 娜 胡No ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- B.pharm-Connective Tissue & SkinDocument73 pagesB.pharm-Connective Tissue & Skin安 娜 胡No ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Intro 2Document55 pagesIntro 2安 娜 胡No ratings yet
- Blood Groups Bpharm 12. 09.11Document18 pagesBlood Groups Bpharm 12. 09.11安 娜 胡No ratings yet
- Question RevisionDocument3 pagesQuestion Revision安 娜 胡No ratings yet
- Transport Across Cell MembraneDocument20 pagesTransport Across Cell Membrane安 娜 胡No ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)