Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Shear Lug Verification Example 4 PDF
Shear Lug Verification Example 4 PDF
Uploaded by
Nasrul AdliOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Shear Lug Verification Example 4 PDF
Shear Lug Verification Example 4 PDF
Uploaded by
Nasrul AdliCopyright:
Available Formats
TECHNICAL CORRECTION PIP STE05121
October 2006 Anchor Bolt Design Guide
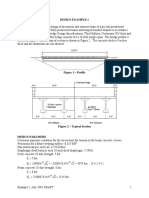
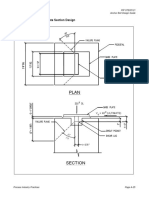
EXAMPLE 3 - Shear Lug Plate Section Design
Design a shear lug plate for a 14-in. square base plate, subject to a factored axial dead load
of 22.5 kips, factored live load of 65 kips, and a factored shear load of 40 kips. The base
plate and shear lug have f ya = 36 ksi and f c' = 3 ksi. The contact plane between the grout and
base plate is assumed to be 1 in. above the concrete. A 2-ft 0-in. square pedestal is
assumed. Ductility is not required.
Vapp = Vua Vf = 40 (0.55)(22.5) = 27.6 kips
Bearing area = Areq = Vapp / (0.85 fc') = 27.6 kips / (0.85*0.65*3 ksi) = 16.67 in. 2
On the basis of base plate size, assume the plate width, W, will be 12 in.
Height of plate = H = A req / W + G = 16.67 in. 2 /12 in. + 1 in. = 2.39 in. Use 3 in.
Ultimate moment = M u = (Vapp / W) * (G + (H G)/2)
= (27.6 kips / 12 in.) * (1 in. + (3 in.-1 in.)/2) = 4.61 k-in. / in.
Thickness = t = [(4 * Mu)/(* fya)] = ((4*4.61 kip-in.)/(0.9*36 ksi)) = 0.754 in. Use 0.75 in.
This 12-in. x 3-in. x 0.75-in. plate will be sufficient to carry the applied shear load and resulting
moment. Design of the weld between the plate section and the base plate is left to the
engineer.
Check concrete breakout strength of the shear lug in shear.
Distance from shear lug to edge of concrete = (24 - 0.75) / 2 = 11.63 in.
AV = 24 * (2+11.63) (12 * 2) = 303 in. 2
Vcb = AVc*4**[fc']0.5 = 303 * 4 * 0.85 * [3000] 0.5 = 56400 lb = 56.4 kips > 27.3 kips OK
Process Industry Practices Page A-26
You might also like
- Presented By: Irfan KhanDocument63 pagesPresented By: Irfan KhanIrfan KhanNo ratings yet
- Design of FootingsDocument102 pagesDesign of FootingsTBCACCOUNTs100% (1)
- SH Wall ExampleDocument7 pagesSH Wall Examplericopadilla79No ratings yet
- Design of Piles Under Cyclic Loading: SOLCYP RecommendationsFrom EverandDesign of Piles Under Cyclic Loading: SOLCYP RecommendationsAlain PuechNo ratings yet
- Example Calculations: Example Problems For Concentrated LoadsDocument4 pagesExample Calculations: Example Problems For Concentrated LoadsKho C AhlNo ratings yet
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IFrom EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume INo ratings yet
- Design of FootingsDocument42 pagesDesign of Footingsxaekne91% (11)
- Pipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook: A Manual of Quick, Accurate Solutions to Everyday Pipeline Engineering ProblemsFrom EverandPipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook: A Manual of Quick, Accurate Solutions to Everyday Pipeline Engineering ProblemsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- Pile Cap Design SolutionDocument43 pagesPile Cap Design SolutionAbhijit HazarikaNo ratings yet
- Flat SlabDocument16 pagesFlat SlabAbdul Hadhi100% (2)
- Composite Beam ExampleDocument4 pagesComposite Beam Examplexxazninvasionxx2697100% (1)
- SlabDocument60 pagesSlabAdigwe George ChimaNo ratings yet
- Industrial BuildingDocument37 pagesIndustrial Buildingrexdindigul70% (10)
- AE401 - Tee Spandrel and SlabsDocument13 pagesAE401 - Tee Spandrel and SlabsThomas MartinNo ratings yet
- Homework 2 SolutionDocument4 pagesHomework 2 SolutionB HIllNo ratings yet
- Design of Reinforced Concrete Shear WallDocument8 pagesDesign of Reinforced Concrete Shear WallklynchelleNo ratings yet
- Design For RC Flat SlabsDocument70 pagesDesign For RC Flat SlabsAil Aafaaq100% (3)
- Girder Slab PDFDocument16 pagesGirder Slab PDFArbi811No ratings yet
- SW1 Shear Wall Design Based On ACI 318-02Document2 pagesSW1 Shear Wall Design Based On ACI 318-02nhulugallaNo ratings yet
- 6000m3 VST DesignDocument17 pages6000m3 VST Designjohney2No ratings yet
- AISC ExamI1&2&3Document11 pagesAISC ExamI1&2&3Dhurai KesavanNo ratings yet
- FootingsDocument56 pagesFootingskKhalid YousafNo ratings yet
- Column Base Plates Prof Thomas MurrayDocument83 pagesColumn Base Plates Prof Thomas Murrayandre2008chipo100% (2)
- Mechanics and Design of Concrete Structures-MIT NOTESDocument162 pagesMechanics and Design of Concrete Structures-MIT NOTESIrfan IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Design of RCC Corbel As Per Aci 318 95Document3 pagesDesign of RCC Corbel As Per Aci 318 95Maad Ahmed Al-Maroof50% (2)
- Pressure Vessel and Stacks Field Repair ManualFrom EverandPressure Vessel and Stacks Field Repair ManualRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Piping Engineering - Tank Nozzle Loads 1Document1 pagePiping Engineering - Tank Nozzle Loads 1Nasrul Adli100% (1)
- Homework 5Document9 pagesHomework 5Omar Calisaya RamosNo ratings yet
- Computational Wind Engineering 1: Proceedings of the 1st International Symposium on Computational Wind Engineering (CWE 92) Tokyo, Japan, August 21-23, 1992From EverandComputational Wind Engineering 1: Proceedings of the 1st International Symposium on Computational Wind Engineering (CWE 92) Tokyo, Japan, August 21-23, 1992S. MurakamiNo ratings yet
- Semi-Integral-Abutment Design Example (USA Unit)Document20 pagesSemi-Integral-Abutment Design Example (USA Unit)Ya YangNo ratings yet
- Composite Floor BeamDocument6 pagesComposite Floor BeamAhmed Ben Hmida50% (2)
- Design For RC Flat SlabsDocument70 pagesDesign For RC Flat SlabsAil AafaaqNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - House DesignDocument18 pagesLecture 4 - House Designkkhan_451062No ratings yet
- Eigen Modes - PDF Timesaving-Torsiondesign-Ia PDFDocument32 pagesEigen Modes - PDF Timesaving-Torsiondesign-Ia PDFGeorge GeorgianNo ratings yet
- Shear Lug Verification Example PDFDocument12 pagesShear Lug Verification Example PDFKarthikeyan PanchatcharamNo ratings yet
- Sample - Solution Manual For Structural Steel Design 2nd Edition Abi AghayereDocument10 pagesSample - Solution Manual For Structural Steel Design 2nd Edition Abi Aghayereاسلام الثورNo ratings yet
- Simpson Anchors 2008-03 by Jason Oakley PDFDocument31 pagesSimpson Anchors 2008-03 by Jason Oakley PDFaomareltayebNo ratings yet
- Example 24.7-Design For Depth of Footing On Piles: × 8.5 FT × 16 inDocument6 pagesExample 24.7-Design For Depth of Footing On Piles: × 8.5 FT × 16 inSeptian BrandalzxNo ratings yet
- Forklift Truck LoadingDocument7 pagesForklift Truck LoadingJurie Sulistio KumaraNo ratings yet
- ASDIP Steel - Composite Beam Verification ExampleDocument6 pagesASDIP Steel - Composite Beam Verification ExampleEdwin VizueteNo ratings yet
- ACI Alternative Method For Out-of-Plane Slender Wall Analysis and The Impact of Substituting High Strength Reinforcement-08-23Document12 pagesACI Alternative Method For Out-of-Plane Slender Wall Analysis and The Impact of Substituting High Strength Reinforcement-08-23Sergio UrbanoNo ratings yet
- Ce591plategirders F13Document67 pagesCe591plategirders F13cocococo1100% (1)
- One Way Slab DSMDocument35 pagesOne Way Slab DSMIthihas SeventyoneNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12Document37 pagesLecture 12pddiosNo ratings yet
- 2022-07-05 Blog #14 ShareDocument13 pages2022-07-05 Blog #14 ShareSergio UrbanoNo ratings yet
- CE305 Reinforced Concrete Design: Topics: Examples On T Beam Design WEEK: 11 Level: 6 Prerequisites: NoneDocument22 pagesCE305 Reinforced Concrete Design: Topics: Examples On T Beam Design WEEK: 11 Level: 6 Prerequisites: NoneAsadullah Khan GhalibNo ratings yet
- PSCExample1 FHWASeminar JLS Jul05Document48 pagesPSCExample1 FHWASeminar JLS Jul05Jose HaroNo ratings yet
- LRFD-Composite Beam Desing With MetaldeckDocument12 pagesLRFD-Composite Beam Desing With MetaldeckMaria FabianaNo ratings yet
- Substation Structure DesignDocument27 pagesSubstation Structure Designpaulc227No ratings yet
- Example I-1 PDFDocument6 pagesExample I-1 PDFboone37No ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - Strap Footing DesignDocument16 pagesMicrosoft Word - Strap Footing DesignChanna SannNo ratings yet
- Pile Caps 01Document3 pagesPile Caps 01bankboyNo ratings yet
- One Way+ Two Way Joist System SafiDocument71 pagesOne Way+ Two Way Joist System SafiUmair RazaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionFrom EverandAdvanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionNo ratings yet
- The Fatigue Strength of Transverse Fillet Welded Joints: A Study of the Influence of Joint GeometryFrom EverandThe Fatigue Strength of Transverse Fillet Welded Joints: A Study of the Influence of Joint GeometryNo ratings yet
- Job Information: Engineer Checked Approved Name: Date: Structure TypeDocument2 pagesJob Information: Engineer Checked Approved Name: Date: Structure TypeNasrul AdliNo ratings yet
- Exhibit II Compliance To Technical RequirementsDocument1 pageExhibit II Compliance To Technical RequirementsNasrul AdliNo ratings yet
- Asme Sect8 Div1 - SAMPLE Calculation-COVERDocument1 pageAsme Sect8 Div1 - SAMPLE Calculation-COVERNasrul AdliNo ratings yet
- Malaysia Public Holidays & School Holidays 2018 CalendaR-ALL PDFDocument4 pagesMalaysia Public Holidays & School Holidays 2018 CalendaR-ALL PDFNasrul AdliNo ratings yet
- What Is Piping 2Document1 pageWhat Is Piping 2Nasrul AdliNo ratings yet
- B31 3 (Mygaz) - 1Document1 pageB31 3 (Mygaz) - 1Nasrul AdliNo ratings yet
- PDMS 2Document1 pagePDMS 2Nasrul AdliNo ratings yet
- Pipes. Maxi 8 PDFDocument1 pagePipes. Maxi 8 PDFNasrul AdliNo ratings yet
- Shear Lug Verification Example 12Document1 pageShear Lug Verification Example 12Nasrul AdliNo ratings yet
- Pipes. Maxi 8 PDFDocument1 pagePipes. Maxi 8 PDFNasrul AdliNo ratings yet
- Shear Lug Verification Example 3Document1 pageShear Lug Verification Example 3Nasrul AdliNo ratings yet
- Shear Lug Verification Example 2Document1 pageShear Lug Verification Example 2Nasrul AdliNo ratings yet
- Shear Lug Verification Example 12Document1 pageShear Lug Verification Example 12Nasrul AdliNo ratings yet