Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Summary of Reaction Pathways in Organic Chemistry
Summary of Reaction Pathways in Organic Chemistry
Uploaded by
ANUZ DUETOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Summary of Reaction Pathways in Organic Chemistry
Summary of Reaction Pathways in Organic Chemistry
Uploaded by
ANUZ DUETCopyright:
Available Formats
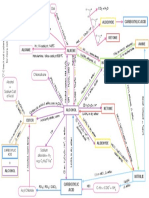
SUMMARY OF REACTION PATHWAYS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
ALKANES POLYALKENES
PRIMARY AMINES
ALKENES DIHALOALKANES
HALOALKANES ALKYL
HYDROGEN EPOXYALKANES DIOLS
SULPHATES
ALCOHOLS
NITRILES
CARBONYLS
CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
You need to know the equations, conditions, reagents and type of reaction for all these
reactions.
You need to know the mechanism for some of them.
1. Alkane chloroalkane
reagents: Cl2
conditions: UV light
mechanism: free radical substitution
equation: RH + Cl2 RCl + HCl
2. Alkene polyalkene
Conditions: low T, high p.
Equation:
C C
n C C
Type of reaction: addition polymerisation (free radical)
3. Alkene bromoalkane
Reagent: HX(g)
Conditions: room T
Equation:
C C + H Br C C
Br H
Type of reaction: electrophilic addition
4. Alkene dibromoalkane
Reagent: Br2 in water or in an organic solvent
Conditions: room T
Equation:
C C + Br Br C C
Br Br
Mechanism: electrophilic addition
5. Alkene alkylhydrogensulphate
Reagent: concentrated sulphuric acid
Conditions: cold
Equation:
C C + H OSO3H C C
H OSO3H
Mechanism: electrophilic addition
6. Alkylhydrogensulphate alcohol
Reagent: water
Conditions: warm
Equation:
C C
C C +
+ H2O H OSO3H
H OSO3H
H OH
Type of reaction: hydrolysis
7. Alkene alcohol
Reagent: steam
Conditions: 300 oC, 60 atm, H3PO4 catalyst
Equation:
H H
C C + O C C
OH H
Type of reaction: hydration
8. Haloalkane alcohol
Reagent: NaOH(aq) or KOH(aq)
Conditions: warm under reflux
Equation: R-X + OH- R-OH + X-
Type of reaction: nucleophilic substitution
9. Haloalkane nitrile
Reagent: KCN in aqueous ethanol
Conditions: boil under reflux
Equation: R-X + CN- R-CN + X-
Type of reaction: nucleophilic substitution
10. Haloalkane Amine
Reagent: ammonia in ethanol in a sealed tube
Conditions: heat
Equation: R-X + 2NH3 R-NH2 + NH4X
Type of reaction: nucleophilic substitution
11. Haloalkane alkene
Reagent: KOH in ethanol
Conditions: heat
Equation:
H R R R
C C -
R C C X + X + H2O
R R
R R
Type of reaction: elimination
12. Primary alcohol aldehyde
Reagent: potassium dichromate and dilute sulphuric acid
Conditions: warm, distillation
Equation: RCH2OH + [O] RCHO + H2O
Type of reaction: mild oxidation
13. Secondary alcohol ketone
Reagent: potassium dichromate and dilute sulphuric acid
Conditions: heat, distillation
Equation: R1CH(OH)R2 + [O] R1COR2 + H2O
Type of reaction: oxidation
14. aldehyde carboxylic acid
Reagent: potassium dichromate and dilute sulphuric acid
Conditions: heat, reflux
Equation: R-CHO + [O] R-COOH
Type of reaction: oxidation
15. Alcohols alkenes
Reagent: concentrated sulphuric acid
Conditions: heat
Equation:
C C H C C + H2O
OH
Type of reaction: elimination
16. glucose ethanol
reagent: yeast
conditions: 35 55 oC, no air
equation: C6H12O6 2C2H5OH + 2CO2
type of reaction: fermentation
You might also like
- Come From Away LibrettoDocument91 pagesCome From Away LibrettoJustMajestical.94% (34)
- Mastering Diabetes Ultimate Nutrition and Recipe GuideDocument75 pagesMastering Diabetes Ultimate Nutrition and Recipe GuideBrenda Danielle89% (19)
- Chapter12 WorkedExamplesDocument17 pagesChapter12 WorkedExamplesHalil EmreNo ratings yet
- SET-NET Pericyclic ReactionsDocument61 pagesSET-NET Pericyclic ReactionsBapu ThoratNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Stereoelectronic Effects On ReactivityDocument19 pagesLecture 5 - Stereoelectronic Effects On Reactivityhoang12310100% (1)
- PMR Spectroscopy: Solved Problems Volume : IIFrom EverandPMR Spectroscopy: Solved Problems Volume : IIRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Organic Chemistry I: The Unofficial Reaction SheetDocument11 pagesOrganic Chemistry I: The Unofficial Reaction SheetKarl WilsonNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Natural Products PDFDocument21 pagesChemistry of Natural Products PDFhosseini_9864No ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument20 pagesOrganic ChemistryGirish RaguvirNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry ReactionDocument3 pagesOrganic Chemistry ReactionGAMEPORIUMNo ratings yet
- AromaticityDocument24 pagesAromaticitymilindthakare75No ratings yet
- Welcome To Chem 206: Fall Term, 2005, David A. EvansDocument22 pagesWelcome To Chem 206: Fall Term, 2005, David A. EvanseraborNo ratings yet
- SGDGDDDocument33 pagesSGDGDDyopoboy100% (1)
- Aromaticity CompleteDocument104 pagesAromaticity Completewahidalwahdi100% (1)
- 04 Reactive IntermediatesDocument115 pages04 Reactive IntermediatesMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 32-235 Practice Questions For Exam #2: 2. Consider The SDocument9 pagesOrganic Chemistry 32-235 Practice Questions For Exam #2: 2. Consider The Ssweta KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Protecting GroupsDocument45 pagesProtecting GroupsSait MalkonduNo ratings yet
- Retrosynthetic Analysis PDFDocument6 pagesRetrosynthetic Analysis PDFNoleNo ratings yet
- Pericyclics-2014 Handout PDFDocument79 pagesPericyclics-2014 Handout PDFnavchemNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem Midterm 1mech++keyDocument1 pageOrganic Chem Midterm 1mech++keyNorma Leticia RamosNo ratings yet
- 18 Aromatic SubstitutionsDocument67 pages18 Aromatic SubstitutionsJun LyNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry IIDocument7 pagesOrganic Chemistry IIRoberto SIlvaNo ratings yet
- Protecting Group HandoutDocument5 pagesProtecting Group HandoutRafaelle Sanvictores SilongNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry sn2 sn1 E2 E1 PDFDocument3 pagesOrganic Chemistry sn2 sn1 E2 E1 PDFAakanksha SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Vollhardt 6e Lecture PowerPoints - Chapter 11Document58 pagesVollhardt 6e Lecture PowerPoints - Chapter 11superfr3shmNo ratings yet
- Organic Conversion A & B Revise Before NEETDocument2 pagesOrganic Conversion A & B Revise Before NEETAquib JavedNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Alcohols: Organic Chemistry, 7Document53 pagesReactions of Alcohols: Organic Chemistry, 7haha_le12100% (1)
- GOC1 HybridizationDocument10 pagesGOC1 Hybridizationthe chemistry guru100% (1)
- Huckel Rule of Aromaticity 2 PDFDocument25 pagesHuckel Rule of Aromaticity 2 PDFUmar Farooq100% (1)
- Stereochemistry Basic Concepts Useful Notes For StudentsDocument26 pagesStereochemistry Basic Concepts Useful Notes For StudentsReddappaNo ratings yet
- Mesomeric EffectDocument21 pagesMesomeric EffectAwais Arshad100% (2)
- Inductive EffectDocument38 pagesInductive EffectJoe JNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry-All Reaction MechanismsDocument30 pagesOrganic Chemistry-All Reaction MechanismsParameshwari kumar100% (1)
- Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument24 pagesChapter 10 Haloalkanes and HaloarenesSuhas GowdaNo ratings yet
- 09 Stereo NotesDocument48 pages09 Stereo NotesZoran PavlovicNo ratings yet
- FMO LectureDocument14 pagesFMO Lecturebooks4free23No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 2021Document76 pagesOrganic Chemistry 2021Arah Mae BonillaNo ratings yet
- Electron Delocalization and ResonanceDocument9 pagesElectron Delocalization and ResonanceMariana LizethNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Organic Reactions 1Document23 pagesMechanism of Organic Reactions 1Suresh Vedpathak100% (2)
- Organic 2 PDFDocument864 pagesOrganic 2 PDFaisyahNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Practice ProblemsDocument1 pageOrganic Chemistry Practice ProblemsSushant KumarNo ratings yet
- TerpenoidsDocument17 pagesTerpenoidsSayli Sawant100% (1)
- Csir Model QuestionsDocument15 pagesCsir Model QuestionsbaluNo ratings yet
- Ugi ReactionsDocument36 pagesUgi ReactionsHarjinder Singh Bhatia100% (1)
- Ch1b Ps3 Key SerDocument7 pagesCh1b Ps3 Key SerRichard ZhuNo ratings yet
- E1 and E2 ReactionsDocument30 pagesE1 and E2 ReactionsVidhu Pandey100% (1)
- Organometallic CompoundsDocument66 pagesOrganometallic CompoundsJon Ho100% (1)
- Csir Ugc JRF Net Chemistry Paper 1 (Part B) Series - 1Document22 pagesCsir Ugc JRF Net Chemistry Paper 1 (Part B) Series - 1polamrajuNo ratings yet
- Master Organic Chemistry SubstitutionDocument43 pagesMaster Organic Chemistry SubstitutionArsalan Khan GhauriNo ratings yet
- Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols: Organic Chemistry, 7Document52 pagesStructure and Synthesis of Alcohols: Organic Chemistry, 7haha_le12100% (1)
- Moon - Exam 2 - Summer 2011Document10 pagesMoon - Exam 2 - Summer 2011Andres Pena100% (2)
- Organic Chemistry Midterm 1 Dir+eff++keyDocument1 pageOrganic Chemistry Midterm 1 Dir+eff++keyNorma Leticia RamosNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem FlowchartDocument1 pageOrganic Chem Flowchartcadence98No ratings yet
- Comparing The SN1 and SN2 Reactions - Master Organic ChemistryDocument5 pagesComparing The SN1 and SN2 Reactions - Master Organic Chemistryprince ranaNo ratings yet
- Organometallic Transition Metal Catalysis: A Holistic Approach to Understanding and Predicting their MechanismsFrom EverandOrganometallic Transition Metal Catalysis: A Holistic Approach to Understanding and Predicting their MechanismsNo ratings yet
- Enantioselective Chemical Synthesis: Methods, Logic, and PracticeFrom EverandEnantioselective Chemical Synthesis: Methods, Logic, and PracticeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Esperis EssentialsDocument2 pagesEsperis Essentialssibanda ThabaniNo ratings yet
- Eman Abdelhalim Portfolio With No IdDocument29 pagesEman Abdelhalim Portfolio With No Idrakan aldossariNo ratings yet
- Jump Rope For Heart ProgramDocument8 pagesJump Rope For Heart Programapi-659270607No ratings yet
- CASE NO.1. Lew-Mark Baking Company The CompanyDocument3 pagesCASE NO.1. Lew-Mark Baking Company The CompanyMae Lingan-LasqueroNo ratings yet
- Speak English With Vanessa: Free PDF WorksheetDocument8 pagesSpeak English With Vanessa: Free PDF Worksheetmillaelite1No ratings yet
- PERSUASIVE PRESETATION SDocument10 pagesPERSUASIVE PRESETATION SESDRAS FERNANDO ISLAS CABALLERONo ratings yet
- TEST 7 Copy RepairedDocument16 pagesTEST 7 Copy RepairedThị VyNo ratings yet
- Learning Task 2: Identify The Meaning of The Words With Prefixes Below. Color The Correct Answer With Color GreenDocument9 pagesLearning Task 2: Identify The Meaning of The Words With Prefixes Below. Color The Correct Answer With Color GreenNhez LacsamanaNo ratings yet
- Directions: Read Each Item Carefully. Encircle The Letter of The Correct Answer For Each QuestionDocument6 pagesDirections: Read Each Item Carefully. Encircle The Letter of The Correct Answer For Each Questionedwin dumopoyNo ratings yet
- Ajmal - PDF - Perfume - Perfumery PDFDocument1 pageAjmal - PDF - Perfume - Perfumery PDFharpalsingh19No ratings yet
- Buku Bahasa Inggris SD Kelas 2Document16 pagesBuku Bahasa Inggris SD Kelas 2bedhoe marvelNo ratings yet
- Sarasvathy 2001 Causation and EffectuationDocument21 pagesSarasvathy 2001 Causation and EffectuationMariana TelloNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument3 pagesDocumentNir DinerNo ratings yet
- Extrinsic RewardDocument6 pagesExtrinsic RewardKhánh NgọcNo ratings yet
- Constants of Fats and Other Fatty SubstancesDocument13 pagesConstants of Fats and Other Fatty SubstancesMrl AshiaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 ReadingDocument6 pagesUnit 1 Readingkim bíchNo ratings yet
- Homemade Kombucha The Simple Guide To Kickass KombuchaDocument1 pageHomemade Kombucha The Simple Guide To Kickass KombuchaJessica CapeceNo ratings yet
- Intake of Purine-Rich Foods, Protein, and Dairy Products and Relationship To Serum Levels of Uric AcidDocument7 pagesIntake of Purine-Rich Foods, Protein, and Dairy Products and Relationship To Serum Levels of Uric Acidnadita erischaNo ratings yet
- Product Information: Fish Species and OriginDocument1 pageProduct Information: Fish Species and OriginIRENENo ratings yet
- Progress Test Elementary Units 4 To 5 KIPPDocument3 pagesProgress Test Elementary Units 4 To 5 KIPPemmrodriguez8No ratings yet
- 2024 Jaris - K - All Media Kit - RemovedDocument85 pages2024 Jaris - K - All Media Kit - RemoveddokumentasiNo ratings yet
- RPMI-1640: With L-Glutamine Without Glucose and Sodium Bicarbonate Product Code: AT150Document2 pagesRPMI-1640: With L-Glutamine Without Glucose and Sodium Bicarbonate Product Code: AT150Gayathri MaigandanNo ratings yet
- Food Storage Chart - Food Storage GuidelinesDocument16 pagesFood Storage Chart - Food Storage GuidelinesMozvrt BlackNo ratings yet
- 1-2014 Adult Intake FormDocument6 pages1-2014 Adult Intake Formrfizza15No ratings yet
- Hospitality Product DevelopmentDocument11 pagesHospitality Product DevelopmentAman Bhattacharya100% (4)
- Biscuit Manufacturing: Different Types of BiscuitDocument15 pagesBiscuit Manufacturing: Different Types of Biscuit9889187549No ratings yet
- Science Test PaperDocument24 pagesScience Test PaperMenaga A/P IlangkovanNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4.pronounsDocument7 pagesExercise 4.pronounsruddenNo ratings yet