Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Two Prices For P, and The Average of The Two Quantities For Q
The Two Prices For P, and The Average of The Two Quantities For Q
Uploaded by
John Sudarsanam0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views4 pagesThe document discusses the concept of price elasticity of demand. It provides three methods to calculate elasticity between two points: (1) calculating elasticity between points A to B and B to A, (2) using the midpoint method of average price and quantity, and (3) measuring elasticity at a single point with a very small price change which gives the same answer for all three methods. It defines inelastic demand as having a price elasticity of less than 1, elastic demand as greater than 1, and unit elasticity as equal to 1. Total revenue increases with inelastic demand, decreases with elastic demand, and stays the same with unit elastic demand when price increases. Income elasticity of demand is also discussed,
Original Description:
Elasticity - Ohio State Macroeconomics
Original Title
EconH200L5
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the concept of price elasticity of demand. It provides three methods to calculate elasticity between two points: (1) calculating elasticity between points A to B and B to A, (2) using the midpoint method of average price and quantity, and (3) measuring elasticity at a single point with a very small price change which gives the same answer for all three methods. It defines inelastic demand as having a price elasticity of less than 1, elastic demand as greater than 1, and unit elasticity as equal to 1. Total revenue increases with inelastic demand, decreases with elastic demand, and stays the same with unit elastic demand when price increases. Income elasticity of demand is also discussed,
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views4 pagesThe Two Prices For P, and The Average of The Two Quantities For Q
The Two Prices For P, and The Average of The Two Quantities For Q
Uploaded by
John SudarsanamThe document discusses the concept of price elasticity of demand. It provides three methods to calculate elasticity between two points: (1) calculating elasticity between points A to B and B to A, (2) using the midpoint method of average price and quantity, and (3) measuring elasticity at a single point with a very small price change which gives the same answer for all three methods. It defines inelastic demand as having a price elasticity of less than 1, elastic demand as greater than 1, and unit elasticity as equal to 1. Total revenue increases with inelastic demand, decreases with elastic demand, and stays the same with unit elastic demand when price increases. Income elasticity of demand is also discussed,
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
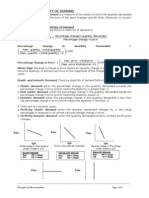
For the elasticity between two points, the
formula can depend on whether we move
from point A to point B, or point B to point
A.
A: Price = $4, Quantity = 120
B: Price = $6, Quantity = 80
A to B: Elasticity = (40/2)(4/120) = 2/3
B to A: Elasticity = (40/2)(6/80) = 1.5
The midpoint method: Use the average of
the two prices for P, and the average of the
two quantities for Q.
Elasticity = (40/2)(5/100) = 1
When we measure the elasticity at a single
point (by considering a very small price
change), all 3 computations give the same
answer.
When economists refer to demand as inelastic,
we mean a price elasticity of demand that is less
than 1.
Demand is elastic when the price elasticity of
demand is greater than one.
When the price elasticity of demand is one, we
say that demand has unit elasticity.
Total Revenue and the Price Elasticity of Demand
How does total revenue, PQ, change when we
increase the price?
Revenue increases if demand is inelastic,
Revenue decreases if demand is elastic, and
Revenue stays the same if demand is unit
elastic.
Income Elasticity of Demand
Income elasticity of demand =
Percentage change in quantity demanded
Percentage change in income
Q I
= ___ ___
I Q
For normal goods, the income elasticity of
demand is positive.
For luxury goods, the income elasticity of
demand is greater than 1.
For inferior goods, the income elasticity of
demand is negative.
You might also like
- Economics for CFA level 1 in just one week: CFA level 1, #4From EverandEconomics for CFA level 1 in just one week: CFA level 1, #4Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Elasticity of Supply and DemandDocument36 pagesElasticity of Supply and DemandRio Vina Ado SubongNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand and SupplyDocument42 pagesElasticity of Demand and SupplyAgatha Diane HonradeNo ratings yet
- Elesticity of DemandDocument48 pagesElesticity of DemandDr.Ashok Kumar Panigrahi100% (1)
- Elasticity of DemandDocument7 pagesElasticity of DemandLakshmiRengarajan100% (2)
- Chapter 4 PresentationDocument50 pagesChapter 4 Presentationhosie.oqbeNo ratings yet
- 1-Price Elasticity of DemandDocument51 pages1-Price Elasticity of DemandMOHIT SIGIRISETTYNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Elasticity of Demand and SupplyDocument61 pagesLecture 2 Elasticity of Demand and SupplyJoanne FerrerNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand and Supply: MAS 202 / MW / 12:30 - 2:00 Mr. CaducoyDocument37 pagesElasticity of Demand and Supply: MAS 202 / MW / 12:30 - 2:00 Mr. CaducoyStefanie FerminNo ratings yet
- ME Session 6 7Document31 pagesME Session 6 7vaibhav khandelwalNo ratings yet
- The Elasticity of DemandDocument53 pagesThe Elasticity of DemandShekhar SinghNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of DemandDocument42 pagesElasticity of DemandRichie ChanNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand: Price, Income and Cross ElasticityDocument59 pagesElasticity of Demand: Price, Income and Cross Elasticitynithinsp92No ratings yet
- ECON7002 Lecture 3 Semester 1 2021 UpdatedDocument62 pagesECON7002 Lecture 3 Semester 1 2021 UpdatedNima MoaddeliNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand: Prof. T.R. PanigrahiDocument21 pagesElasticity of Demand: Prof. T.R. PanigrahiAnimesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of DemandDocument27 pagesElasticity of Demandpimavi9908No ratings yet
- Elasticity of DemandDocument28 pagesElasticity of Demandshweta3547No ratings yet
- Elasticity Price Elasticity of DemandDocument5 pagesElasticity Price Elasticity of DemandArrini TsaltsaNo ratings yet
- Elasticity: Prof. (DR.) Vandana BhavsarDocument27 pagesElasticity: Prof. (DR.) Vandana BhavsarAkhil JosephNo ratings yet
- Elasticity and Its ApplicationDocument6 pagesElasticity and Its ApplicationSavannah Simone PetrachenkoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: ElasticityDocument9 pagesChapter 3: ElasticityJaja ColeenNo ratings yet
- Be 313 - Unit Learning CDocument19 pagesBe 313 - Unit Learning Cmhel cabigonNo ratings yet
- 3 Lec 5 Elasticity of Demand and SupplyDocument21 pages3 Lec 5 Elasticity of Demand and SupplyUtkarshNo ratings yet
- Elasticity ReportDocument28 pagesElasticity ReportJaja Coleen100% (1)
- Demand and Supply - 2nd PartDocument56 pagesDemand and Supply - 2nd PartsuryaabhimaniNo ratings yet
- Group 8 Report DEMANDDocument22 pagesGroup 8 Report DEMANDMa'am Roma GualbertoNo ratings yet
- Man EcoDocument18 pagesMan EcoRicha mae JumadiaoNo ratings yet
- Elasticity and Revenue: Learning ObjectivesDocument14 pagesElasticity and Revenue: Learning ObjectivesShivaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 ElasticityDocument47 pagesLecture 3 Elasticityzhanghongrui0723No ratings yet
- Basic Microeconomics Day 3 LectureDocument16 pagesBasic Microeconomics Day 3 LectureRoentgen Djon Kaiser IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Elasticityofdemand 160929101605 PDFDocument27 pagesElasticityofdemand 160929101605 PDFAkriti SinghNo ratings yet
- ElasticityDocument58 pagesElasticityAryan AggarwalNo ratings yet
- ElasticityDocument31 pagesElasticitySurya Bhagavan ThavvaNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand and SupplyDocument62 pagesElasticity of Demand and SupplySANSKRITI YADAV 22DM236No ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand and SupplyDocument29 pagesElasticity of Demand and SupplyEmily Canlas DalmacioNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand and SupplyDocument9 pagesElasticity of Demand and SupplyAlex HongoNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand-3Document25 pagesElasticity of Demand-3vismayNo ratings yet
- Chap 3-Elasticity of DemandDocument22 pagesChap 3-Elasticity of DemandRabinNo ratings yet
- Case On ElastisityDocument8 pagesCase On ElastisityFarah AhmedNo ratings yet
- Elasticity: - Dr. Shubhada A. JoshiDocument20 pagesElasticity: - Dr. Shubhada A. JoshiVijay KhandareNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of DemandDocument8 pagesElasticity of Demandgyanendra_paudelNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand and SupplyDocument19 pagesElasticity of Demand and Supplydev.m.dodiyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter No 1Document16 pagesChapter No 1Daima Surgical InstrumentNo ratings yet
- Ch.3-1-Elasticity and Its ApplicationDocument25 pagesCh.3-1-Elasticity and Its ApplicationLexNoLexNo ratings yet
- Class 6 ElasticityDocument18 pagesClass 6 Elasticityria maheshwariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Econ SummaryDocument7 pagesChapter 4 Econ SummaryAiza Bernadette NahialNo ratings yet
- Presentation On: ElasticityDocument58 pagesPresentation On: ElasticityRI NANo ratings yet
- The Concept of Elasticity Elasticity of Demand and SupplyDocument31 pagesThe Concept of Elasticity Elasticity of Demand and SupplySergio ConjugalNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of DemandDocument19 pagesElasticity of Demandunknownunkown01012001No ratings yet
- Chap 4 ElasticityDocument14 pagesChap 4 ElasticityLâmViênNo ratings yet
- ElasticityDocument21 pagesElasticityBob MarshellNo ratings yet
- Academic Tutorials: Ec 115 NotesDocument13 pagesAcademic Tutorials: Ec 115 NotesDixie CheeloNo ratings yet
- Elasticity: in Economics, Elasticity Is The Measurement of How Changing One Economic Variable Affects Others. andDocument36 pagesElasticity: in Economics, Elasticity Is The Measurement of How Changing One Economic Variable Affects Others. andFidez PerezNo ratings yet
- DIHE - Notes.elasticiy of DemandDocument5 pagesDIHE - Notes.elasticiy of DemandjavedhanifNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes: 2: Why Do Firms Supply More at A Higher Price?Document6 pagesLecture Notes: 2: Why Do Firms Supply More at A Higher Price?Adarsh SudheerNo ratings yet
- Price, Income and Cross ElasticityDocument24 pagesPrice, Income and Cross ElasticityparthabhiNo ratings yet
- Elasticity EconomicsDocument14 pagesElasticity EconomicsYiwen LiuNo ratings yet
- Economics Lecture 3: Micro-Economics of Product MarketsDocument43 pagesEconomics Lecture 3: Micro-Economics of Product MarketsAnanna AfroseNo ratings yet
- CH. 3 Applications of Supply and DemandDocument26 pagesCH. 3 Applications of Supply and Demandsamah.fathi3No ratings yet