0% found this document useful (0 votes)
386 views16 pagesIntro to Algorithm Pseudocode
This document provides examples of algorithm pseudocode for calculating the sum of integers from 1 to n, where n is provided by the user. Each example is given a score out of 5 based on how complete and clear the pseudocode is. The final and highest scored example (score of 5/5) uses a for loop to iterate from 1 to n, adding each number to a running sum variable mySum before printing the final result.
Uploaded by
hasib_07Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
386 views16 pagesIntro to Algorithm Pseudocode
This document provides examples of algorithm pseudocode for calculating the sum of integers from 1 to n, where n is provided by the user. Each example is given a score out of 5 based on how complete and clear the pseudocode is. The final and highest scored example (score of 5/5) uses a for loop to iterate from 1 to n, adding each number to a running sum variable mySum before printing the final result.
Uploaded by
hasib_07Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
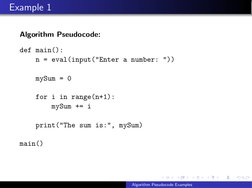
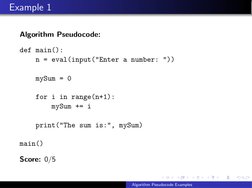
- Example 1: Basic Addition: Introduces a basic programming task to find the sum of the first n integers.
- Example 1 Pseudocode: Provides pseudocode for calculating the sum of integers, illustrating basic loop structures.
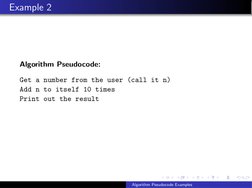
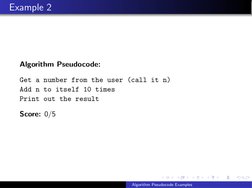
- Example 2: Repeated Addition: Describes an algorithm where a number is added to itself multiple times, explaining the repeated addition process.
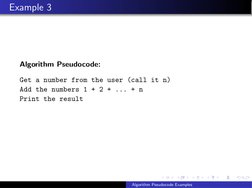
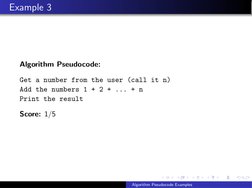
- Example 3: Sum Sequence: Explains how to compute the sum of a sequence from 1 to n using pseudocode.
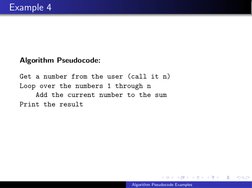
- Example 4: Loop Summation: Demonstrates a loop-based approach to summing numbers, emphasizing iteration over a numerical range.
- Example 5: While Loop Sum: Covers using a while loop to sum integers, showcasing control structures in programming.
- Example 6: For Loop Sum: Illustrates summation using a for loop to iterate over a defined range in pseudocode.
- Example 7: Adaptive Summation: Involves summing numbers with a refined for loop approach, demonstrating adaptivity in code design.