0% found this document useful (0 votes)
153 views3 pagesShoulder Examination
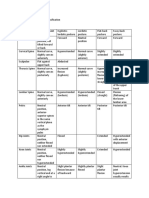
The document outlines the aims and process of examining the shoulder. It discusses examining patients by age group for common diseases like trauma, tendonitis, stiffness or arthritis. The examination involves inspection of the shoulder from different angles, palpation of key areas, and assessment of movement, muscles, nerves and vascular system. Special tests are used to check for issues like instability, impingement or rotator cuff problems. The goal is to identify any abnormalities through a thorough history and physical examination of the shoulder.
Uploaded by
Tausif HuqCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
Topics covered
- Sulcus Sign,
- Muscle Power Assessment,
- Clinical Assessment,
- Skin Inspection,
- Shoulder Pain,
- Apprehension Test,
- Infections,
- Special Tests,
- Brachial Plexus,
- Axillary Nerve
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
153 views3 pagesShoulder Examination
The document outlines the aims and process of examining the shoulder. It discusses examining patients by age group for common diseases like trauma, tendonitis, stiffness or arthritis. The examination involves inspection of the shoulder from different angles, palpation of key areas, and assessment of movement, muscles, nerves and vascular system. Special tests are used to check for issues like instability, impingement or rotator cuff problems. The goal is to identify any abnormalities through a thorough history and physical examination of the shoulder.
Uploaded by
Tausif HuqCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
Topics covered
- Sulcus Sign,
- Muscle Power Assessment,
- Clinical Assessment,
- Skin Inspection,
- Shoulder Pain,
- Apprehension Test,
- Infections,
- Special Tests,
- Brachial Plexus,
- Axillary Nerve