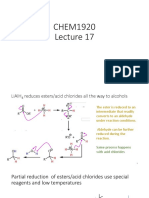
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GlycoProfile 2-AB Labeling Kit Technical Bulletin
Uploaded by
Jime nitaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GlycoProfile 2-AB Labeling Kit Technical Bulletin
Uploaded by
Jime nitaCopyright:
Available Formats
GlycoProfile 2-AB Labeling Kit
Catalog Number PP0520
Store at Room Temperature
TECHNICAL BULLETIN
Product Description O Dye
OH
H2N O
Schiff's base
Glycan analysis has become an increasingly critical H2N RO
OH
aspect of glycomics and proteomics, due to the role of HO N
glycoproteins in cell signaling, cell adhesion, immune H2N NHAc
1
response, and disease states. Because glycans tend +
to have low spectral activity in both UV and visible light,
Glycan
it is often necessary to label them in order to enhance OH Reductant
detection. OH
RO
HO O
The fluorophores 2-AB (2-aminobenzamide) and 2-AA NHAc OH
H2N O
(anthranilic acid or 2-aminobenzoic acid) provide RO
OH
cyclic/acyclic H
valuable tools for glycan analysis, due to their ( in equilibrium
) HO N
2
sensitivity and stability when bound to glycans. NHAc
Samples containing mixed pools of glycans can often
Labeled Glycan
be detected at picomolar concentrations. While 2-AB is
somewhat less sensitive than 2-AA, it is suitable for
downstream glycan analysis by HPAE (high- Components
performance anion-exchange), HPLC, and ESI-MS The kit contains sufficient reagents for labeling up to
(electrospray mass spectroscopy) methods.
3-9 36 samples. Two sets of components have been
Although suitable for the same applications, 2-AA is provided. Each set is sufficient for labeling up to
better suited for SDS-PAGE. 18 samples based on a 5 l reaction volume (to
accommodate use with the GlycoProfile Glycan
Glycan binding to both dyes is very robust with no Clean-up Cartridges, Catalog Number G4548). Prior to
degradation during post-cleanup analysis. Labeling can the clean-up step, larger samples can be split
be performed on either purified or pooled samples, accordingly.
including a variety of sources, such as N-linked,
O-linked, and GPI anchored glycans. For samples Mixed glycan samples should contain between
containing sialated oligosaccharides, sialic acid loss is 100 picomoles to 50 nanomoles of purified glycans.
negligible. Other commonly used methods such as With a single pure glycan, as little as 5 picomoles may
radiolabels, antibody labels, and various probes do not be labeled and detected in subsequent HPLC analysis.
display the stability, flexibility, and ease of use
observed with 2-AA and 2-AB. 2-AB (2-Aminobenzamide) 2 5 mg
(Catalog Number A9478)
Glycans with a free reducing sugar exist in equilibrium
between the cyclic (closed ring) and acyclic (open ring) DMSO (Dimethyl sulfoxide) 2 1 vial
structures. A stable Schiff’s base is formed when the (Catalog Number D4942)
carbonyl carbon of an acyclic reducing sugar is linked 350 l per vial
to the amine moiety of the dye in a nucleophilic manner.
Following formation of the Schiff’s base, the resulting Acetic Acid, Glacial 2 200 l
imine group is reduced using sodium cyano- (Catalog Number A9353)
borohydride, resulting in a stable labeled glycan.
Reductant (Sodium Cyanoborohydride) 2 6 mg
(Catalog Number R5153)
Equipment Required but Not Provided. 3. Prepare the Labeling Solution immediately prior to
GlycoProfile Glycan Clean-Up Cartridges labeling.
(Catalog Number G4548) a. Tap or briefly spin down component vials to
avoid loss of reagent in the cap or on the walls
Precautions and Disclaimer of ampules. To open ampules, hold both the
This product is for R&D use only, not for drug, body and the top of the ampule, then gently,
household, or other uses. Please consult the Safety but firmly, snap open at the colored break-ring,
Data Sheet for information regarding hazards and safe directing the break away from your body.
handling practices. b. Add 150 l of Acetic Acid, Glacial (Catalog
Number A9353) to the entire ampule of DMSO
It is recommended that the entire Technical Bulletin (Catalog Number D4942).
be read prior to starting the procedure. Note: DMSO forms a semi-solid at cooler
temperatures, hence warming may be required.
Labeling of glycans with 2-AB is covered under c. Add 100 l of the DMSO/Acetic Acid mixture
US Patent No 5,747,347 and its foreign equivalents. (step 3b) to the entire vial of 2-AB (Product
Code A9478). Mix until dissolved; vortexing
Storage/Stability may be required.
The kit, as supplied, is stable for at least one year when d. Add the entire volume from step 3c to the vial
stored unopened at room temperature. The 2-AB of Reductant (Catalog Number R5153). Mix
reagent (Catalog Number A9478) is light-sensitive and until completely dissolved. If insoluble
must be stored in the dark. Labeled glycans should be particulates remain, the solution may be heated
stored at –20 C in the dark. For optimal results, the to 65 C for up to 3 minutes. Any remaining
labeling reagent should be used within one hour of particulates can be dissolved by adding 10 l of
component reconstitution and preparation. water, (HPLC grade or better). This is the
Labeling Solution and should be protected from
Procedure light. It is stable for 1 hour.
Glycan samples may be prepared by enzymatic 4. Add 5 l of the Labeling Solution (step 3d) to each
deglycosylation or chemical deglycosylation via dried glycan sample. Cap and mix thoroughly. Tap
hydrazinolysis. For mixed pools of glycans, the optimal or spin down to collect the dissolved sample in the
sample size is 100 pmol to 50 nmol. For purified bottom of each vial.
samples of a single glycan, much lower amounts may 5. Incubate glycan samples for 3 hours at 65 C in a
be labeled. As little as 5 pmol of a single purified heating block, dry oven, or sand tray. Avoid moist
glycan be detected in post-labeling analysis by HPLC. heat, if possible. If a water bath or moist heat is
used, the vials must be tightly sealed.
1. Prior to labeling, glycan samples should be purified Note: Incubation periods of 2–4 hours will not
to remove protein, peptides, salts, detergents, and significantly affect results.
any additional contaminating substances. 6. If insoluble particulates are present, vortex the
2. Transfer the glycan sample solutions into the pre-heated samples from step 5 for 30 minutes.
reaction vials and dry completely. Excess moisture 7. Following incubation, briefly spin the vials to
will have negative effects on labeling and stability. recollect each sample at the bottom of the reaction
a. Optimal results are obtained when samples are vial. Allow the samples to cool to ambient
dried by centrifugal evaporation. Use caution temperature prior to proceeding with post-labeling
with lyophilization. Ensure that each sample analysis.
dries as a concentrated mass at the bottom of a. Extended periods of time between incubation
the vials. and analysis may result in desialylation of
b. Do not expose samples to extreme pH or high labeled glycans and consequently should be
temperatures. avoided.
i. Temperatures 28 C and/or low pH will b. Sample clean up using GlycoProfile Glycan
result in desialylation. Clean-Up Cartridges (Catalog Number G4548)
ii. Exposure to high pH may result in is recommended to remove excess dye and
epimerization of reducing sugars. labeling reagents. A purification protocol is
included with the cartridges.
Analysis of 2-AB labeled glycans 9. Guile, G.R., et al., Anal. Biochem., 240(2), 210-226
The 2-AB reagent has an excitation range of (1996).
200–450 nm, with an excitation peak at 330 nm. The 10. Ruhaak, L.R., et al., Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 397(8),
emission range for 2-AB is 300–750 nm, with an 3457-3481 (2010).
emission peak at 420 nm. 11. Mechref, Y., et al., Mol. Cell. Proteomics, 12(4),
874-884 (2013).
Once the glycans have been labeled, various methods 12. Orlando, R., Methods Mol. Biol., 951, 197-215
exist to analyze them. The most common techniques (2013).
employ fluorescent detection after separation by HPLC
or CE. These include separation by ion exchange (i.e., LICENSE TO USE
high-performance anion exchange), normal phase Purchase of this 2-AB Labeling Kit grants a Use
HPLC, and size exclusion chromatography. Sublicense under Glyko's 2-AB patents. By accepting
delivery of the GlycoProfile 2-AB Labeling Kit
Labeled glycans can also be detected using SDS- [Material(s)] and by subsequently using it in glycan
PAGE and mass spectrometry. The dye linkage is analysis, Recipient agrees to be bound by the following
stable to both of these methods. Mass spectrometry terms and restrictions:
can be performed with either an electrospray ionization
(ESI) or by matrix assisted laser absorption ionization 1. A Use Sublicense is granted Recipient for in-house
10-12
(MALDI) ion source. use of Material(s) only.
Related Products 2. The Material(s) will not be made available by
Enzymatic Deglycosylation Kit Recipient to any outside parties in any form,
(Catalog Number EDEGLY) separately or in combinations, for any monetary or
PNGase F (Catalog Number P7367) other consideration or at no charge, except that the
O-Glycosidase (Catalog Number G1163) Materials may be made available to outside parties
who agree to be bound by all the terms and
References restrictions of this Agreement for purposes of
1. Novotny, M.V., and Alley, W.R., Jr., Curr. Opin. evaluation only.
Chem. Biol., 17(5), 832-840 (2013).
2. Bigge, J.C., et al., Anal. Biochem., 230(2), 229-238 3. Recipient will not make commercial use of the
(1995). Material(s) unless it first secures a license
3. Merry, A.H., et al., Anal. Biochem., 304(1), 91-99 agreement for such commercial use.
(2002).
4. Delaney, J., and Vouros, P., Rapid Commun. Mass 4. Recipient is solely responsible for qualification of
Spectrom., 15(5), 325-334 (2001). the products for the Recipient's specific use.
5. Rudd, P.M., et al., Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev.,
16, 1-21(1999). 5. The Material(s) will not be used in vivo in humans.
6. Anumula, K.R., and Dhume, S.T., Glycobiology,
8(7), 685-694 (1998). Labeling of glycans with 2-AB is covered under
7. Hardy, M.R., “Glycan labeling with the fluorophores US Patent No 5,747,347 and its foreign equivalents.
2-aminobenzamide and anthranilic acid”, from
Techniques in Glycobiology (R.R. Townsend and GlycoProfile is a trademark of Sigma-Aldrich Co. LLC.
A.T. Hotchkiss, Jr., eds.), Marcel Dekker, Inc. (New
York, NY), pp. 359-375 (1997). JP,ANK,GCY,MAM, 04/16-1
8. Townsend, R.R., et al., Anal. Biochem., 239(2),
200-207 (1996).
Troubleshooting Guide
The glycan content of an unknown sample may be estimated. The average
Estimating sample size glycosylation of proteins is 2–5% with an average glycan molecular mass of
1,000 Da. A 1 mg sample of glycoprotein contains 50 g of glycans.
Improper temperature control during incubation. Ensure that samples remain at
65 C throughout the entire incubation period by preheating heat blocks. Do not over
or under heat. Dye incorporation declines sharply at incubation temperatures below
65 C. Higher temperatures will not increase dye incorporation, but will contribute to
Poor dye incorporation desialylation.
Incomplete solubilization – Glycans must be completely solubilized for maximal
labeling efficiency. Ensure thorough mixing at each stage of the procedure.
Vortexing for 30 minutes during the incubation period may be necessary (see
Procedure, step 6).
Sample may contain contaminants that interfere with dye incorporation. Ensure
glycans have been properly purified prior to labeling.
Contamination
Degraded Labeling Solution. The Labeling Solution must be freshly prepared
immediately prior to use. The Labeling Solution begins to degrade after one hour.
Loss or absence of free reducing sugar. The aldehyde group on the free reducing
sugars must be available for 2-AB conjugation. Glycans that have been conjugated
at their reducing termini (glycolipids, previously labeled glycans, glycopeptides) leave
Lower than expected no open site for conjugation to occur.
concentration of glycans Loss of glycans or incomplete binding of glycans to membrane during clean-up
process. Refer to the technical bulletin provided with the GlycoProfile Glycan
Clean-up Cartridges (Catalog Number G4548) for troubleshooting guide and
recommended solutions.
Desialylation Exposure to acidic conditions or heating at temperatures 65 C may result in
of glycans desialylation.
High background, non- This may indicate the presence of an aldehyde-bearing contaminant that readily
glycan fluorescence reacts with 2-AB dye. Ensure adequate clean-up procedure prior to labeling.
2016 Sigma-Aldrich Co. LLC. All rights reserved. SIGMA-ALDRICH is a trademark of Sigma-Aldrich Co. LLC, registered in the US and other
countries. Sigma brand products are sold through Sigma-Aldrich, Inc. Purchaser must determine the suitability of the product(s) for their
particular use. Additional terms and conditions may apply. Please see product information on the Sigma-Aldrich website at
www.sigmaaldrich.com and/or on the reverse side of the invoice or packing slip.
You might also like
- Cell Culture Bioprocess EngineeringDocument337 pagesCell Culture Bioprocess EngineeringNathan Galicia100% (1)
- VITEK-Hypochlorous Acid-2020 PDFDocument24 pagesVITEK-Hypochlorous Acid-2020 PDFWaiyan Htet AungNo ratings yet
- 5991 2852enDocument8 pages5991 2852enMohammad SamsudinNo ratings yet
- Gen Z Social MediaDocument32 pagesGen Z Social MediaJime nitaNo ratings yet
- Chejov Ivanov PDFDocument61 pagesChejov Ivanov PDFJime nitaNo ratings yet
- McKinsey Problem Solving Test - Practice TestBDocument28 pagesMcKinsey Problem Solving Test - Practice TestBproyecto20132014No ratings yet
- UNIT II Glycoproteins: (Chapter 46 - Harper's)Document6 pagesUNIT II Glycoproteins: (Chapter 46 - Harper's)Aine CebedoNo ratings yet
- TracertechniqueDocument14 pagesTracertechniqueVijetha PendyalaNo ratings yet
- s41557-024-01473-5Document9 pagess41557-024-01473-5annanekalra7976267448No ratings yet
- Application Note: Determination of C2-C12 Aldehydes in Water by SPME On-Fiber Derivatiza-Tion and GC/MSDocument6 pagesApplication Note: Determination of C2-C12 Aldehydes in Water by SPME On-Fiber Derivatiza-Tion and GC/MSAli AhmedNo ratings yet
- Glycosides Classification and TypesDocument25 pagesGlycosides Classification and TypesVikash KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Mild Asymmetric Reductions of Unsaturated KetonesDocument9 pagesMild Asymmetric Reductions of Unsaturated KetonesDiogomussumNo ratings yet
- Tetrahedron: Huanhuan Wang, Shengqing Ye, Hanpeng Jin, Jianping Liu, Jie WuDocument7 pagesTetrahedron: Huanhuan Wang, Shengqing Ye, Hanpeng Jin, Jianping Liu, Jie WuValentina RoznovNo ratings yet
- Bioorganic Chemistry: SciencedirectDocument11 pagesBioorganic Chemistry: SciencedirectWalid Ebid ElgammalNo ratings yet
- Thurl Et Al. - 1996 - Quantification of Individual Oligosaccharide CompoDocument5 pagesThurl Et Al. - 1996 - Quantification of Individual Oligosaccharide CompoValerie WeinbornNo ratings yet
- K Nova NagelDocument8 pagesK Nova NagelSiddhesh Umesh MestryNo ratings yet
- Estimation Influences of Green Tea As A Medical Herb For Treating Diabetes MellitusDocument10 pagesEstimation Influences of Green Tea As A Medical Herb For Treating Diabetes MellitusHaleelu Abdul JaleelNo ratings yet
- Separation of Salicylic Acid Impurities With DiffeDocument4 pagesSeparation of Salicylic Acid Impurities With Diffemic92833292No ratings yet
- Synthesis and Characterization of 2,5-Dihydroxy Substituted ChalconesDocument6 pagesSynthesis and Characterization of 2,5-Dihydroxy Substituted ChalconesGanesamoorthy ThirunarayananNo ratings yet
- IntershipDocument33 pagesIntershipKhatija BanooNo ratings yet
- Acute Ethylene Glycol İntoxication - Part II.Document9 pagesAcute Ethylene Glycol İntoxication - Part II.taner_soysuren100% (1)
- Toocj 2 107Document3 pagesToocj 2 107Enzo ArevaloNo ratings yet
- Direct Reductive Amination and Selective 1,2-ReductionDocument4 pagesDirect Reductive Amination and Selective 1,2-ReductionJ-Paul DétoNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous SystemDocument77 pagesCentral Nervous SystemPriti tiwariNo ratings yet
- Analysis Methods For Zinc Plating BrightenersDocument5 pagesAnalysis Methods For Zinc Plating BrightenersYasir ZohaNo ratings yet
- Sodium Bis (2-Methoxyethoxy) Aluminum HydrideDocument8 pagesSodium Bis (2-Methoxyethoxy) Aluminum HydridejavasoloNo ratings yet
- Cho ReactionsDocument124 pagesCho Reactionsssr SNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument16 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenesnadeemmessi30No ratings yet
- Alkyl Halides & Aryl Halides-01 - TheoryDocument32 pagesAlkyl Halides & Aryl Halides-01 - TheoryRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Module 15 Drug Design and Discovery: Trimox (Antibiotic) Zoloft (Antidepresent)Document6 pagesModule 15 Drug Design and Discovery: Trimox (Antibiotic) Zoloft (Antidepresent)Jithin Raphi KollannurNo ratings yet
- Synthesis and Evaluation of Antioxidant Semicarbazone DerivativesDocument5 pagesSynthesis and Evaluation of Antioxidant Semicarbazone DerivativesWalid EbaiedNo ratings yet
- Kirihara 2017Document13 pagesKirihara 2017Fernand AtipoNo ratings yet
- Halo PurineDocument7 pagesHalo PurinealderumbraNo ratings yet
- NP2016-9364091 TRES INDocument10 pagesNP2016-9364091 TRES INjorge.arredondoNo ratings yet
- Sulfuric Acid Immobilized On Silica An Excellent Catalyst ForDocument5 pagesSulfuric Acid Immobilized On Silica An Excellent Catalyst ForJoseph HoffmanNo ratings yet
- Highly Selective Oxidation and Depolymerization of Diol Protected LigninDocument6 pagesHighly Selective Oxidation and Depolymerization of Diol Protected LigninGRagaNo ratings yet
- Thermofisher Instructions Nhs and Edc ReactionDocument4 pagesThermofisher Instructions Nhs and Edc ReactionSergio Rodríguez MolinaNo ratings yet
- Previo 2Document3 pagesPrevio 2david liraNo ratings yet
- Hydrogenation of 2-EthylanthraquinoneDocument14 pagesHydrogenation of 2-EthylanthraquinonemaryammsazeemNo ratings yet
- AN 521 Analysis Badge Bfdge Derivatives Canned Food Beverages AN63361 EDocument4 pagesAN 521 Analysis Badge Bfdge Derivatives Canned Food Beverages AN63361 EmigueljovanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry TestDocument8 pagesChemistry Testistna nafi azzahraniNo ratings yet
- Tetrahedron Letters - J A HadfieldDocument5 pagesTetrahedron Letters - J A HadfieldDaniel JiménezNo ratings yet
- DSC, NMRDocument9 pagesDSC, NMRDoaa FarahNo ratings yet
- Disconnection in Organic SynthesisDocument31 pagesDisconnection in Organic SynthesisSwami Prabhu100% (2)
- Characterization of Chemical Warfare Agent Hydrolysis Products by SERSDocument7 pagesCharacterization of Chemical Warfare Agent Hydrolysis Products by SERSjakalae5263No ratings yet
- Glycosides classification and nomenclatureDocument25 pagesGlycosides classification and nomenclaturexIRONxWOLFxNo ratings yet
- CHEM1920 Lecture 17v2Document29 pagesCHEM1920 Lecture 17v2Mr SpaciousNo ratings yet
- Specification Sheet: Product: Salted Anchovy in BarrelsDocument1 pageSpecification Sheet: Product: Salted Anchovy in BarrelsPoesía PeruanaNo ratings yet
- List of Reagents of All Chapters and Their Function - askIITiansDocument11 pagesList of Reagents of All Chapters and Their Function - askIITiansall India TamilNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Antiphlogistic Activity of Synthesized Chalconesemicarbazone DerivativesDocument9 pagesEvaluation of Antiphlogistic Activity of Synthesized Chalconesemicarbazone Derivativessunaina agarwalNo ratings yet
- s44160-022-00080-x SEMINARIODocument6 pagess44160-022-00080-x SEMINARIOMarcos GNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRY: Proteins 2: Physical PropertiesDocument7 pagesBIOCHEMISTRY: Proteins 2: Physical PropertiesCon ChinNo ratings yet
- The Stabilization of L-Ascorbic Acid in Aqueous Solution and Water-In-Oil-In-Water Double Emulsion by Controlling PH and Electrolyte ConcentrationDocument12 pagesThe Stabilization of L-Ascorbic Acid in Aqueous Solution and Water-In-Oil-In-Water Double Emulsion by Controlling PH and Electrolyte ConcentrationTi MaNo ratings yet
- Erba ALBUMIN PDFDocument2 pagesErba ALBUMIN PDFAniket dubeyNo ratings yet
- Bioorganic & Medicinal ChemistryDocument6 pagesBioorganic & Medicinal Chemistryilham ditamaNo ratings yet
- Direct Arylation and Applications of Ruthenium Olefin Metathesis Catalysts - Aldrichimica Acta Vol. 40 No. 2Document28 pagesDirect Arylation and Applications of Ruthenium Olefin Metathesis Catalysts - Aldrichimica Acta Vol. 40 No. 2Sigma Aldrich Chemistry100% (2)
- Arterial Blood Gas Interpretation NotesDocument3 pagesArterial Blood Gas Interpretation NotesJewel Yap100% (1)
- 10.1007@s12039 020 01775 4Document9 pages10.1007@s12039 020 01775 4Md. BadrulNo ratings yet
- Chap 6 GlycosidesDocument66 pagesChap 6 GlycosidesUkash sukarmanNo ratings yet
- Porg Finals All LessonDocument13 pagesPorg Finals All LessonLazaro, Javen Andrie A.No ratings yet
- IM-Lecture-Acid-Base-ImbalanceDocument8 pagesIM-Lecture-Acid-Base-ImbalanceCHYNNA ALBERTNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes, Alcohols and Amines. Problem Sheet 1Document2 pagesHaloalkanes, Alcohols and Amines. Problem Sheet 1Kundan Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Sugar Alcohols: AnalysisDocument7 pagesSugar Alcohols: AnalysisTeera YimyooNo ratings yet
- Colloidal Gold: Principles, Methods, and ApplicationsFrom EverandColloidal Gold: Principles, Methods, and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Ad 9915Document47 pagesAd 9915Jime nitaNo ratings yet
- Distributions HandbookDocument202 pagesDistributions HandbookMubangaNo ratings yet
- A Simple PDFDocument2 pagesA Simple PDFJaheer MakalNo ratings yet
- GenZ FinalDocument51 pagesGenZ FinalJohn O'ConnorNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Allergenicity of Genetically Modified FoodsDocument30 pagesEvaluation of Allergenicity of Genetically Modified FoodsChirag EducationNo ratings yet
- Azucares DeterminaciónDocument362 pagesAzucares DeterminaciónfelipeNo ratings yet
- A Systematic Review of ESN Nutritional Bioactive Compounds Health Benefits As Functional Food and Recent Development As Functional Food and Recent Development As Bioactive ESN Glycopeptide HydrolysateDocument17 pagesA Systematic Review of ESN Nutritional Bioactive Compounds Health Benefits As Functional Food and Recent Development As Functional Food and Recent Development As Bioactive ESN Glycopeptide HydrolysateSze JackNo ratings yet
- What Is The Sugar Code?Document24 pagesWhat Is The Sugar Code?Daniela RangelNo ratings yet
- Varki EssentialsofGlycobiologyLibroDocument710 pagesVarki EssentialsofGlycobiologyLibroladyerato100% (1)
- ICH Q6B Service LeafletDocument2 pagesICH Q6B Service LeafletM-ScanNo ratings yet
- Mass Spectrometry-Based Glycoprofiling of Biopharmaceuticals by Using An Automated Data Processing Tool - SimGlycan®Document10 pagesMass Spectrometry-Based Glycoprofiling of Biopharmaceuticals by Using An Automated Data Processing Tool - SimGlycan®yun baiNo ratings yet
- Kishimoto 2020Document9 pagesKishimoto 2020Yeye123No ratings yet
- US HUPO Abstract BookDocument165 pagesUS HUPO Abstract BookBrianna FlinkNo ratings yet
- Waters Specific ConsumablesDocument18 pagesWaters Specific ConsumablesRodrigo BordonNo ratings yet
- Glycosylation Controls Animal Cell Culture QualityDocument51 pagesGlycosylation Controls Animal Cell Culture QualityMahesh Aithal0% (1)
- Post Translational ModificationsDocument3 pagesPost Translational ModificationsIzzat RozaliNo ratings yet
- 2017 Book SingleCellAnalysisDocument277 pages2017 Book SingleCellAnalysisÁlvaro Brown Garcia100% (1)
- Monoclonal Antibodies:: Beyond The PlatformDocument20 pagesMonoclonal Antibodies:: Beyond The PlatformBalaNo ratings yet
- US HUPO 2022 Abstract BookDocument166 pagesUS HUPO 2022 Abstract BookBrianna FlinkNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate ChemistryDocument461 pagesCarbohydrate ChemistryAlexis DragonNo ratings yet
- GlycanAge - Sample ReportDocument18 pagesGlycanAge - Sample ReportDomagoj BakotaNo ratings yet
- TS Glycobiology in Cancer EbookDocument8 pagesTS Glycobiology in Cancer EbookDaisy Joanna Castañeda MataNo ratings yet
- Nej MR A 1206793Document13 pagesNej MR A 1206793David LeónNo ratings yet
- Glycans AplicacionesDocument180 pagesGlycans AplicacionesIvanaColinNo ratings yet
- The Molecular Biology of Coronaviruses David Cavanaght: MichaelDocument100 pagesThe Molecular Biology of Coronaviruses David Cavanaght: MichaelAchi JackNo ratings yet
- Glycosylation Methods and Analysis SigmaDocument87 pagesGlycosylation Methods and Analysis SigmabogobonNo ratings yet
- 1ST MIDTERM BIOCHEM EVALUATION EXAMDocument2 pages1ST MIDTERM BIOCHEM EVALUATION EXAMMaryNo ratings yet
- 212 Oligosaccharide AnalysisDocument14 pages212 Oligosaccharide AnalysissofianesedkaouiNo ratings yet
- ContentsDocument115 pagesContentsNadeem khanNo ratings yet
- Azides in Carbohydrate Chemistry: A Versatile ToolDocument22 pagesAzides in Carbohydrate Chemistry: A Versatile ToolDaianne PadroniNo ratings yet
- Estructura y Arquitectura Del PeptidoglucanoDocument19 pagesEstructura y Arquitectura Del PeptidoglucanoOleggValVilNo ratings yet
- Research Core: Berenson-Allen Center For Noninvasive Brain Stimulation Clinical Research Coordinator CoreDocument4 pagesResearch Core: Berenson-Allen Center For Noninvasive Brain Stimulation Clinical Research Coordinator CoreMazhar KayaNo ratings yet