0% found this document useful (0 votes)
124 views9 pagesCreating Vectors and Matrices in MATLAB
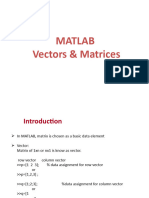
Vectors are one-dimensional arrays, while matrices are two-dimensional arrays. Matlab counts elements from top to bottom and left to right. Common operations include creating, accessing, modifying, and performing calculations on vectors and matrices. Functions like zeros, ones, eye, and rand can generate matrices filled with specific values.
Uploaded by
Zack ObegaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
124 views9 pagesCreating Vectors and Matrices in MATLAB
Vectors are one-dimensional arrays, while matrices are two-dimensional arrays. Matlab counts elements from top to bottom and left to right. Common operations include creating, accessing, modifying, and performing calculations on vectors and matrices. Functions like zeros, ones, eye, and rand can generate matrices filled with specific values.
Uploaded by
Zack ObegaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd