0% found this document useful (0 votes)
85 views1 pagePythagorean Triples in Linear Algebra
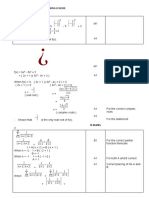
1) The document discusses Pythagorean triples and using matrices to represent linear transformations that preserve the property of being a Pythagorean triple.
2) It provides examples of applying invertible matrices A, B, and C to vectors (x) and shows that the results are also Pythagorean triples, demonstrating that the matrices preserve the property.
3) The document concludes that taking the inverse of the matrices A, B, and C applied to the vector x results in Pythagorean triples in the case of A but not for B and C, since their inverses produce negative values.
Uploaded by
api-296073547Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
85 views1 pagePythagorean Triples in Linear Algebra
1) The document discusses Pythagorean triples and using matrices to represent linear transformations that preserve the property of being a Pythagorean triple.
2) It provides examples of applying invertible matrices A, B, and C to vectors (x) and shows that the results are also Pythagorean triples, demonstrating that the matrices preserve the property.
3) The document concludes that taking the inverse of the matrices A, B, and C applied to the vector x results in Pythagorean triples in the case of A but not for B and C, since their inverses produce negative values.
Uploaded by
api-296073547Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd