Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Neurotransmitters Table PDF
Uploaded by
Marwina Dorie0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Neurotransmitters table.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesNeurotransmitters Table PDF
Uploaded by
Marwina DorieCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
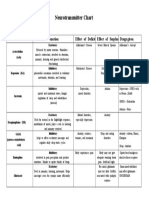
NEUROTRANSMITTERS
Neurotransmitter Function Receptor Action Related drugs/illnesses
Acetylcholine Excitatory Nicotinic ACh-R Ionotropic channels incr gNa, gK, Curare (N1), hexamethonium (N2)
(N1-neuromusc, N2- gCa
NT for many post ganglionic ANS) nd Atropine (M)
Muscarinic ACh-R Metabotropic channels 2
parasympathetics mssrs, phos of channels,
(M1-CNS, GI; M2-
conductance changes
heart)
Norepinephrine (many postgang symp) 1 Tyrosine Dopa Lack of NE may cause manic-depression: Tricyclics
(ie desipramine) inhibit reuptake (by
1- contracts sm musc, bv 2 dopamine NE
autoreceptors); MAO (monoamine oxidase)
2 – autorec of NE (inhibits release) 1 inhibitors increase presynaptic concentration
1 – incr HR, contractility 2 (prevent NE degradation)
2 – relax GI sm musc, some vasc sm
Dopamine Pleasure and reward D1 Gsincr Cocaine, amphetamines – inhibit reuptake (can
Involved in memory D2 cAMPphosphor. have long-term effect-dcr receptors)
BIOGENIC AMINES
Gidecr cAMP Parkinson’s-decr in DA treat with DOPA
Schizophrenia: excess D4 treat with blockers of
receptors (ie phenothiazines)
Serotonin (pleasure) All GPCR except Made from Trp-5-HT SSRIs = selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors ie
5-HT3 (ionotropic) Prozac (fluoxetine) – targets Na-coupled transport
– treat depression, esp anxiety
OCDs – use Paxil (SSRI)
LSD – activates 5-HD2 receptor
MDMA (ecstasy)- elev 5-HT, then decr
Histamine Mediates allergic response; H1-H3= GPCRs in Benadryl (antihistamine) drowsiness
arousal hypothalamus -Can block H1 to decr motion sickness (blocks
vestibular function)
-Block H2 (gastric acid synthesis) to control peptic
ulcers
Glutamate (and Main excitatory NT in the brain 11 metabotropic *NMDA is ligand- and if Glu too much Ca kills cell
Aspartate) Synaptic plasticity – learning receptors voltage-gated: Mg blocking Excitoxin achieves this
*mGluR4 = basis of umami Ionotropic: pore is only moved when V >
kainite, AMPA, -60mV
AMINO ACIDS
NMDA but necessary for Ca influx
GABA (and glycine) Main inhibitory NT in the brain GABAA-ionotropic GABAA incr gCl – opposes depol Barbiturates and benzodiazepines (ie Valium) –
(20% of CNS synapses) GABAB- GABAB Gi decr gCa, inc gK enhance effects of GABA on gCl reduce anxiety,
Gly – incr gCl mainly in SC muscle relaxants
metabotrop
Activation by GABA alone Strychnine – blocks Gly receptors convulsions,
hyperpol; GABA+enhancer more hyperactivity – used by athletes to boost
sustained inhibitory response performance
NEUROTRANSMITTERS
Oxytocin and Uterine contractions, nursing;
vasopressin water reabsorption in kidney
Substance P Mediates pain (found in Can block in depressed patients who
intestine) don’t respond to SSRIs
PEPTIDES
Vasoactive intestinal GI function
peptide (VIP) and
cholecystokinin
Opioid peptides analgesics Same as opiates POMC (pro- May be involved in athletic “high”
opiomelanocortin) - Receptors can also bind morphine,
endorphin and enkephalin codeine
(analgesics)
NO Relaxes smooth muscle NOSGC synth cGMP cGMP hydrolyzed by PDE – block with
Interneuronal messenger in -- phos smooth musc protein Viagra etc.
GASES
brain
CO -- Made from heme-oxygenase
H2S Cardioprotective effect during
--
ischemia
You might also like
- Survival MDDocument206 pagesSurvival MDEddie Kluss III100% (11)
- Neurotransmitter ChartDocument1 pageNeurotransmitter Chartmonster40lbs100% (2)
- Mcfadden S System o 00 Mac FDocument144 pagesMcfadden S System o 00 Mac FcgonzjamNo ratings yet
- Psych Drugs Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesPsych Drugs Cheat SheetHJ G100% (3)
- Drug ListDocument30 pagesDrug ListKristineNo ratings yet
- Psych Drugs Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesPsych Drugs Cheat Sheetfreecouch80% (5)
- Patho Immune System PathologyDocument7 pagesPatho Immune System PathologyCoy Nuñez100% (1)
- Neurotransmitter Cheat Sheet AP ReviewDocument2 pagesNeurotransmitter Cheat Sheet AP ReviewNathania DawitNo ratings yet
- Psych Drugs NursingDocument7 pagesPsych Drugs Nursinglisa100% (2)
- PSYCH 011 Clinical Diagnosis of Neurocognitive DisorderDocument7 pagesPSYCH 011 Clinical Diagnosis of Neurocognitive DisorderKaye NeeNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmitter Function TableDocument2 pagesNeurotransmitter Function TableMaharaniDewiNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System - HandoutsDocument5 pagesAutonomic Nervous System - HandoutsKelly Trainor100% (1)
- CNS NeurotransmittersDocument30 pagesCNS Neurotransmittersdevanshi_582262183100% (1)
- Psychotropic Medications ListDocument1 pagePsychotropic Medications Listapnitickets100% (1)
- Neurotransmitters and Drugs ChartDocument6 pagesNeurotransmitters and Drugs ChartTammy Tam100% (5)
- SDL: Common Cardiac Drugs: Deala, Donna Marie Toledo Advanced Diploma in Medical Surgical-Group 1Document13 pagesSDL: Common Cardiac Drugs: Deala, Donna Marie Toledo Advanced Diploma in Medical Surgical-Group 1Donna Deala100% (2)
- NeurotransmittersDocument63 pagesNeurotransmittersNeelu Soni100% (1)
- Management of Psychotic SymptomsDocument25 pagesManagement of Psychotic Symptomsmisstheatricality130No ratings yet
- Elementary Botany (Groom) 1898 PDFDocument320 pagesElementary Botany (Groom) 1898 PDFsamsij100% (1)
- Sudden Onset (Within 2 Weeks) of at Least One of TheDocument2 pagesSudden Onset (Within 2 Weeks) of at Least One of TheNeicole BandalaNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmitter Pathways: A Tutorial Study GuideFrom EverandNeurotransmitter Pathways: A Tutorial Study GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Cranial Nerves SummaryDocument3 pagesCranial Nerves SummaryJoash F. Pacquing75% (4)
- Neurotransmitters and Psychiatry PDFDocument22 pagesNeurotransmitters and Psychiatry PDFcapriciousbelal93% (14)
- NeuroDocument16 pagesNeuroBrandon Goodman100% (3)
- Glossary of Psychiatric TerminologyDocument20 pagesGlossary of Psychiatric Terminologyphoebe_62002239No ratings yet
- Disorders of ThoughtDocument56 pagesDisorders of ThoughtPriyash JainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Neurobiologic Theories and PsychopharmacologyDocument11 pagesChapter 2 - Neurobiologic Theories and PsychopharmacologyCatia FernandesNo ratings yet
- Psy - DisordDocument18 pagesPsy - DisordShaz Chindhy100% (1)
- NeurotransmittersDocument5 pagesNeurotransmittersJoezerk Jhon Biel100% (1)
- The Theory of Engineering Drawing PDFDocument370 pagesThe Theory of Engineering Drawing PDFYob YnnosNo ratings yet
- AntipsychoticsDocument10 pagesAntipsychoticswawing16No ratings yet
- NeurotransmittersDocument92 pagesNeurotransmittersClare DucutNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument53 pagesDrugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous SystemMatt Stone100% (1)
- Oils of MetalsDocument9 pagesOils of Metalsmichael777No ratings yet
- Onco PharmacologyDocument9 pagesOnco Pharmacologyarn0ld21No ratings yet
- Psychiatric Agents: By: Paula Rose Mae Cuario Evita Lalaine Del Mundo Dennis Ragudo Sheena ZarsueloDocument80 pagesPsychiatric Agents: By: Paula Rose Mae Cuario Evita Lalaine Del Mundo Dennis Ragudo Sheena ZarsueloDennis RagudoNo ratings yet
- NeurotransmittersDocument29 pagesNeurotransmittersashupathakaNo ratings yet
- Spinal Tracts: DR - Krishna Madhukar Dept. of Orthopaedics Bharati HospitalDocument65 pagesSpinal Tracts: DR - Krishna Madhukar Dept. of Orthopaedics Bharati HospitalKrishna Madhukar100% (1)
- Pharmacology in PsychiatryDocument33 pagesPharmacology in PsychiatryKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- Disorders of ThoughtDocument22 pagesDisorders of ThoughtMohammad Farouq OmarNo ratings yet
- 2 Thyroid and Antithyroid DrugsDocument24 pages2 Thyroid and Antithyroid DrugsLiza Marie de Guzman100% (1)
- Cognitive Disorders PresentationDocument70 pagesCognitive Disorders PresentationWasiu AfoloabiNo ratings yet
- Seven MetalsDocument40 pagesSeven MetalsMaik Moura100% (1)
- Psychotic DisordersDocument38 pagesPsychotic DisordersMala Rasaily100% (2)
- Biochemistry 1.3 NeurotransmittersDocument10 pagesBiochemistry 1.3 Neurotransmitterslovelots1234No ratings yet
- Basic PsychoPharma MnemonicsDocument21 pagesBasic PsychoPharma MnemonicsJoseph Rommel Castro CortezNo ratings yet
- Psycho PharmaDocument8 pagesPsycho PharmaMark JosephNo ratings yet
- Cancer DrugsDocument5 pagesCancer DrugsLinh HoangNo ratings yet
- B2B Psychopharmacology 2015Document128 pagesB2B Psychopharmacology 2015Soleil DaddouNo ratings yet
- Table of NeurotransmittersDocument10 pagesTable of NeurotransmittersAmanda Shabrina PutriNo ratings yet
- Drug ClassDocument13 pagesDrug ClassEdfren Salazar Colon100% (1)
- Biological Bases Study GuideDocument13 pagesBiological Bases Study Guideapi-421695293No ratings yet
- Neurotransmitters: A. Paracrine Regulators (Tissue Hormones)Document11 pagesNeurotransmitters: A. Paracrine Regulators (Tissue Hormones)Prasana100% (1)
- Consolidated Set of The GRI Standards 2021Document654 pagesConsolidated Set of The GRI Standards 2021Yob YnnosNo ratings yet
- Geas 1Document84 pagesGeas 1Mariz-Elaine Noceja Rodriguez100% (7)
- Physical Examination of The NewbornDocument70 pagesPhysical Examination of The NewbornBeaflor Javier CaldozoNo ratings yet
- 2019 Psych Updated 2Document9 pages2019 Psych Updated 2Nae OrdanozoNo ratings yet
- AntipsychoticsDocument29 pagesAntipsychoticsTyler Lawrence Coye100% (5)
- Antidepressants and Mood StabilizersDocument4 pagesAntidepressants and Mood Stabilizers우정은No ratings yet
- Necrotising Enterocolitis in Infants On NICU JCG0038 v2Document11 pagesNecrotising Enterocolitis in Infants On NICU JCG0038 v2RatnaArdianaNoviantiNo ratings yet
- Pipe Problems & Elements (With Answer and Solution)Document36 pagesPipe Problems & Elements (With Answer and Solution)Lourence Arazo Enanod55% (11)
- TiroidDocument26 pagesTiroidJoni Riana MustaqimNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic Drug MnemonicsDocument1 pageCholinergic Drug Mnemonicssunshine151100% (1)
- Steven - Neurotransmitter ChartDocument3 pagesSteven - Neurotransmitter ChartSteven SunNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic AgentsDocument57 pagesAdrenergic AgentsAn Lo100% (1)
- SchizophreniaDocument5 pagesSchizophreniaapi-3765584100% (3)
- Antidepressant DrugsDocument21 pagesAntidepressant DrugsKashis SharmaNo ratings yet
- Limbic SystemDocument11 pagesLimbic SystemStd DlshsiNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Nursing ReviewDocument44 pagesPsychiatric Nursing ReviewramemgarNo ratings yet
- AnxiolyticsDocument8 pagesAnxiolyticsAlfie16No ratings yet
- Autonomic DrugsDocument107 pagesAutonomic DrugsMaria Mercedes LeivaNo ratings yet
- Rational Expressions - OverviewDocument23 pagesRational Expressions - OverviewYob YnnosNo ratings yet
- Factoring Polynomials - GCF and Difference of Two SquaresDocument29 pagesFactoring Polynomials - GCF and Difference of Two SquaresYob YnnosNo ratings yet
- Factoring Polynomials - OverviewDocument28 pagesFactoring Polynomials - OverviewYob YnnosNo ratings yet
- Perfect Square Trinomials and Quadratic Trinomials With A 1Document25 pagesPerfect Square Trinomials and Quadratic Trinomials With A 1Yob YnnosNo ratings yet
- Homework Discussion - Multiplication and Division of Rational ExpressionsDocument17 pagesHomework Discussion - Multiplication and Division of Rational ExpressionsYob YnnosNo ratings yet
- Functions of Several VariablesDocument26 pagesFunctions of Several VariablesYob YnnosNo ratings yet
- Schedule - National Center For Mental Health 2020Document9 pagesSchedule - National Center For Mental Health 2020Yob YnnosNo ratings yet
- GRI 306 - Waste 2020Document30 pagesGRI 306 - Waste 2020Yob YnnosNo ratings yet
- GRI 3 - Material Topics 2021Document30 pagesGRI 3 - Material Topics 2021Yob YnnosNo ratings yet
- In Defense of Hiya As A Filipino VirtueDocument14 pagesIn Defense of Hiya As A Filipino VirtueYob YnnosNo ratings yet
- Taal VolcanoDocument13 pagesTaal VolcanoYob YnnosNo ratings yet
- EraserheadsDocument17 pagesEraserheadsYob YnnosNo ratings yet
- Swift (Programming Language)Document17 pagesSwift (Programming Language)Yob YnnosNo ratings yet
- LysineDocument18 pagesLysineYob YnnosNo ratings yet
- Neoclassical EconomicsDocument8 pagesNeoclassical EconomicsYob YnnosNo ratings yet
- Saint Rose of LimaDocument7 pagesSaint Rose of LimaYob YnnosNo ratings yet
- Salesians of Don BoscoDocument9 pagesSalesians of Don BoscoYob YnnosNo ratings yet
- TTM Grand RoundsDocument47 pagesTTM Grand Roundsapi-590340413100% (1)
- CCDocument4 pagesCCJaymih Santos AbasoloNo ratings yet
- Formative Assessment Intro To Metabolismm PDFDocument3 pagesFormative Assessment Intro To Metabolismm PDFJoy VergaraNo ratings yet
- Swastika v1 n3 Mar 1907Document67 pagesSwastika v1 n3 Mar 1907pesquisas literáriasNo ratings yet
- Cri 201 Pre Compre ExaminationDocument6 pagesCri 201 Pre Compre ExaminationKyle Adrian FedranoNo ratings yet
- I. ConclusionDocument1 pageI. ConclusionJARISSA DIZON GALLAZANo ratings yet
- 2021 Level L Biology Practical Based QuestionsDocument61 pages2021 Level L Biology Practical Based Questions-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument492 pagesUntitledKku KkyNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume DisturbancesDocument36 pagesFluid Volume Disturbancesafricanviolets9100% (1)
- Blood Cell - An Overview of Studies in Hematology PDFDocument360 pagesBlood Cell - An Overview of Studies in Hematology PDFnaresh sharmaNo ratings yet
- EC 1 12H Leaflet Eng PDFDocument2 pagesEC 1 12H Leaflet Eng PDFancaNo ratings yet
- SLH S 20 00050Document34 pagesSLH S 20 00050VsnuNo ratings yet
- EnterobakterDocument36 pagesEnterobakterUttari DalemNo ratings yet
- Morfologi DaunDocument34 pagesMorfologi DaunTasyaChNo ratings yet
- 1.2.3 Transport in PlantsDocument11 pages1.2.3 Transport in PlantsMo_Bash1No ratings yet
- Concept Map Critical CareDocument6 pagesConcept Map Critical Careapi-508559825No ratings yet
- Peripheral Arterial DseDocument2 pagesPeripheral Arterial Dsemiss RNNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Children With BurnsDocument52 pagesNursing Care of Children With Burnskarpagamanbu100% (5)
- Trigeminal Nerve (CN V) : TemporalisDocument3 pagesTrigeminal Nerve (CN V) : Temporalisمحمد سعدون موسى عزيزNo ratings yet
- Cannabis and Cannabinoids in The Perioperative PeriodDocument15 pagesCannabis and Cannabinoids in The Perioperative PeriodyenuginNo ratings yet
- UretrotomyDocument10 pagesUretrotomySatria Adi MarhendraNo ratings yet
- Obstetric Hemorrhage AnestDocument9 pagesObstetric Hemorrhage AnestjefeNo ratings yet