Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SJMCR-57438-440
Uploaded by
Dwi PascawitasariOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SJMCR-57438-440
Uploaded by
Dwi PascawitasariCopyright:
Available Formats
DOI: 10.
21276/sjmcr
Scholars Journal of Medical Case Reports ISSN 2347-6559 (Online)
Sch J Med Case Rep 2017; 5(7):438-440 ISSN 2347-9507 (Print)
©Scholars Academic and Scientific Publishers (SAS Publishers)
(An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Multiple Purulent Arthritis, Epidural Abscess, and Panophthalmitis Induced By
Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. Equisimilis infection
Akihiko Kondo MD1, Kazuhiko Omori MD.PhD2, Hiroki Nagasawa MD3, Ikuto Takeuchi MD4, Kei Jitsuiki MD5,
Hiromichi Ohsaka MD.PhD6, Kouhei Ishikawa MD.PhD7, Youichi Yanagawa MD.PhD8
1-8
Department of Acute Critical Care Medicine, Juntendo University Shizuoka Hospital, Japan
*Corresponding author
Dr. Youichi Yanagawa
Email: yyanaga@juntendo.ac.jp
Abstract: An 80-year-old female who had had difficulty moving for the previous week was transferred to a local medical
facility. After obtaining a diagnosis of multiple organ failure with multiple purulent arthritis and epidural abscess, she
was transported to our department. She had a history of diabetes mellitus. She had also been complicated with left
panophthalmitis. She developed complications with thrombocytopenia and died of alveolar hemorrhaging. This is the
first case of multiple purulent arthritis, epidural abscess, and panophthalmitis induced by SDSE infection. Physicians
should consider invasive SDSE infections when treating elderly patients with underlying comorbidities, such as diabetes
mellitus.
Keywords: Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. Equisimilis; diabetes mellitus; epidural abscess; warfarin
INTRODUCTION back pain and painful bilateral knee swellings. Chest
Among clinically isolated β-hemolytic roentgen and electrocardiogram findings were negative.
streptococci, Streptococcus pyogenes and S. agalactiae Her arterial gas (under 3 L/minO2) revealed a pH of
were considered the main pathogens in humans until 7.42, PCO2 of 24 mmHg, PO2 of 107 mmHg, HCO3- of
recently [1]. In 1996, S. dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis 16.2 mmol/L, and base excess of -6 mmol/L. The
(SDSE) was proposed as a novel taxon among human- results of the biochemical analyses of the blood on
derived streptococcal isolates [1]. SDSE has Lancefield arrival were as follows: white blood cells, 22,000/μl;
group C or G antigens, exhibits strong β-hemolysis, and hemoglobin, 11.0 g/dl; platelets, 20.1×10 4/μl; aspartate
exerts streptokinase activity upon human plasminogen aminotransferase, 258 IU/L; alanine aminotransferase,
and proteolytic activity upon human fibrin [1]. SDSE 132 IU/L; glucose, 180 mg/dl; blood urea nitrogen,
may exist among the normal flora of the skin, 134.1 mg/dl; creatinine, 5.3 mg/dl; sodium, 140 mEq/L;
oropharynx, and gastrointestinal and genitourinary potassium, 4.8 mEq/L; chloride, 93 mEq/L; creatine
tracts [1]. In the 21stcentury, invasive SDSE infection phosphokinase, 4389 IU/L; prothrombin time 14.4
(i.e. cellulitis, urosepsis, and pneumonia) leading to (12.2) sec; activated partial thromboplastin time, 25.3
various disseminated diseases is being diagnosed (28.0) sec; 33.1 μg/ml.
increasingly in Japan and elsewhere in Asia, Europe,
and America [1]. The patient underwent tracheal intubation. As
she had multiple organ failure due to septic shock, he
We herein report a case of multiple purulent received tracheal intubation with mechanical
arthritis, epidural abscess and panophthalmitis induced ventilation, continuous infusion of vasopressor,
by SDSE. continuous hemodiafiltration, and antibiotics
(meropenem and vancomycin) after drainage of
CASE REPORT thebilateral knee abscesses. Surgical drainage for the
An 80-year-old female who had had difficulty epidural abscess was not performed, at the behest of the
moving for the previous week was transferred to a local orthopedician, due to the patient’s severe medical
medical facility. After obtaining a diagnosis of multiple condition.
organ failure with multiple purulent arthritis and
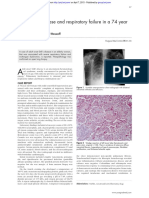
epidural abscess (Figure 1), she was transported to our On the third hospital day, SDSE infection was
department for intensive care the same day as she was confirmed based on the results of culture from the knee.
transferred. She had a history of diabetes mellitus. At Antibiotics were switched to ampicillin based on the
arrival, her vital signs were as follows: Glasgow Coma sensitivity of the culture, and continuous
Scale, E3V4M6; blood pressure, 88/56 mmHg; pulse hemodiafiltration was ceased after obtaining urinary
rate, 88 beats per minute; respiratory rate, 24 breaths flow. Her circulation and respiration improved, and
per minutes; and body temperature, 36.6 °C. She had extubation was performed on the seventh day. After
Available Online: http://saspjournals.com/sjmcr 438
Akihiko Kondo et al.; Sch J Med Case Rep, Jul 2017; 5(7):438-440
extubation, she complained of left eye and shoulder with thrombocytopenia 2 days later. Her platelet level
pain. She had also been complicated with left purulent suddenly decreased to 1,100 from 20.6 × 104 μl without
arthritis at the shoulder and left panophthalmitis. She any signs of an exacerbation of infection or thrombosis.
could not move, so she underwent continuous infusion Transfusion and the infusion of steroids as well as
of heparin on the eighth hospital day. The left eyeball ceasing warfarin failed to increase the platelet count,
was removed on the 14th hospital day. She was able to and she eventually died of alveolar hemorrhaging on the
feed herself but still could not walk because of pain in 32nd day. Antibodies for both heparin-induced
the bilateral knees. After being prescribed warfarin to thrombocytopenia and idiopathic thrombocytopenia
prevent deep vein thrombosis instead of the infusion of were negative.
heparin on the 27th day, she developed complications
Fig-1: Lumbar magnetic resonance image (MRI) obtained at a local medical facility showing the epidural abscess
(Left: T1, Middle T2, Right: STIR image).
DISCUSSION effects. Radical treatment including bilateral amputation
This is the first case of multiple purulent of the knees and surgical drainage of the epidural
arthritis, epidural abscess, and panophthalmitis induced abscess might have allowed the patient to achieve a
by SDSE infection. SDSE infection can range in survival outcome [7,8]. However, she was elderly and
severity from relatively mild skin and soft tissue would have become totally dependent on others in her
conditions, such as wound infection, erysipelas, and daily life after such radical procedures.
cellulitis, to life-threatening necrotizing fasciitis and
streptococcal toxic shock syndrome, thus sharing a Warfarin-induced thrombocytopenia has not been
clinical picture with S. pyogenes [2-4]. The most reported in the English literature. This case might be
common clinical manifestation of bacteremia is HIT please spell out all abbreviations at first mention
cellulitis [3]. Arthritis and ophthalmitis induced by because the patient met three of the four Ts [9,10].
SDSE have been reported; however, epidural abscess or However, one case report concerning thrombocytopenia
the combination of arthritis and ophthalmitis induced by induced by warfarin has been published in Japan [11].
SDSE has not been reported [5,6]. Invasive forms of This case was confirmed as being due to an
this infection are most commonly found in elderly unintentional challenge test of warfarin. As such, the
patients with underlying comorbidities, such as diabetes thrombocytopenia observed in the present case might
mellitus, similar to the present case [1-4]. The fatality have been induced by warfarin.
rate for bacteremia has been reported to be 15%-18%
[1]. We performed drainage of the bilateral knee REFERENCES
abscesses and removed the infected eyeball in addition 1. Takahashi T, Ubukata K, Watanabe H. Invasive
to infusing appropriate anti biotics. The present case infection caused by Streptococcus dysgalactiae
showed temporary relief of the patient’s severe medical subsp. equisimilis: characteristics of strains and
conditions, but she unfortunately died due to drug side
Available Online: http://saspjournals.com/sjmcr 439
Akihiko Kondo et al.; Sch J Med Case Rep, Jul 2017; 5(7):438-440
clinical features. Journal of Infection and
Chemotherapy. 2011 Jan 1; 17(1):1-0.
2. Leitner E, Zollner-Schwetz I, Zarfel G, Masoud-
Landgraf L, Gehrer M, Wagner-Eibel U, Grisold
AJ, Feierl G. Prevalence of emm types and
antimicrobial susceptibility of Streptococcus
dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis in Austria.
International Journal of Medical Microbiology.
2015 Dec 31; 305(8):918-24.
3. Rantala S. Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp.
equisimilis bacteremia: an emerging infection.
European journal of clinical microbiology &
infectious diseases. 2014 Aug 1;33(8):1303-10.
4. Takahashi T, Sunaoshi K, Sunakawa K, Fujishima
S, Watanabe H, Ubukata K. Clinical aspects of
invasive infections with Streptococcus dysgalactiae
ssp. equisimilis in Japan: differences with respect
to Streptococcus pyogenes and Streptococcus
agalactiae infections. Clinical Microbiology and
Infection. 2010 Aug 1;16(8):1097-103.
5. Astete CA, Gómez NS, Alarcón ML. Septic
Arthritis by Streptococcus equi. Reumatología
Clínica (English Edition). 2016;4(12):237-8.
6. Yong AS, Lau SY, Woo TH, Li JY, Yong TY.
Streptococcus dysgalactiae endocarditis presenting
as acute endophthalmitis. Infectious disease
reports. 2012 Jan 2; 4(1).
7. Horowitz DL, Katzap E, Horowitz S, Barilla-
LaBarca ML. Approach to septic arthritis.
American family physician. 2011 Sep 15; 84(6).
8. Pourtaheri S, Issa K, Stewart T, Patel Y, Sinha K,
Hwang K, Emami A. When Do You Drain
Epidural Abscesses of the Spine?. Surgical
technology international. 2016 Oct; 29:374-8.
9. Ahmed I, Majeed A, Powell R. Heparin induced
thrombocytopenia: diagnosis and management
update. Postgraduate medical journal. 2007 Sep
1;83(983):575-82.
10. Favaloro EJ, McCaughan G, Pasalic L. Clinical and
laboratory diagnosis of heparin induced
thrombocytopenia: an update. Pathology. 2017 Apr
23.
11. Nito U, Hahara T. A case of thrombocytopenia
induced by war farin. Kotu Igaku 62:22, 2008. In
Japanese
Available Online: http://saspjournals.com/sjmcr 440
You might also like
- Ijam-3775 CDocument3 pagesIjam-3775 Carunkumar kumararunNo ratings yet
- Dengue Shock Syndrome Complicated With Acute Liver Failure and Kidney Injury, Infective Endocarditis, and Deep Vein ThrombosisDocument4 pagesDengue Shock Syndrome Complicated With Acute Liver Failure and Kidney Injury, Infective Endocarditis, and Deep Vein ThrombosisputiridhaNo ratings yet
- Sub Acute Haemophilus Parainfluenzae Endocarditis: A Case Report and Review of LiteratureDocument6 pagesSub Acute Haemophilus Parainfluenzae Endocarditis: A Case Report and Review of LiteratureIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Dengue Perimyocarditis: A Case Report: PL GohDocument3 pagesDengue Perimyocarditis: A Case Report: PL GohDenny IntanNo ratings yet
- A Rare Cause of Endocarditis: Streptococcus PyogenesDocument3 pagesA Rare Cause of Endocarditis: Streptococcus PyogenesYusuf BrilliantNo ratings yet
- Rhizomucor Scedosporium: Case ReportDocument6 pagesRhizomucor Scedosporium: Case ReportPaul ColburnNo ratings yet
- DeSanto 3057Document8 pagesDeSanto 3057Maryka CociuNo ratings yet
- Endocarditis Caused by Unusual Streptococcus Species (Streptococcus Pluranimalium)Document4 pagesEndocarditis Caused by Unusual Streptococcus Species (Streptococcus Pluranimalium)Soria M JorgeNo ratings yet
- Dengue Oral ManifestationDocument7 pagesDengue Oral ManifestationGowthamChandraSrungavarapuNo ratings yet
- 415-Article Text-2894-1-10-20200228Document3 pages415-Article Text-2894-1-10-20200228Gianni CoccoNo ratings yet
- Acute Fulminant Leptospirosis with Multi-Organ FailureDocument4 pagesAcute Fulminant Leptospirosis with Multi-Organ FailureMuhFarizaAudiNo ratings yet
- LepsDocument4 pagesLepslynharee100% (1)
- HANTAVIRUS Case Report - Trud Za ObjavuvanjeDocument7 pagesHANTAVIRUS Case Report - Trud Za ObjavuvanjeKeti JanevskaNo ratings yet
- DRESS Syndrome in A Patient On Sulfasalazine For Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument4 pagesDRESS Syndrome in A Patient On Sulfasalazine For Rheumatoid ArthritisChistian LassoNo ratings yet
- A Case of Vaccine-Associated Myocarditis Following Pneumococcal Immunization Leading To Acute Mitral RegurgitationDocument8 pagesA Case of Vaccine-Associated Myocarditis Following Pneumococcal Immunization Leading To Acute Mitral RegurgitationAlina Elisabeta Tiniuc căs LehaciNo ratings yet
- Infectious Endocarditissecondary To Neisseria SPP in Patients With Cardiac Prostheses: Rare Entity and Difficult DiagnosisDocument6 pagesInfectious Endocarditissecondary To Neisseria SPP in Patients With Cardiac Prostheses: Rare Entity and Difficult DiagnosisIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Neumonia Anciano 2014Document8 pagesNeumonia Anciano 2014Riyandi MardanaNo ratings yet
- Al Muthanna International Trauma Conference MAY 9 - 11, 2020 Samawa, IraqDocument5 pagesAl Muthanna International Trauma Conference MAY 9 - 11, 2020 Samawa, IraqKhaliel AlsarafNo ratings yet
- Endocard BartonDocument4 pagesEndocard BartonKrull TTTeamNo ratings yet
- Native Mitral Valve Fungal Endocarditis Caused 2024 International Journal ofDocument4 pagesNative Mitral Valve Fungal Endocarditis Caused 2024 International Journal ofRonald QuezadaNo ratings yet
- Vascular Complications of Serious Vipers Envenomation: About A CaseDocument5 pagesVascular Complications of Serious Vipers Envenomation: About A CaseIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Leptospirosis Presenting As Severe Cardiogenic Shock: A Case ReportDocument3 pagesLeptospirosis Presenting As Severe Cardiogenic Shock: A Case ReportFirdha GitaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory and Pulmonary Medicine: ClinmedDocument3 pagesRespiratory and Pulmonary Medicine: ClinmedGrace Yuni Soesanti MhNo ratings yet
- Elizabeth King I ADocument3 pagesElizabeth King I AAlba UrbinaNo ratings yet
- Case Report: Fatal Staphylococcal Infection Following Classic Dengue FeverDocument4 pagesCase Report: Fatal Staphylococcal Infection Following Classic Dengue FeverRia Septi HarmiaNo ratings yet
- Skleroderma Dan ILD A Case ReportDocument3 pagesSkleroderma Dan ILD A Case ReportdethachaniagoNo ratings yet
- Sepsis: R. Dwi HendradiankoDocument36 pagesSepsis: R. Dwi HendradiankoSukamdani Rachman100% (1)
- 1882-Article Text-7722-1-10-20200608 PDFDocument6 pages1882-Article Text-7722-1-10-20200608 PDFRyanNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Leptospirosis: Iralphuaborque Md14thbatch Hds DocharlabardaDocument15 pagesCardiac Leptospirosis: Iralphuaborque Md14thbatch Hds DocharlabardaJr. CesingNo ratings yet
- Jeyasuriya Et AlDocument3 pagesJeyasuriya Et AlInternational Journal of Clinical and Biomedical Research (IJCBR)No ratings yet
- 278 977 1 SMDocument2 pages278 977 1 SMMohamed MukhrizNo ratings yet
- ISCA-IRJMedS-2014-058Document3 pagesISCA-IRJMedS-2014-058KarenNo ratings yet
- Dengue CKDDocument5 pagesDengue CKDbamhoi07No ratings yet
- Delay in Diagnosis of Extra-Pulmonary Tuberculosis by Its Rare Manifestations: A Case ReportDocument5 pagesDelay in Diagnosis of Extra-Pulmonary Tuberculosis by Its Rare Manifestations: A Case ReportSneeze LouderNo ratings yet
- Staphylococcus Lugdunensis Vascular Aortic Graft Infection: A Report of First CaseDocument2 pagesStaphylococcus Lugdunensis Vascular Aortic Graft Infection: A Report of First Caseom mkNo ratings yet
- Use of Chloroquine in Asymptomatic Elderly Covid19 Patients, A Placebo or Rather A Source of Complications: A Case ReportDocument8 pagesUse of Chloroquine in Asymptomatic Elderly Covid19 Patients, A Placebo or Rather A Source of Complications: A Case ReportIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Isolated Thrombocytopenia A Rare Presenting Feature of Enteric FeverDocument2 pagesIsolated Thrombocytopenia A Rare Presenting Feature of Enteric FeverputiridhaNo ratings yet
- Internal MedicineDocument38 pagesInternal MedicineRoxana Alexandra BogosNo ratings yet
- Thromboembolic Complications After Splenectomy For Hematologic DiseasesDocument5 pagesThromboembolic Complications After Splenectomy For Hematologic DiseasesDipen GandhiNo ratings yet
- Envenimations ViperinesDocument6 pagesEnvenimations ViperinesIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Adult Still's Disease and Respiratory Failure in A 74 Year Old WomanDocument3 pagesAdult Still's Disease and Respiratory Failure in A 74 Year Old WomanEduardo Romero StéfaniNo ratings yet
- A Case of Snake Bite With Unusual Complications and Review of LiteratureDocument8 pagesA Case of Snake Bite With Unusual Complications and Review of LiteratureIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Acute OsteomyelitisDocument6 pagesAcute OsteomyelitisImran TaufikNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Challenge of Tuberculosis in Systemic Lupus ErythematosusDocument9 pagesDiagnostic Challenge of Tuberculosis in Systemic Lupus ErythematosusBelinda Putri agustiaNo ratings yet
- 94 JMSCRDocument3 pages94 JMSCRmaria lisaNo ratings yet
- JurnalDocument9 pagesJurnalMelita Amalia AyubaNo ratings yet
- Sme PropofolDocument2 pagesSme PropofolAntonella Jazmín AssadNo ratings yet
- Ijccm 18 540Document3 pagesIjccm 18 540dr muddssar sattarNo ratings yet
- Mediterranean Spotted Fever With Encephalitis: Case ReportDocument5 pagesMediterranean Spotted Fever With Encephalitis: Case Reportracut_khansatraNo ratings yet
- Internal MedicineDocument36 pagesInternal MedicineRoxana Alexandra BogosNo ratings yet
- Management of HemophagocyticDocument10 pagesManagement of HemophagocyticAlexander CanoNo ratings yet
- SepsisDocument36 pagesSepsisWan FaizuddinNo ratings yet
- Stenotrophomonas. Maltophilia - A Rare Cause of Bacteremia in A Patient of End Stage Renal Disease On Maintenance HemodialysisDocument3 pagesStenotrophomonas. Maltophilia - A Rare Cause of Bacteremia in A Patient of End Stage Renal Disease On Maintenance HemodialysisInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)No ratings yet
- Treatment of Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Materials and MethodsDocument3 pagesTreatment of Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Materials and Methodscharlietuna1No ratings yet
- Living For 11 Years in A Permanent Vegetative StateDocument8 pagesLiving For 11 Years in A Permanent Vegetative StateAndrei RusmirNo ratings yet
- Typhoid Fever Case Presenting with Multiple ComplicationsDocument4 pagesTyphoid Fever Case Presenting with Multiple ComplicationsCleo CaminadeNo ratings yet
- Islam 2010Document3 pagesIslam 2010koniskoNo ratings yet
- Ofy 038Document5 pagesOfy 038Rosandi AdamNo ratings yet
- Acute Epiglottitis in The Immunocompromised Host: Case Report and Review of The LiteratureDocument5 pagesAcute Epiglottitis in The Immunocompromised Host: Case Report and Review of The Literaturerosandi sabollaNo ratings yet
- Secondary HypertensionFrom EverandSecondary HypertensionAlberto MorgantiNo ratings yet
- Hubungan Facial Injury Severity Scale Dengan Lama Rawat Inap Pasien Trauma MaksilofasialDocument5 pagesHubungan Facial Injury Severity Scale Dengan Lama Rawat Inap Pasien Trauma MaksilofasialDwi PascawitasariNo ratings yet
- Multidetector Coputed Tomographic Evaluation of Maxilofacial TraumaDocument5 pagesMultidetector Coputed Tomographic Evaluation of Maxilofacial TraumaDwi PascawitasariNo ratings yet
- Understanding Mixed Phenotype Acute Leukemia (MPAL): Diagnosis, Treatment and Case ReportDocument23 pagesUnderstanding Mixed Phenotype Acute Leukemia (MPAL): Diagnosis, Treatment and Case ReportDwi PascawitasariNo ratings yet
- Hubungan Antara Fraktur Maksilofasial Dengan Terjadinya Lesi IntrakranialDocument5 pagesHubungan Antara Fraktur Maksilofasial Dengan Terjadinya Lesi IntrakranialAnonymous s013ck7No ratings yet
- Volume 1 PDFDocument782 pagesVolume 1 PDFEmina SaeedNo ratings yet
- JofIMAB2013vol19b2p282 285 PDFDocument4 pagesJofIMAB2013vol19b2p282 285 PDFAlung Padang SiraitNo ratings yet
- Prevention, Diagnosis, and Management of Acute Postoperative Bacterial EndophthalmitisDocument16 pagesPrevention, Diagnosis, and Management of Acute Postoperative Bacterial EndophthalmitisNiñoTanNo ratings yet
- Endogenous EndophthalmitisDocument11 pagesEndogenous EndophthalmitisDwi PascawitasariNo ratings yet
- Cardio Book PDFDocument34 pagesCardio Book PDFDwi PascawitasariNo ratings yet
- Endophthalmitis - Prophylaxis - For - Cataract - Surgery PDFDocument6 pagesEndophthalmitis - Prophylaxis - For - Cataract - Surgery PDFDwi PascawitasariNo ratings yet
- Prevention, Diagnosis, and Management of Acute Postoperative Bacterial EndophthalmitisDocument16 pagesPrevention, Diagnosis, and Management of Acute Postoperative Bacterial EndophthalmitisNiñoTanNo ratings yet
- ESCRS EndophthalmitisDocument52 pagesESCRS EndophthalmitisKaveh Vahdani100% (2)
- ESCRS EndophthalmitisDocument52 pagesESCRS EndophthalmitisKaveh Vahdani100% (2)
- Endogenous EndophthalmitisDocument11 pagesEndogenous EndophthalmitisDwi PascawitasariNo ratings yet
- Twelve-Step Programs Addiction RecoveryDocument6 pagesTwelve-Step Programs Addiction RecoveryDwi PascawitasariNo ratings yet
- Twelve-Step Programs Addiction RecoveryDocument6 pagesTwelve-Step Programs Addiction RecoveryDwi PascawitasariNo ratings yet
- Vagal Nerve Block JournalDocument8 pagesVagal Nerve Block JournalDwi PascawitasariNo ratings yet
- Vagal Nerve Block JournalDocument10 pagesVagal Nerve Block JournalDwi PascawitasariNo ratings yet
- CellulitisDocument5 pagesCellulitisKrishna PendemNo ratings yet
- CMC Steroid Then SurgeryDocument9 pagesCMC Steroid Then SurgeryAabra AhmedNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Infectious Diseases. Vaccination ProgramsDocument44 pagesPediatric Infectious Diseases. Vaccination ProgramsShubhra PaulNo ratings yet
- Care Planning for Diabetic Patient with CellulitisDocument7 pagesCare Planning for Diabetic Patient with Cellulitissahilchaudhary7No ratings yet
- Assasment, Treatment CelulitisDocument7 pagesAssasment, Treatment CelulitisSulistiyawati CuplizNo ratings yet
- Choosing Wisely RecommendationsDocument186 pagesChoosing Wisely Recommendationspedropedro1954No ratings yet
- Infection & Specific Wound InfectionsDocument39 pagesInfection & Specific Wound InfectionsAhmed ShorshNo ratings yet
- Spontaneous Primary Myopathies in Domestic Mammals A ReviewDocument18 pagesSpontaneous Primary Myopathies in Domestic Mammals A Reviewkadek ayu ichaNo ratings yet
- Cellulitis - Practice Essentials, Background, PathophysiologyDocument14 pagesCellulitis - Practice Essentials, Background, PathophysiologyginNo ratings yet
- V V V V Nonpurulent: Keflex (Cephalexin) or Cefadroxil V Purulent: I & D Gold Standard If Systemic MRSA CoverageDocument1 pageV V V V Nonpurulent: Keflex (Cephalexin) or Cefadroxil V Purulent: I & D Gold Standard If Systemic MRSA CoverageCyndiNo ratings yet
- Therap Case 3Document18 pagesTherap Case 3Safoora RafeeqNo ratings yet
- Submental Abscess After Deoxycholic Acid Injection: ReferenceDocument1 pageSubmental Abscess After Deoxycholic Acid Injection: Referencechash75No ratings yet
- Quiz IntegumentaryDocument44 pagesQuiz IntegumentaryMedShare100% (5)
- Cutaneous Abscess Furuncles and CarbuclesDocument25 pagesCutaneous Abscess Furuncles and Carbuclesazmmatgowher_1219266No ratings yet
- Pathogenesis of Group A Streptococcal InfectionsDocument59 pagesPathogenesis of Group A Streptococcal InfectionsHerdwin Limas IINo ratings yet
- Bacterial and Rickettsial InfectionsDocument51 pagesBacterial and Rickettsial Infectionslilis lestariNo ratings yet
- Complication of Sinus DiseaseDocument27 pagesComplication of Sinus DiseaseukhuholicNo ratings yet
- DIABETES Nursing ManagementDocument11 pagesDIABETES Nursing ManagementKaloy KamaoNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Skin and Soft Tissue InfectionsDocument5 pagesBacterial Skin and Soft Tissue InfectionsFarid Gusranda100% (2)
- Combined Cellulitis - FinalDocument78 pagesCombined Cellulitis - Finalsaru_patel0% (1)
- IWGDF Guideline On The Classification of Diabetic Foot UlcersDocument15 pagesIWGDF Guideline On The Classification of Diabetic Foot Ulcersdr. Ellen FernandaNo ratings yet
- General Pathology Presentation (Cellulitis)Document17 pagesGeneral Pathology Presentation (Cellulitis)Lames Ali Sayed Ahmed AttiaNo ratings yet
- Preseptal cellulitis: eyelid infection under 40 charsDocument4 pagesPreseptal cellulitis: eyelid infection under 40 charsKm PlegariaNo ratings yet
- Daman Wound Care MangmentDocument5 pagesDaman Wound Care Mangmentriyas mhdNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Infections of The SkinDocument41 pagesBacterial Infections of The Skinleenaloveu100% (2)
- 50 Item Integumentary Exam-BudekDocument8 pages50 Item Integumentary Exam-BudekLj FerolinoNo ratings yet
- Red EyesDocument3 pagesRed EyesirijoaNo ratings yet
- Boy's Ankle Pain Leads to Staphylococcus aureus Osteomyelitis and Septic ArthritisDocument36 pagesBoy's Ankle Pain Leads to Staphylococcus aureus Osteomyelitis and Septic ArthritisFernando Román RubioNo ratings yet
- All Questions DikanatDocument212 pagesAll Questions DikanatAli ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- PBL OsteomyelitisDocument27 pagesPBL OsteomyelitisNabilah SufianNo ratings yet