Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Histology of the Breast: Lobules, Alveoli and Ducts
Uploaded by
Ibrahim Sugiyono0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
82 views2 pagesThe document discusses the histology of the breast. The mammary glands are modified apocrine sweat glands containing 15-25 lobes divided into lobules containing alveoli and ducts. An inactive mammary gland has small ducts, undeveloped alveoli, and few lobules, while an active gland during pregnancy and lactation shows proliferation of alveoli and extensive branching of the duct system. During lactation, alveolar epithelial cells produce milk through merocrine and apocrine secretion which accumulates in the duct system. Post-lactation, alveoli degenerate through apoptosis and macrophages remove debris.
Original Description:
Histologi Payudara
Original Title
Histology of Breast
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the histology of the breast. The mammary glands are modified apocrine sweat glands containing 15-25 lobes divided into lobules containing alveoli and ducts. An inactive mammary gland has small ducts, undeveloped alveoli, and few lobules, while an active gland during pregnancy and lactation shows proliferation of alveoli and extensive branching of the duct system. During lactation, alveolar epithelial cells produce milk through merocrine and apocrine secretion which accumulates in the duct system. Post-lactation, alveoli degenerate through apoptosis and macrophages remove debris.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
82 views2 pagesHistology of the Breast: Lobules, Alveoli and Ducts
Uploaded by
Ibrahim SugiyonoThe document discusses the histology of the breast. The mammary glands are modified apocrine sweat glands containing 15-25 lobes divided into lobules containing alveoli and ducts. An inactive mammary gland has small ducts, undeveloped alveoli, and few lobules, while an active gland during pregnancy and lactation shows proliferation of alveoli and extensive branching of the duct system. During lactation, alveolar epithelial cells produce milk through merocrine and apocrine secretion which accumulates in the duct system. Post-lactation, alveoli degenerate through apoptosis and macrophages remove debris.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Histology of Breast
Mammary glands are modified from apocrine sweat gland, contain 15-25 lobes. Lobes are divided into
lobules. Inside lobules there are alveoli and intralobular duct.
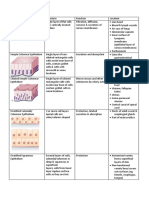
General Histology
Areola: thin skin with sebaceous gland and high level of melanin
Nipple: keratized stratified squamous epithelial cell with many nerve ends
Lactiferous duct opening: stratified squamous epithelial cells
Lactiferous sinus: stratified cuboidal epithelial cells
Lactifeous duct: simple cuboidal epithelium
Interlobular duct: simple cuboidal epithelium
Intralobular duct: simple cuboidal epithelium that surrounded by myoepithelium
Inactive Mammary Gland (resting, not pregnant, not lactating)
Small duct, Undeveloped alveoli, and Few lobules
Active mammary gland (pregnant, lactating)
Proliferation of alveoli, duct system is grow and extensively branched, gland is active
In late pregnancy, alveoli and ducts are filled with colostrumsdilated
Milk production
Estrogen and progesterone prolactin milk production
Alveolar epithelial cells enlage and active in milk production
protein made by rough ER packages into secretory vesicleexocytosis by merocrine secretion
lipidextension of fatty acid chainpackaged by apical cell exocytosis by apocrine secretion
Lactosemade in GAexcretion with …..
Those material are accumulated in duct system as milk
Post lactational regression of mammary gland
Breast feeding is stoppedalveoli degenerates by apotosis and sloughing of cells. Dead cells and debris
are removed by autophagy of macrophages
Elderly woman: fat deposition, loss of fiboblast, collagen, and elastic fibers ins troma, atrophy of
glandular tissuebreast size
You might also like
- MCQ EmbryoDocument78 pagesMCQ EmbryoAyesha Rajpoot100% (1)
- Tissues: Types, Functions & ClassificationDocument18 pagesTissues: Types, Functions & ClassificationZainab Ali100% (1)
- Physiology Comprehensive Exam Pointers PDFDocument108 pagesPhysiology Comprehensive Exam Pointers PDFRaynalynGimoros100% (1)
- PBL SS 2 - Fetal DevelopmentDocument3 pagesPBL SS 2 - Fetal DevelopmentJellie MendozaNo ratings yet
- Notes About BiologyDocument81 pagesNotes About BiologyRichard Coffey100% (1)
- DPP XI Chapter - 16 Digestion and Absorption 12Document12 pagesDPP XI Chapter - 16 Digestion and Absorption 12Riya MondalNo ratings yet
- Staining Techniques Guide Under 40 CharactersDocument11 pagesStaining Techniques Guide Under 40 CharactersJermaine BalbanidaNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive HistologyDocument59 pagesFemale Reproductive HistologyIta Indriani100% (2)
- Chapt 4 5 6 7 Practice TestDocument18 pagesChapt 4 5 6 7 Practice TestOregon190100% (6)
- Bone Tissues 1Document38 pagesBone Tissues 1ms_pianist100% (1)
- Thecytoskeleton PPTDocument11 pagesThecytoskeleton PPTseenu mohapatraNo ratings yet
- Histology of The Upper GITDocument43 pagesHistology of The Upper GITBenedict OkotNo ratings yet
- DVPT of Female Genital TractDocument31 pagesDVPT of Female Genital TractThomas Cherian0% (1)
- 3rd Lecture On The Histology of Female Reproductive System by Dr. RoomiDocument19 pages3rd Lecture On The Histology of Female Reproductive System by Dr. RoomiMudassar RoomiNo ratings yet
- Histo Slides Volume IDocument67 pagesHisto Slides Volume IKristian CadaNo ratings yet
- Histology DigestiveDocument87 pagesHistology DigestiveAnang Yanuar RamadhanNo ratings yet
- 01 Emryology The BeginningDocument117 pages01 Emryology The BeginningOsman Saidu SesayNo ratings yet
- Tissues 4Document65 pagesTissues 4marianisie448100% (3)
- Histo Slides LabelledDocument32 pagesHisto Slides LabelledFatima BkNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissues 2Document71 pagesConnective Tissues 2Asma AijazNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Histology SlidesDocument4 pagesCharacteristics of Histology SlidesLaiq Khan100% (1)
- Histology of GIT Part 1 Esophagus PDFDocument20 pagesHistology of GIT Part 1 Esophagus PDFJeffrey RamosNo ratings yet
- Development of the Female Reproductive SystemDocument37 pagesDevelopment of the Female Reproductive SystemGodwin ZengeniNo ratings yet
- Histo Slides Volume IIDocument21 pagesHisto Slides Volume IIKristian CadaNo ratings yet
- 1st To 3rd Weeks of DevelopmentDocument60 pages1st To 3rd Weeks of DevelopmentJérômeLkNo ratings yet
- Embryonic Period: Dr. Khin Ma MADocument34 pagesEmbryonic Period: Dr. Khin Ma MAIbrahim FoondunNo ratings yet
- Embryology - Updates and Highlights On Classic TopicsDocument222 pagesEmbryology - Updates and Highlights On Classic TopicsIndera Vyas100% (1)
- HistoDocument8 pagesHistoFatima AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Histology Slides: Epithelial TissueDocument35 pagesHistology Slides: Epithelial Tissuesaurabhsinghspeaks3543No ratings yet
- Histology of Ear and EyeDocument2 pagesHistology of Ear and EyeAnny AlvrzNo ratings yet
- 4+5 Tissue Types and Epithelial TissueDocument44 pages4+5 Tissue Types and Epithelial Tissueyasser100% (1)
- Connective TissueDocument20 pagesConnective TissueWadabiNo ratings yet
- Notes From Dental Articles ANATOMYDocument6 pagesNotes From Dental Articles ANATOMYpatelpurvivNo ratings yet
- Embryology-Nervous System DevelopmentDocument157 pagesEmbryology-Nervous System DevelopmentGheavita Chandra DewiNo ratings yet
- Intrdoduction Gis 2 (Associated Organs) : Maya Tejasari Histology DepartmentDocument24 pagesIntrdoduction Gis 2 (Associated Organs) : Maya Tejasari Histology DepartmentIpan YustiartaNo ratings yet
- 1378968054.1856 - Histochemistry and Enzyme HistochemistryDocument39 pages1378968054.1856 - Histochemistry and Enzyme HistochemistryCarlos Ivan Cruz Cardenas100% (1)
- Oogenesis and Ovarian Cycle, Uterus, Menstrual Cycle ABORTION TERATOLOGYDocument72 pagesOogenesis and Ovarian Cycle, Uterus, Menstrual Cycle ABORTION TERATOLOGYElizabeth OmobolanleNo ratings yet
- Histology of The Circulatory SystemDocument24 pagesHistology of The Circulatory SystemFatima Zehra YusefNo ratings yet
- Embryology McqsDocument2 pagesEmbryology McqsMoses Ajiweka100% (1)
- 2 AND 3 WEEKS OF DEVELOPMENTDocument40 pages2 AND 3 WEEKS OF DEVELOPMENTjabirNo ratings yet
- HIS.K.1.Histology of BloodDocument16 pagesHIS.K.1.Histology of BloodMayaPasaribuNo ratings yet
- Membrane TransportDocument24 pagesMembrane Transportolawandeilo123No ratings yet
- Bones of Upper and Lower Limbs - RevisionDocument15 pagesBones of Upper and Lower Limbs - RevisionChess Nuts100% (1)
- Histology Lecture: Minerva Diana A. Dichoso, RMTDocument108 pagesHistology Lecture: Minerva Diana A. Dichoso, RMTVernadel ApolloNo ratings yet
- MCQsDocument6 pagesMCQsMuhammad Qasim TararNo ratings yet
- Upper LimbDocument90 pagesUpper Limbapi-324160601100% (1)
- Neurulation Refers To The Folding Process in Vertebrate Embryos, Which Includes TheDocument6 pagesNeurulation Refers To The Folding Process in Vertebrate Embryos, Which Includes Theaaliya saaheenNo ratings yet
- Cells: USC Messed Up The Following QuestionsDocument119 pagesCells: USC Messed Up The Following Questionsopeyemi idaeworNo ratings yet
- Histology Exam IV Review Part 2Document26 pagesHistology Exam IV Review Part 2ashdmb217No ratings yet
- Histology RespiratoryDocument35 pagesHistology Respiratorykhiks34100% (2)
- Embryo Lab Exercise 1Document7 pagesEmbryo Lab Exercise 1Karmina Santos100% (1)
- Histology SummaryDocument24 pagesHistology SummaryaelsehamyNo ratings yet
- Type of Epithelium CellDocument3 pagesType of Epithelium CellHo Shi XianNo ratings yet
- Gastrulation in Frog, Chick and Human ComparedDocument1 pageGastrulation in Frog, Chick and Human ComparedClaire BolalinNo ratings yet
- Developmental Biology of Frog Egg and SpermDocument21 pagesDevelopmental Biology of Frog Egg and SpermRavindra MadurNo ratings yet
- Complete Histology of Respiratory SystemDocument66 pagesComplete Histology of Respiratory Systemhassam qaziNo ratings yet
- 2.histologi DarahDocument38 pages2.histologi DarahIrfanNo ratings yet
- 1 Red Blood Cells Anemia and PolycythemiaDocument43 pages1 Red Blood Cells Anemia and PolycythemiaGeevee Naganag VentulaNo ratings yet
- Ukuran VenueDocument2 pagesUkuran VenueIbrahim SugiyonoNo ratings yet
- CHT - Hfa - Girls - Z - 2 - 5 WHO Growth ChartDocument1 pageCHT - Hfa - Girls - Z - 2 - 5 WHO Growth ChartEvan KeeNo ratings yet
- Properties of EnzymeDocument1 pageProperties of EnzymeIbrahim SugiyonoNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Growth Hormone SecretionDocument4 pagesRegulation of Growth Hormone SecretionIbrahim Sugiyono100% (1)
- Carcinogenic Agent: Irreversible and Has "Memory." This Is Illustrated by Group 3, in Which Tumors WereDocument4 pagesCarcinogenic Agent: Irreversible and Has "Memory." This Is Illustrated by Group 3, in Which Tumors WereIbrahim SugiyonoNo ratings yet