Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Paper No. 670: Year Project State/states PQ Limits GQ Ew GSDP Rank
Paper No. 670: Year Project State/states PQ Limits GQ Ew GSDP Rank
Uploaded by
shaikh a n0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views1 pageThis document presents data on various highway projects in India from 2008-2009. It includes the project name, states involved, prequalification (PQ) limits for technical and financial capacity, and each state's gross state domestic product (GSDP) rank for the project year.
Some key findings are:
- PQ limits did not always correlate with GSDP rank, possibly due to a lack of private parties during the early recession years of 2008-2009.
- Regression analysis found technical capacity was on average 108.873% of project cost, while financial capacity averaged 21.362% of cost.
- Not all projects adhered to Planning Commission guidelines for 100-200% of cost for technical
Original Description:
Original Title
p51.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document presents data on various highway projects in India from 2008-2009. It includes the project name, states involved, prequalification (PQ) limits for technical and financial capacity, and each state's gross state domestic product (GSDP) rank for the project year.
Some key findings are:
- PQ limits did not always correlate with GSDP rank, possibly due to a lack of private parties during the early recession years of 2008-2009.
- Regression analysis found technical capacity was on average 108.873% of project cost, while financial capacity averaged 21.362% of cost.
- Not all projects adhered to Planning Commission guidelines for 100-200% of cost for technical
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views1 pagePaper No. 670: Year Project State/states PQ Limits GQ Ew GSDP Rank
Paper No. 670: Year Project State/states PQ Limits GQ Ew GSDP Rank
Uploaded by
shaikh a nThis document presents data on various highway projects in India from 2008-2009. It includes the project name, states involved, prequalification (PQ) limits for technical and financial capacity, and each state's gross state domestic product (GSDP) rank for the project year.
Some key findings are:
- PQ limits did not always correlate with GSDP rank, possibly due to a lack of private parties during the early recession years of 2008-2009.
- Regression analysis found technical capacity was on average 108.873% of project cost, while financial capacity averaged 21.362% of cost.
- Not all projects adhered to Planning Commission guidelines for 100-200% of cost for technical
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
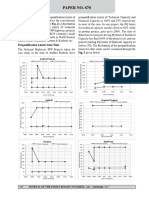
Paper No.
670
Year Project State/States PQ Limits GQ EW GSDP
Rank
2008 Madhya Pradesh/Maharashtra 1. Madhya 50.00 22.05 11 1
Border-Nagpur Section of NH-7 Pradesh
2. Maharashtra
2008 Four-Laning of Baihata Chariali 1.Assam 50.01 20.76 18
to Tezpur section of NH-52
2008 Six Laning of Pune-Satara Section 1. Maharashtra 50.00 15.00 1
of NH 4
2008 Six Laning of Udaipur - 1. Rajasthan 50.00 15.00 8 5
Ahmedabad Section of NH-8 2. Gujarat
2009 Four Laning of existing 2 lane of 1. Bihar 66.17 25.00 15
Mokama- Munger Of NH-80
2009 Six Laning of NH-4 from Tumkur 2. Karnataka 50.00 22.04 7
to Chitradurga
#Notations – TC: Technical Capacity; FC: Financial Capacity; GQ: Golden Quadrilateral; EW: Expressway;
S1: State 1; S2: State 2; PQ: Prequalification.
c) GSDP and Tender Year to be 21.362 % of the project cost. Furthermore,
Higher the GSDP of a state and its neighboring there is not much significant variation in the
states, higher is the traffic density and willingness technical capacity and financial capacity with
to pay for the road services. Therefore, pre- variation of the project cost (represented
qualification limits for projects in the state having by the project cost coefficient 0.004). Thus,
high GSDP will be higher and for state with low the interpretation of these numbers are that,
GSDP will be lower. However, the data presented irrespective of projects cost, 108% of the project
in Table 1 above does not support this fact. The cost seems to be technical capacity and 21 % of
reason for this may be attributed to inadequate the estimated project cost seems to be the financial
number of private parties in the tendering year. capacity of the projects. This is justified in most
Some projects have low prequalification limits in of the projects adopted by National Highway
even though the projects were in high GSDP state. Authority of India (NHAI), the nodal agency for
Those projects were tendered in the year 2008 implementation of national highway projects
and 2009 as shown in Table 2. Since PPP was in in India, as they have followed the Planning
the early year of recession during that time, there Commission’s recommendation to set the
might not be interested private players. technical capacity limit to 100% and financial
capacity to 25% of the estimated project cost.
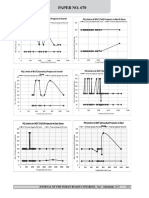
8. Discussion
Planning Commission (2014) has also specified
In the regression equation, the point of interest lies that maximum limit to be 200% of the estimated
with two coefficients namely regression constant project cost.
and coefficient of the independent variable. The
constant intercept gives the average PQ limits All the projects, however, have not adopted the
without the influence of independent variable. Then, specified limits of PQ by the Planning Commission.
based on the coefficient of independent variable, The proportion of projects that have not adhered
the increase of the PQ limits is suggested. It has to the specified limit is about 23% of the sample.
been observed that the technical capacity of most Amongst these projects, the PQ limits of some of
of projects are close to 108.873 % of the project the projects have been set as 50% of the prescribed
cost, represented by the coefficient of intercept in PQ limits. Lower limits were used in case of some of
the regression equation. Similarly, the financial the projects which have adopted BOT (Toll) model
capacity coefficient of intercept has been observed where the private investors recoup their investments
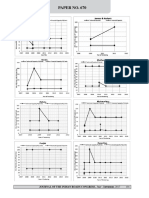
106 Journal of the indian Roads Congress, July - September, 2017
You might also like
- Retirement Planning CalculatorDocument4 pagesRetirement Planning CalculatorkitchaaNo ratings yet
- Economy Lecture HandoutDocument38 pagesEconomy Lecture HandoutEdward GallardoNo ratings yet
- JY1Y9Z.final JBVNL Cost Data Book 2022-23Document219 pagesJY1Y9Z.final JBVNL Cost Data Book 2022-23Sahil MohammedNo ratings yet
- CMP RMCDocument115 pagesCMP RMCManthanNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of RECRUITMENT of Public and Private Bank SectorDocument91 pagesComparative Analysis of RECRUITMENT of Public and Private Bank Sectorlokesh_045100% (4)
- Monthly Progress ReportDocument38 pagesMonthly Progress ReportNagaraj Patil100% (1)
- Application Form For IncubatorDocument5 pagesApplication Form For IncubatorVipul AgnihotriNo ratings yet
- Kutehr-IE Phase1 ReportDocument96 pagesKutehr-IE Phase1 ReportL.C. GOYALNo ratings yet
- Water and Urban - CWRD - Lu Shen - FinalDocument10 pagesWater and Urban - CWRD - Lu Shen - FinalWalter PoickNo ratings yet
- Paper No. 670: Prequalification Limits Zone Wise and PPP Mode WiseDocument1 pagePaper No. 670: Prequalification Limits Zone Wise and PPP Mode Wiseshaikh a nNo ratings yet
- Balaghat Mpphed Water DPR 2Document91 pagesBalaghat Mpphed Water DPR 2Manoj AhirwarNo ratings yet
- 3 NHAI ReportDocument69 pages3 NHAI Reportkarunamoorthi_p2209100% (1)
- GEC Corridor CostingDocument20 pagesGEC Corridor CostingaakashNo ratings yet
- Causes and Effects of Cost and Time Overrun of Road Construction Projects in GujaratDocument11 pagesCauses and Effects of Cost and Time Overrun of Road Construction Projects in GujaratBikesh ManandharNo ratings yet
- Pink City Expressway Limited: Long-Term Bank Loan Care BBBDocument4 pagesPink City Expressway Limited: Long-Term Bank Loan Care BBBJaydeep ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Government of Rajasthan Nirman Bhawan, Jacob Road, Jaipur: Public Works DepartmentDocument127 pagesGovernment of Rajasthan Nirman Bhawan, Jacob Road, Jaipur: Public Works DepartmentAnonymous eKt1FCDNo ratings yet
- Rajasthan Mega Highways ProjectDocument45 pagesRajasthan Mega Highways ProjectRohit RameshNo ratings yet
- Tender Notice Datecor1Document116 pagesTender Notice Datecor1Kunal PaulNo ratings yet
- Sector Specific Inventory & Institutional Strengthening For PPP MainstreamingDocument54 pagesSector Specific Inventory & Institutional Strengthening For PPP MainstreamingsharathNo ratings yet
- Vacancy RLDA Contract 02Document4 pagesVacancy RLDA Contract 02ManojkumarNo ratings yet
- Paper No. 670: 10. ConclusionsDocument1 pagePaper No. 670: 10. Conclusionsshaikh a nNo ratings yet
- Paper No. 670: Prequalification Limits State Wise Fig. 5 Given BelowDocument1 pagePaper No. 670: Prequalification Limits State Wise Fig. 5 Given Belowshaikh a nNo ratings yet
- Government of Karnataka: National HighwayDocument30 pagesGovernment of Karnataka: National Highwayakshatjain3001No ratings yet
- Presentation BOS 16112016 1 ModifiedDocument31 pagesPresentation BOS 16112016 1 ModifiedniranjanchouNo ratings yet
- National Highways Authority of IndiaDocument252 pagesNational Highways Authority of Indiaanamika singhNo ratings yet
- EOI NoDocument72 pagesEOI NoMurali GawandeNo ratings yet
- Request For Expression of Interest (Reoi) Cum Request For Proposal (RFP) - DocumentDocument40 pagesRequest For Expression of Interest (Reoi) Cum Request For Proposal (RFP) - Documentsacheendra singhNo ratings yet
- China Pakistan Economic Corridor: Overview, Opportunities and RisksDocument25 pagesChina Pakistan Economic Corridor: Overview, Opportunities and RisksRukhsar TariqNo ratings yet
- Meghnaghat Power Project in BangladeshDocument10 pagesMeghnaghat Power Project in BangladeshIndependent Evaluation at Asian Development BankNo ratings yet
- Office of The Superintending Engineer, N.H. Planning & Design CircleDocument8 pagesOffice of The Superintending Engineer, N.H. Planning & Design CircleKarfa SambitNo ratings yet
- Paper No. 670: Year Project State/states PQ Limits GQ Ew GSDP Rank TC FC s1 s2 Projects With High Prequalification LimitsDocument1 pagePaper No. 670: Year Project State/states PQ Limits GQ Ew GSDP Rank TC FC s1 s2 Projects With High Prequalification Limitsshaikh a nNo ratings yet
- Patratu Masculiskiganj Hendegir TechDocument97 pagesPatratu Masculiskiganj Hendegir Techashish kumarNo ratings yet
- A Project by Saten On PMGSYDocument94 pagesA Project by Saten On PMGSYAmar RajputNo ratings yet
- CPEC Presentation NIMDocument25 pagesCPEC Presentation NIMNaila ChNo ratings yet
- 867 File2213519862Document128 pages867 File2213519862AkashNo ratings yet
- Status Report July Sept07Document296 pagesStatus Report July Sept07Vikash BhartiNo ratings yet
- Transport and Communications: Modes of TransportationDocument29 pagesTransport and Communications: Modes of TransportationRk SunnyNo ratings yet
- Dewas Bhopal Corridor P LTDDocument20 pagesDewas Bhopal Corridor P LTDsurya401No ratings yet
- RFP-AE NH-730-KmDocument120 pagesRFP-AE NH-730-KmLaxmipathi Rao LakkarajuNo ratings yet
- Das-Jlr Revised PMC DocumentDocument226 pagesDas-Jlr Revised PMC DocumentArvind Sharma0% (1)
- National Highways Authority of India'sDocument30 pagesNational Highways Authority of India'sMaheedhar KolliparaNo ratings yet
- EOI Cum RFPDocument129 pagesEOI Cum RFPBC ECNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Compliance Audit Observations Relating To Power Sector Undertakings of Report No 1 of 2020 Public Sector Undertakings Government of KeralaDocument16 pagesChapter 2 Compliance Audit Observations Relating To Power Sector Undertakings of Report No 1 of 2020 Public Sector Undertakings Government of KeralaSubramoni RajuNo ratings yet
- Vol IDocument208 pagesVol Isk sharmaNo ratings yet
- 1547708711खड्केटारि-पञ्चासे दोबिल्ला सडक DPR (Volume-1)Document134 pages1547708711खड्केटारि-पञ्चासे दोबिल्ला सडक DPR (Volume-1)Anil GautamNo ratings yet
- Project Document OF The Asian Infrastructure Investment BankDocument51 pagesProject Document OF The Asian Infrastructure Investment BankVishal DaveNo ratings yet
- 202109301632984233-Market Rate System 2021Document804 pages202109301632984233-Market Rate System 2021Shams KhattakNo ratings yet
- Metro FY22 Budget - Outreach Presentation - FinalDocument18 pagesMetro FY22 Budget - Outreach Presentation - FinalMetro Los AngelesNo ratings yet
- Report On Mega Projects (Rs.1000 Crores and Above) February, 2010Document21 pagesReport On Mega Projects (Rs.1000 Crores and Above) February, 2010PrashanthMNairNo ratings yet
- Internship Btech Mtech NH 00020Document6 pagesInternship Btech Mtech NH 00020sourabh pandeyNo ratings yet
- 640 File228729760 PDFDocument278 pages640 File228729760 PDFAbhishek MathurNo ratings yet
- PNC Challakere (Karnataka) Highways Private LimitedDocument4 pagesPNC Challakere (Karnataka) Highways Private LimitedSrujan ReddyNo ratings yet
- Project of Royal Government of BhutanDocument47 pagesProject of Royal Government of BhutanUgyen YoezrNo ratings yet
- Paper No. 670: Deviation From The Conventional Pre-Qualification LimitsDocument1 pagePaper No. 670: Deviation From The Conventional Pre-Qualification Limitsshaikh a nNo ratings yet
- File-Wed Jul 26 2023 22 - 55 - 17 GMT+0530 (India Standard Time)Document8 pagesFile-Wed Jul 26 2023 22 - 55 - 17 GMT+0530 (India Standard Time)Goriparthi SambasievaraavNo ratings yet
- Tendernotice 1Document27 pagesTendernotice 1Shashikant VermaNo ratings yet
- To Be Stage: Road Works Phase-VDocument1 pageTo Be Stage: Road Works Phase-Vshravan38No ratings yet
- Presentation On Loktak Downstream DT 20.01.2020Document21 pagesPresentation On Loktak Downstream DT 20.01.2020Loktak DownstreamNo ratings yet
- PMC NH627 Package-I AssamDocument524 pagesPMC NH627 Package-I AssamAdilNo ratings yet
- 189 File36656Document102 pages189 File36656PIDCL WITH SUBUDHINo ratings yet
- Performance-Based Road Maintenance Contracts in the CAREC RegionFrom EverandPerformance-Based Road Maintenance Contracts in the CAREC RegionNo ratings yet
- Facilitating Power Trade in the Greater Mekong Subregion: Establishing and Implementing a Regional Grid CodeFrom EverandFacilitating Power Trade in the Greater Mekong Subregion: Establishing and Implementing a Regional Grid CodeNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy Tariffs and Incentives in Indonesia: Review and RecommendationsFrom EverandRenewable Energy Tariffs and Incentives in Indonesia: Review and RecommendationsNo ratings yet
- Harmonizing Power Systems in the Greater Mekong Subregion: Regulatory and Pricing Measures to Facilitate TradeFrom EverandHarmonizing Power Systems in the Greater Mekong Subregion: Regulatory and Pricing Measures to Facilitate TradeNo ratings yet
- Basics of LED (Light Emitting Diode)Document1 pageBasics of LED (Light Emitting Diode)shaikh a nNo ratings yet
- JGJS-STTP onAIML-SVPMDocument3 pagesJGJS-STTP onAIML-SVPMshaikh a nNo ratings yet
- Ipfide Profile 2023Document16 pagesIpfide Profile 2023shaikh a nNo ratings yet
- 15basics of LEDDocument12 pages15basics of LEDshaikh a nNo ratings yet
- Generative AI UsingDocument2 pagesGenerative AI Usingshaikh a nNo ratings yet
- 13basics of LEDDocument11 pages13basics of LEDshaikh a nNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering and Allied Sem 3 1Document1 pageCivil Engineering and Allied Sem 3 1shaikh a nNo ratings yet
- 14basics of LEDDocument12 pages14basics of LEDshaikh a nNo ratings yet
- 12basics of LEDDocument10 pages12basics of LEDshaikh a nNo ratings yet
- 11basics of LEDDocument9 pages11basics of LEDshaikh a nNo ratings yet
- 3basics of LEDDocument2 pages3basics of LEDshaikh a nNo ratings yet
- 8basics of LEDDocument7 pages8basics of LEDshaikh a nNo ratings yet
- 4basics of LEDDocument3 pages4basics of LEDshaikh a nNo ratings yet
- 6basics of LEDDocument5 pages6basics of LEDshaikh a nNo ratings yet
- Ahmh101 PDFDocument20 pagesAhmh101 PDFshaikh a nNo ratings yet
- 1.1.6 Loads and Forces: Version 2 CE IIT, KharagpurDocument1 page1.1.6 Loads and Forces: Version 2 CE IIT, Kharagpurshaikh a nNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of LED (Light Emitting Diode)Document1 pageCharacteristics of LED (Light Emitting Diode)shaikh a nNo ratings yet
- Paper No. 670: Deviation From The Conventional Pre-Qualification LimitsDocument1 pagePaper No. 670: Deviation From The Conventional Pre-Qualification Limitsshaikh a nNo ratings yet
- Objectives and Methods of Analysis and DesignDocument1 pageObjectives and Methods of Analysis and Designshaikh a nNo ratings yet
- Paper No. 670: Journal of The Indian Roads CongressDocument1 pagePaper No. 670: Journal of The Indian Roads Congressshaikh a nNo ratings yet
- Paper No. 670: Fig. 2 Minimum Prequalification Limits Year WiseDocument1 pagePaper No. 670: Fig. 2 Minimum Prequalification Limits Year Wiseshaikh a nNo ratings yet
- Paper No. 670: Grant and PremiumDocument1 pagePaper No. 670: Grant and Premiumshaikh a nNo ratings yet
- Paper No. 670: Prequalification Limits PPP Mode WiseDocument1 pagePaper No. 670: Prequalification Limits PPP Mode Wiseshaikh a nNo ratings yet
- Paper No. 670: Prequalification Limits State Wise Fig. 5 Given BelowDocument1 pagePaper No. 670: Prequalification Limits State Wise Fig. 5 Given Belowshaikh a nNo ratings yet
- Paper No. 670: Journal of The Indian Roads CongressDocument1 pagePaper No. 670: Journal of The Indian Roads Congressshaikh a nNo ratings yet
- 5309 ITMAX QR 2022-09-30 ITMAXQ3FY2022InterimfinancialreportFINAL08122022 - 1252950768Document21 pages5309 ITMAX QR 2022-09-30 ITMAXQ3FY2022InterimfinancialreportFINAL08122022 - 1252950768Quint WongNo ratings yet
- Exhibit HDocument3 pagesExhibit HMatias SmithNo ratings yet
- Bharti AXA Life Insurance-DineshDocument91 pagesBharti AXA Life Insurance-DineshVineet SinghNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 01 The Purpose of A BDocument18 pagesCHAPTER 01 The Purpose of A BCosmin MogaNo ratings yet
- Session 2: Capital Investment Appraisal (An Introduction)Document41 pagesSession 2: Capital Investment Appraisal (An Introduction)ttzaxsanNo ratings yet
- Vitrox q42022Document16 pagesVitrox q42022Dennis AngNo ratings yet
- PFM Act IRR AnalysisDocument50 pagesPFM Act IRR AnalysisMarvin OlidNo ratings yet
- Lec 03 - The Recording ProcessDocument74 pagesLec 03 - The Recording ProcessIbraheem rabeeNo ratings yet
- 06 - Chapter2 QuestionDocument71 pages06 - Chapter2 QuestionGeo AlexNo ratings yet
- FIN380 Case 2 - Derivatives at Banc OneDocument7 pagesFIN380 Case 2 - Derivatives at Banc OneJeremy SchweizerNo ratings yet
- T & D Life InsuranceDocument54 pagesT & D Life InsuranceSamuel DavisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document20 pagesChapter 14Kim Joshua Bolo100% (1)
- B4RN Business Plan v4.1Document26 pagesB4RN Business Plan v4.1b4rnNo ratings yet
- FinmanDocument4 pagesFinmanabcdefgNo ratings yet
- 18neb RulesDocument12 pages18neb RulesbobprobstNo ratings yet
- Swot Analysis of A Sacco SocietyDocument7 pagesSwot Analysis of A Sacco Societymwangiky100% (1)
- CF 2023 Module IDocument272 pagesCF 2023 Module IFabio MotaNo ratings yet
- Chandigarh Real Estate Overview ICICI March 13Document24 pagesChandigarh Real Estate Overview ICICI March 13dotpolkaNo ratings yet
- A Report On Diageo PLC Financial StatementDocument14 pagesA Report On Diageo PLC Financial Statementjoshua.o.adenijiNo ratings yet
- Passion Reborn": Internship Report On Bank of PunjabDocument99 pagesPassion Reborn": Internship Report On Bank of PunjabAleena Shah100% (1)
- PreferenceShares - March 27 2018Document1 pagePreferenceShares - March 27 2018Tiso Blackstar GroupNo ratings yet
- Docket 314 - DeFazio V Hollister - Fourth Amended Complaint - ERISADocument41 pagesDocket 314 - DeFazio V Hollister - Fourth Amended Complaint - ERISAgovernorwattsNo ratings yet
- Kean Dry Cleaners Is Owned and Operated by Wally Lowman ADocument1 pageKean Dry Cleaners Is Owned and Operated by Wally Lowman AM Bilal SaleemNo ratings yet
- RiskDocument80 pagesRiskanie190715360% (1)
- Presentation Adrian Lupusor MoldovaDocument26 pagesPresentation Adrian Lupusor MoldovaAna ProdanNo ratings yet
- Nabha Power Limited-10082012Document4 pagesNabha Power Limited-10082012Milind DhandeNo ratings yet